Microsoft has unveiled the Maia 200, adding to a growing roster of custom processors developed by hyperscalers, which includes offerings from AWS and Google. These AI chips are primarily engineered to enhance inference efficiency and streamline internal cost structures, although certain platforms also accommodate large-scale training tasks. Among these competitors, Google’s solution stands out as the most developed, boasting a more extensive production history and broader training capabilities.
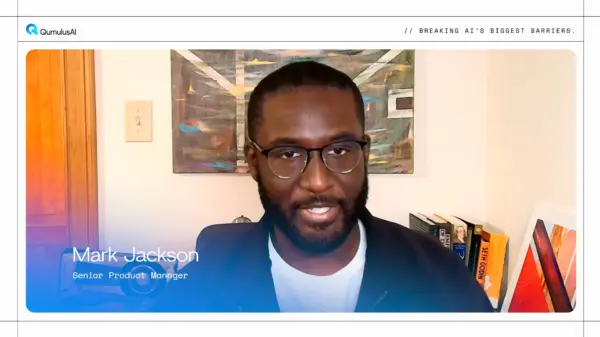
Mark Jackson, Senior Product Manager at QumulusAI, noted that this trend indicates a move toward segmentation rather than disruption within the realm of AI development teams. He elaborated that hyperscaler silicon is frequently fine-tuned to address specific workload patterns within a singular cloud environment. Despite the arrival of custom chips like the Maia 200, Jackson emphasized that NVIDIA GPUs continue to be the preferred choice for advanced training and projects that demand cross-cloud flexibility.
Jackson further highlighted NVIDIA’s established ecosystem and operational maturity, which provide the company with a competitive edge in the arena of cutting-edge AI development. While custom chips like the Maia 200 are being deployed in more narrowly optimized scenarios, NVIDIA’s products are viewed as the standard for tasks requiring a wider range of capabilities.
This competitive landscape reflects a broader trend in the tech industry where major cloud providers are increasingly investing in proprietary hardware to optimize performance and costs. As organizations continue to shift towards AI-driven solutions, the demand for more efficient and specialized processing capabilities is likely to grow, pushing hyperscalers to refine their custom offerings further. This could lead to a diversification of AI development strategies across various cloud platforms.
In the wake of these developments, companies are faced with important decisions regarding their AI infrastructure. The choice between adopting specialized chips like the Maia 200 or sticking with NVIDIA’s proven GPUs will hinge on their specific needs and workload requirements. As the market matures, the implications of these choices could shape not only the performance of AI applications but also the overall cost structures that govern them.
Looking ahead, the introduction of chips like the Maia 200 is set to intensify competition among cloud providers, potentially leading to innovations that further enhance AI capabilities. As hyperscalers refine their technologies, the landscape of AI development is poised for significant transformation, with implications that extend beyond individual firms to the industry at large.
See also Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032
AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032 Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs
Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs Wall Street Recovers from Early Loss as Nvidia Surges 1.8% Amid Market Volatility
Wall Street Recovers from Early Loss as Nvidia Surges 1.8% Amid Market Volatility