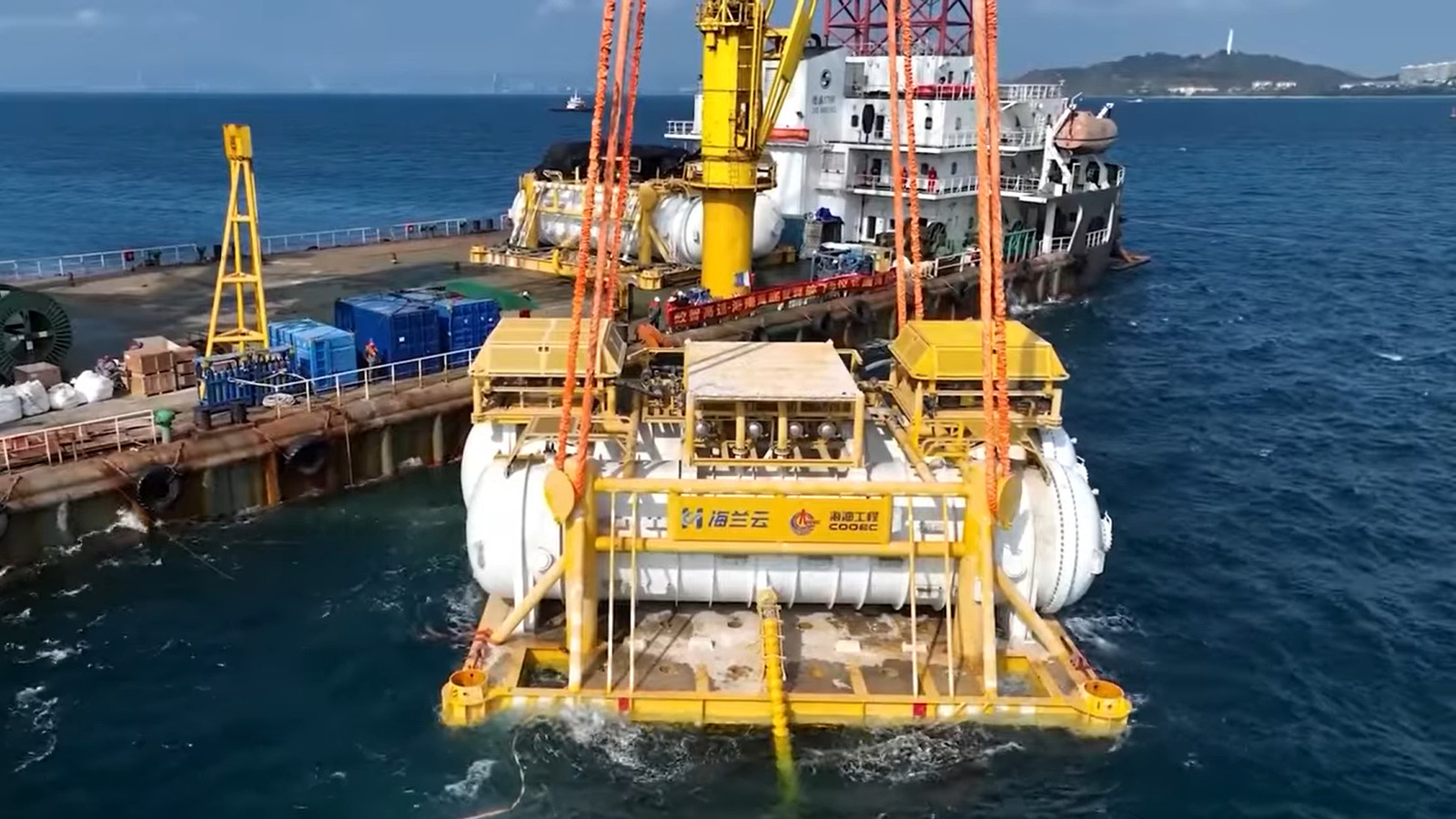
The significant water demands of data centers are increasingly raising concerns regarding their environmental impact. These facilities typically consume large quantities of potable water for cooling, thereby straining local water supplies and competing with agricultural and household usage. In response, China has pioneered a solution by establishing data centers in oceanic locations, utilizing non-potable seawater for cooling. Among these projects, the only operational underwater data center currently exists in Hainan Province, China, which has recently transitioned into a large-scale artificial intelligence (AI) computing hub.
This underwater facility, sealed within steel capsules on the seabed near Lingshui, is now capable of executing tasks akin to those of traditional data centers: processing data, running cloud services, and training AI algorithms. By leveraging the surrounding seawater as a natural cooling mechanism, it significantly reduces energy consumption compared to conventional air-conditioning systems. This shift towards high-density AI computing marks a culmination of efforts to enhance computational efficiency while simultaneously minimizing energy use and land requirements.
Although the facility itself is not entirely new, having deployed its initial modules in 2022, it only began commercial operations in 2023. Recent upgrades to its hardware and the addition of more modules have enabled it to undertake more demanding AI tasks, evolving it into a comprehensive computing hub. Not far from this operational site, another underwater data center remains under construction near Shanghai.
What are the environmental impacts?
The environmental benefits of underwater data centers are becoming increasingly apparent. Conventional data centers typically require substantial electricity for cooling, while their underwater counterparts utilize the ocean’s natural temperature to dissipate heat, effectively minimizing energy use. Furthermore, these installations mitigate issues related to land use and noise pollution, which often accompany the establishment of traditional data centers. This has prompted some U.S. states to reconsider plans for new AI data centers amid community concerns.
However, the long-term environmental implications of such underwater structures remain largely unexplored. While the cooling process utilizes seawater, it also slightly raises local water temperatures, a factor that could affect sensitive marine species. Research from Microsoft’s earlier Natick project indicated that temperature increases were localized and measured in fractions of a degree, but even minor shifts in temperature can have significant impacts on aquatic biodiversity. A study from the University of Johannesburg highlighted a potential risk of ocean deoxygenation, emphasizing that further deployment of underwater data centers could exacerbate these risks. Potential complications such as leaks or corrosion must also be accounted for.
On a more optimistic note, research suggests that these underwater structures may function similarly to artificial reefs, attracting diverse marine life. Microsoft’s Natick project included monitoring equipment that captured footage of marine ecosystems surrounding the facility, paving the way for future underwater data centers to contribute to marine research. Unfortunately, there is no indication that similar measures are currently being implemented at the Hainan site.
As the demand for AI computing continues to surge, the development and expansion of underwater data centers could represent a paradigm shift in how data storage and processing are conducted. The intersection of technology and environmental sustainability will play a crucial role in shaping the future of data centers, potentially transforming them into more eco-friendly alternatives that lessen their burden on local resources. This evolution in data infrastructure will require ongoing evaluation and adaptation to balance technological advancement with environmental stewardship.
See also Nvidia Acquires $5B Stake in Intel, Igniting 100% Surge in Stock Value
Nvidia Acquires $5B Stake in Intel, Igniting 100% Surge in Stock Value Tesseract Launches Site Manager and PRISM Vision Badge for Job Site Clarity
Tesseract Launches Site Manager and PRISM Vision Badge for Job Site Clarity Affordable Android Smartwatches That Offer Great Value and Features
Affordable Android Smartwatches That Offer Great Value and Features Russia”s AIDOL Robot Stumbles During Debut in Moscow
Russia”s AIDOL Robot Stumbles During Debut in Moscow AI Technology Revolutionizes Meat Processing at Cargill Slaughterhouse
AI Technology Revolutionizes Meat Processing at Cargill Slaughterhouse