KNOXVILLE, TN, December 26, 2025 /24-7PressRelease/ — A recent study has shed light on the dual role of large language models (LLMs) in modern technology, revealing both their potential to foster innovation and the ethical and security risks they introduce. Conducted by researchers from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and East China Normal University, the study systematically reviewed 73 papers and highlighted concerns surrounding the widespread use of LLMs in fields such as writing, coding, and problem-solving.
LLMs, including widely recognized models like the generative pre-trained transformer (GPT), bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT), and T5, have transformed various sectors, from education to healthcare. Their fluency in generating human-like text facilitates automation and enhances information workflows. However, this same capability raises alarms regarding vulnerabilities to cyber-attacks, misinformation, and social biases that could mislead users or exacerbate inequalities.
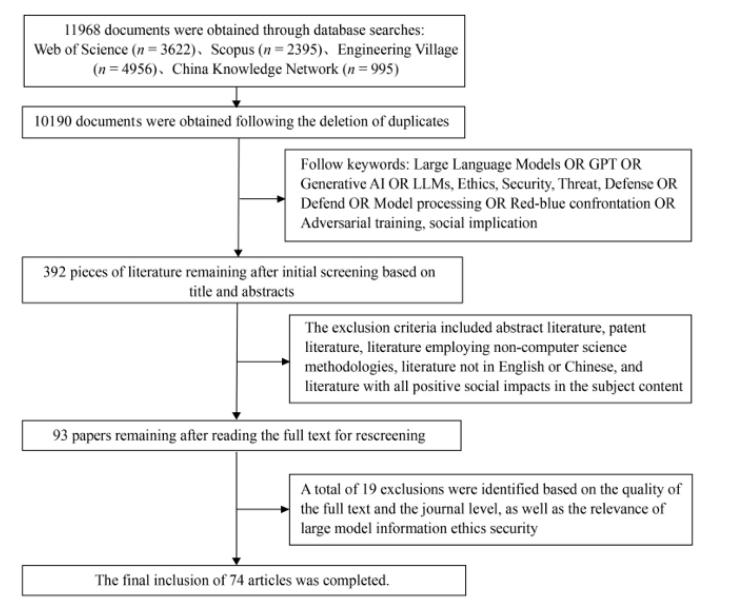
The comprehensive study, published in the journal Frontiers of Engineering Management (DOI: 10.1007/s42524-025-4082-6), screened over 10,000 documents to distill key threats associated with LLMs. These threats include phishing attacks, data leakage, malicious code generation, and the risk of model manipulation through techniques like prompt injection and jailbreaking. Researchers warn that without systematic regulation and robust defense mechanisms, misuse of LLMs could jeopardize data security, public trust, and social stability.
LLM-related security threats are categorized into two primary domains: misuse-based risks and malicious attacks targeting the models themselves. Misuse encompasses practices such as crafting phishing emails with almost indistinguishable fluency, scripting automated malware, and producing large volumes of false information. On the other hand, malicious attacks can occur at both the data and model levels, with risks including model inversion, data poisoning, and extraction, as well as user interaction vulnerabilities.
The study also evaluated existing defense strategies, summarizing three major technical routes. Parameter processing aims to minimize attack exposure by removing redundant parameters. Input preprocessing employs techniques to paraphrase prompts or detect adversarial triggers without necessitating model retraining. Adversarial training, which includes red-teaming frameworks that simulate attacks to enhance robustness, represents an evolving area of focus. Detection technologies like semantic watermarking and CheckGPT are also highlighted for their potential to accurately identify model-generated text.
Despite these advancements, the authors note a significant gap between the pace of developing defense mechanisms and the evolving tactics used by attackers. They stress the need for scalable, low-cost, and multilingual-adaptive solutions to strengthen defenses against emerging threats.
The researchers also emphasize that technical safeguards must be paired with ethical oversight. They argue that issues such as hallucination, bias, privacy violations, and misinformation should be viewed as societal risks rather than mere engineering challenges. Moving forward, the authors advocate for integrating transparency, verifiable content traceability, and cross-disciplinary oversight into the development of future LLMs. Establishing ethical review frameworks, dataset audit mechanisms, and public awareness campaigns will be essential in mitigating misuse and safeguarding vulnerable populations.
The study posits that the secure and ethical development of LLMs will dictate how societies adapt to artificial intelligence. Effective defense systems could protect financial sectors from phishing attacks, reduce medical misinformation, and safeguard scientific integrity. Additionally, adopting watermark-based traceability and red-teaming could become industry standards for model deployment, paving the way for responsible governance and unified regulatory frameworks. If properly managed, LLMs have the potential to serve as reliable tools, bolstering education, digital healthcare, and innovation ecosystems while minimizing the associated risks of cybercrime and social misinformation.
References
DOI: 10.1007/s42524-025-4082-6
Funding Information
This study was supported by the Beijing Key Laboratory of Behavior and Mental Health, Peking University, China.
 PlantIF Achieves 96.95% Accuracy in Plant Disease Diagnosis Using Multimodal Learning
PlantIF Achieves 96.95% Accuracy in Plant Disease Diagnosis Using Multimodal Learning Tsinghua and Shengshu Open-Source TurboDiffusion, Boosting AI Video Generation by 97×
Tsinghua and Shengshu Open-Source TurboDiffusion, Boosting AI Video Generation by 97× Leonardo DiCaprio Critiques AI’s Role in Art, Citing Job Loss and Lack of Humanity
Leonardo DiCaprio Critiques AI’s Role in Art, Citing Job Loss and Lack of Humanity LLMs Transform Undergraduate Education, Offering Personalized Learning and New Challenges
LLMs Transform Undergraduate Education, Offering Personalized Learning and New Challenges Chinese Researchers Reveal TurboDiffusion, Achieving 200x Faster AI Video Creation
Chinese Researchers Reveal TurboDiffusion, Achieving 200x Faster AI Video Creation