Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly becoming a staple in personal finance management, offering tools that assist users in everything from budgeting to comprehending complex financial concepts. As consumers weigh their options among AI platforms like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Microsoft Copilot, and Claude by Anthropic, it is essential to understand the distinct advantages and limitations each brings to personal finance management.
ChatGPT excels in educational contexts, capable of breaking down intricate financial topics and adapting to a wide array of user prompts. Its conversational style makes it particularly accessible for those looking to grasp the fundamentals of personal finance. Google Gemini, on the other hand, offers seamless integration with Google Workspace applications such as Gmail and Google Sheets, making it a strong contender for users who frequently operate within this ecosystem. Microsoft Copilot shines for those embedded in the Microsoft environment, providing functionality that enhances productivity in applications like Outlook and Excel. Lastly, Claude stands out when it comes to processing lengthy documents, making it especially useful when reviewing materials from financial advisors.
While these AI assistants present considerable benefits, they are not without their drawbacks. A notable concern is the accuracy of the information these platforms provide. Users may encounter misleading or incorrect data, which could lead to poor financial decisions if they rely solely on AI for advice. Privacy is another critical issue, as many users are understandably cautious about sharing sensitive financial information with AI tools. Each platform has its own privacy policies, and users would be wise to familiarize themselves with these to ensure their data remains secure.
The strengths of these AI assistants lie in their ability to educate and analyze. For example, users can leverage AI to audit their spending habits, summarize complex financial documents, or even help formulate questions for financial planning discussions. However, users should approach these tools as supplementary aids rather than replacements for professional financial advice. Relying entirely on AI could jeopardize one’s financial well-being, especially given the nuanced and personalized nature of effective financial planning.
For practical use, AI can assist with a variety of tasks. Users can upload bank transaction data to analyze spending patterns or summarize 401(k) plan documents to clarify employer contributions and investment options. Additionally, AI can help create tailored debt repayment schedules by analyzing individual debts and suggesting efficient strategies for pay-off. However, users should always sanitize any uploaded data by removing sensitive details, thus minimizing potential privacy risks.
As AI continues to evolve, it is poised to play an increasingly prominent role in personal finance management. Each AI assistant offers unique strengths that cater to different needs and environments, making it essential for users to choose one that aligns with their individual financial situations. With the right precautions in place, AI can serve as a valuable companion for managing day-to-day financial tasks, thereby empowering users to make more informed decisions.
See also Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance Surveys Global AI Adoption in Financial Services
Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance Surveys Global AI Adoption in Financial Services Finance & Facilities Committee Nominates Darryl as New Chair Amid Leadership Concerns
Finance & Facilities Committee Nominates Darryl as New Chair Amid Leadership Concerns UK CFOs Boost AI Investment to 96% Amid Growing Optimism for Productivity Gains
UK CFOs Boost AI Investment to 96% Amid Growing Optimism for Productivity Gains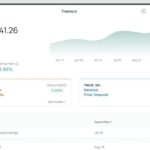 Zeni Launches Treasury Solution Offering Market-Leading Yields and Instant Liquidity
Zeni Launches Treasury Solution Offering Market-Leading Yields and Instant Liquidity McHenry County Finance Committee Approves $500K Reclassification for Court Interpreter Reimbursements
McHenry County Finance Committee Approves $500K Reclassification for Court Interpreter Reimbursements