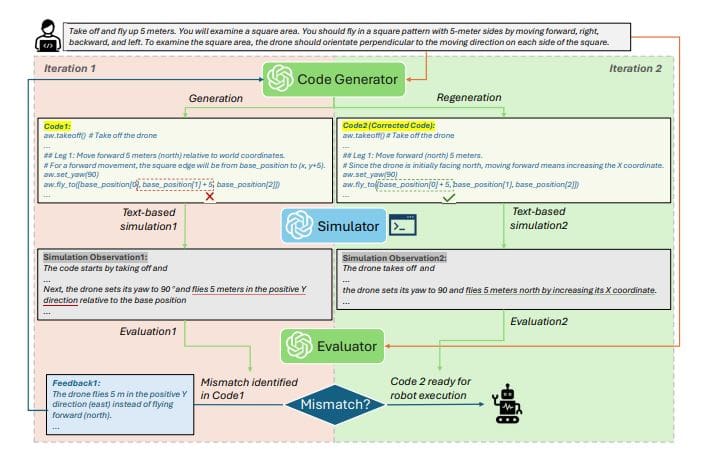
The growing capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in generating robot control code signal a transformative phase for autonomous systems, yet the challenge of ensuring the reliability of this generated code persists. Researchers from the University of Massachusetts Dartmouth, including Wenhao Wang, Yanyan Li, Long Jiao, and Jiawei Yuan, have introduced a novel framework aimed at addressing this issue. Their approach utilizes LLMs for static simulation of robot operation code, effectively eliminating the need for time-consuming physical experiments or intricate simulation environments.
This pioneering system, named Besimulator, allows the LLM to act as a reliable static simulator, facilitating robust code correction through feedback. The methodology empowers the LLM to simulate the outcomes of robot actions prior to execution, enhancing operational reliability, especially in complex or unpredictable environments. This initiative marks a significant shift in robotic control practices, moving away from traditional physics-based simulations toward a more adaptable, knowledge-driven strategy that harnesses the reasoning capabilities inherent in LLMs.
At the heart of this innovation is the ability of the LLM to interpret robot actions, reason through state transitions, and analyze execution outcomes. The research team developed a corrective code generation framework wherein the LLM serves both as a simulator and evaluator, iteratively refining the robot code until it meets specific performance standards. Experiments conducted demonstrated impressive accuracy, with the static simulation achieving over 97.5% correlation to established unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) simulators such as AirSim and PX4-Gazebo.
The corrective code generation framework produced results comparable to leading-edge methods, with an 85%+ success rate and 96.9%+ completeness across a range of UAV systems. Notably, the system achieved a successful completion rate of over 96.9% for required actions, and more than 85% of evaluated tasks were accomplished without error. To further validate adaptability, the framework was assessed on both UAVs and ground robots, consistently recording high success rates above 87.5%, while maintaining completeness exceeding 96.9%.
This research illustrates a significant advancement in LLM-driven robotics, providing an efficient and scalable solution for generating reliable robot operation code. By leveraging the power of large language models, the framework offers a streamlined path for developing dependable robotic systems without the extensive configuration usually associated with traditional simulation methods.
The implications of this work extend beyond simple code generation. By validating robot operation code through a static simulation process, the researchers have established a framework that not only predicts actions and state transitions but does so with high reliability devoid of dynamic execution in real or virtual environments. This advancement represents a practical solution for the complex demands of modern robotics and could substantially accelerate the deployment of autonomous systems across various industries.
As this technology continues to evolve, the potential to reshape how robotic systems are programmed and operated grows clearer. The ability to effectively utilize LLMs in generating and validating robot control code signifies a critical step toward fostering the next generation of autonomous robots, which could fundamentally alter applications in sectors ranging from logistics to healthcare. The research team’s innovative approach underscores the increasing integration of artificial intelligence into practical engineering solutions, presenting a future where robotics can operate with enhanced autonomy and reliability.
See also Amazon Launches Nova Forge Generative AI Model for Custom Data Integration
Amazon Launches Nova Forge Generative AI Model for Custom Data Integration Nano Banana Pro Launches Free AI Tool for High-Quality Health Education Visuals
Nano Banana Pro Launches Free AI Tool for High-Quality Health Education Visuals 123RF Launches AI-Powered Video Comprehension on AWS, Doubles Descriptor Accuracy
123RF Launches AI-Powered Video Comprehension on AWS, Doubles Descriptor Accuracy OpenAI Launches GPT-5.1 with Enhanced Features and 800 Million Weekly Users
OpenAI Launches GPT-5.1 with Enhanced Features and 800 Million Weekly Users Generative AI Model Identifies Blood Cell Abnormalities with 95% Accuracy
Generative AI Model Identifies Blood Cell Abnormalities with 95% Accuracy