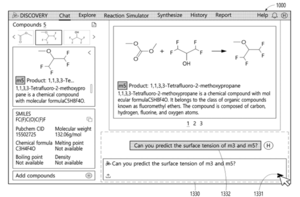
Researchers at NTT in Tokyo have unveiled a method to enhance image classification accuracy, addressing a significant gap between how artificial intelligence learns and how it is applied. In a study led by Shohei Enomoto and Shin’ya Yamaguchi, the team developed a technique that transforms standard image datasets into multimodal formats by using synthetic captions generated by large language models. This innovative approach aligns the multimodal pre-training of AI with the unimodal fine-tuning process, enabling models to better utilize pre-trained visual understanding.
The research demonstrates a novel methodology that bridges the disconnect between multimodal pre-training and unimodal adaptation, a critical limitation in current computer vision practices. By converting unimodal datasets into multimodal datasets, the team utilized Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to generate synthetic captions tailored for fine-tuning models with a multimodal objective. They employed carefully crafted prompts that included class labels and relevant domain context, resulting in high-quality captions that significantly enrich image classification tasks.
Central to this breakthrough is the creation of synthetic datasets that augment existing unimodal data with rich textual information. By leveraging MLLMs, the researchers produced captions that go beyond mere descriptions, incorporating nuanced details relevant to the classification task. This not only expands the dataset but also enhances the fine-tuning model’s understanding of visual content. Additionally, the study introduces a novel supervised contrastive loss function designed to encourage the clustering of representations belonging to the same class during the fine-tuning process.
The methodology was rigorously tested across thirteen diverse image classification benchmarks, confirming the effectiveness of the approach. Results showed significant performance improvements, particularly in challenging few-shot learning scenarios where labeled data is scarce. The team’s technique outperformed baseline methods, marking a new paradigm for dataset enhancement and revealing that aligning pre-training with fine-tuning can dramatically improve model performance on subsequent tasks.
Notably, the researchers’ approach goes beyond just enhancing accuracy; it demonstrates potential for zero-shot image classification. Their method surpassed the performance of fine-tuned models trained with limited data, specifically with 1, 4, and 8 shots per class. This innovation opens new pathways for applying advanced pre-trained models to various image classification challenges, particularly in contexts where acquiring large, labeled datasets is impractical or costly.
The study illustrates the importance of aligning multimodal pre-training with unimodal fine-tuning by creating richer representations for enhanced performance. The findings also reveal that by generating tailored captions and employing a supervised contrastive loss function, the models can significantly improve their ability to generalize and discriminate among classes. The researchers provided access to their code on GitHub, facilitating further adoption and exploration of their methods by the broader scientific community.
In summary, this research not only advances current methodologies in image classification but also highlights the transformative potential of multimodal learning. By bridging the gap between multimodal pre-training and unimodal fine-tuning, the study promises to accelerate progress in computer vision. The ability to utilize synthetic captions for fine-tuning represents a significant stride toward achieving more sophisticated and effective AI systems, paving the way for enhanced image understanding and analysis in various applications.
See also Sam Altman Praises ChatGPT for Improved Em Dash Handling
Sam Altman Praises ChatGPT for Improved Em Dash Handling AI Country Song Fails to Top Billboard Chart Amid Viral Buzz
AI Country Song Fails to Top Billboard Chart Amid Viral Buzz GPT-5.1 and Claude 4.5 Sonnet Personality Showdown: A Comprehensive Test
GPT-5.1 and Claude 4.5 Sonnet Personality Showdown: A Comprehensive Test Rethink Your Presentations with OnlyOffice: A Free PowerPoint Alternative
Rethink Your Presentations with OnlyOffice: A Free PowerPoint Alternative OpenAI Enhances ChatGPT with Em-Dash Personalization Feature
OpenAI Enhances ChatGPT with Em-Dash Personalization Feature