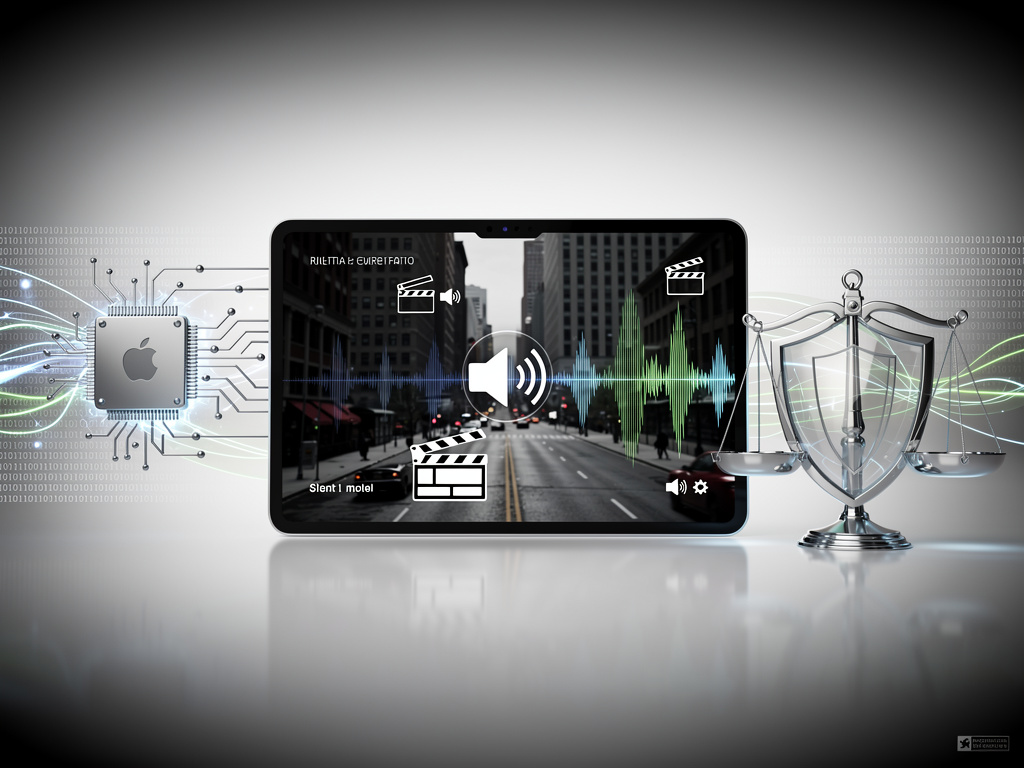
Apple is poised to transform the realm of sound design with its newly developed artificial intelligence model that can generate realistic sound effects and speech from silent video footage. This innovative approach signals a potential shift in filmmaking, accessibility technology, and the content creation industry at large. The model, first reported by 9to5Mac, represents a significant advancement in multimodal AI, enabling the synthesis of audio that corresponds to visual cues rather than merely matching existing sound clips.
Detailing its capabilities, the AI model analyzes visual frames from silent videos to identify objects, movements, and environmental contexts, generating audio in real time. For instance, it can produce the sound of rain, footsteps, or even human speech that aligns with lip movements on screen. This technology not only promises to enhance filmmaking efficiencies but may also redefine accessibility in media consumption.
The underlying architecture of the model highlights Apple’s commitment to expanding its AI capabilities, both on-device and through cloud-based systems. The company has been actively recruiting talent and publishing research that showcases its advancements in machine learning. By leveraging vision transformers and audio diffusion techniques, the model produces high-fidelity sound that synchronizes perfectly with visual elements, ensuring audio realism not just in isolation but in context as well.
Implications for Content Creation
Apple’s approach to AI has historically been more nuanced compared to other tech giants like Google and OpenAI, which have garnered attention with large language models. While Apple has focused on integrating machine learning into its products—enhancing Siri and improving iPhone camera functionalities—this new audio generation capability suggests aspirations that reach far beyond basic enhancements. This foundational technology could be integrated into professional tools like Final Cut Pro and Apple TV+ production workflows, fundamentally changing how sound is created in post-production.
Industry analysts point out that Apple often develops technology quietly in its R&D labs before releasing it in a coordinated manner across its product ecosystem. The trajectory of this video-to-audio model may follow a similar path, first appearing as a tool for developers or within professional software, before trickling down to consumer-facing applications on devices like the iPhone and Mac.
The film and television sectors may experience significant disruption due to this innovation. Traditionally, creating sound effects has involved intricate craftsmanship, with a single scene requiring numerous individually recorded sounds. If AI can autonomously generate these sounds with the necessary quality, it could streamline post-production processes, reducing both time and costs. However, seasoned sound designers will remain essential, as the emotional and narrative roles of sound design demand a level of artistry that may elude algorithmic systems.
Beyond the entertainment industry, the potential for enhanced accessibility is substantial. With millions of individuals worldwide facing hearing impairments, the technology could create new avenues for audio descriptions and sound cues that enrich visual content. While captions and sign language have improved accessibility, generating audio from silent video remains less explored. Apple’s model could produce automatic audio narration, making video content more inclusive.
Apple has consistently championed accessibility, and this model fits seamlessly into that framework. With existing features like VoiceOver and Live Captions, the new technology could extend these capabilities, providing real-time audio for video calls or security footage recorded without sound. The possibilities for education are particularly noteworthy, allowing silent instructional videos to be narrated automatically by an AI, thus enhancing learning experiences in classrooms.
However, the introduction of a model that generates realistic speech from silent video also invites ethical considerations. The potential to fabricate audio that could misrepresent individuals poses significant risks, akin to concerns raised by deepfake technologies. Apple is likely cognizant of these issues and may implement safeguards, such as on-device processing and watermarking for AI-generated content, to mitigate potential misuse.
As Apple delves into multimodal AI, the company aims to compete at the forefront of AI innovation, rather than merely adopting external technologies. A model capable of deciphering the interplay between visual and auditory elements could enhance Siri’s performance, improve spatial computing experiences with the Apple Vision Pro, and create new tools for content creators. As the technology matures, Apple’s commitment to careful integration will likely shape its deployment strategy across its diverse product range, impacting millions of users globally.
See also Sam Altman Praises ChatGPT for Improved Em Dash Handling
Sam Altman Praises ChatGPT for Improved Em Dash Handling AI Country Song Fails to Top Billboard Chart Amid Viral Buzz
AI Country Song Fails to Top Billboard Chart Amid Viral Buzz GPT-5.1 and Claude 4.5 Sonnet Personality Showdown: A Comprehensive Test
GPT-5.1 and Claude 4.5 Sonnet Personality Showdown: A Comprehensive Test Rethink Your Presentations with OnlyOffice: A Free PowerPoint Alternative
Rethink Your Presentations with OnlyOffice: A Free PowerPoint Alternative OpenAI Enhances ChatGPT with Em-Dash Personalization Feature
OpenAI Enhances ChatGPT with Em-Dash Personalization Feature