Agentic AI represents a significant shift in the landscape of artificial intelligence, evolving from reactive tools to autonomous systems capable of making decisions, planning intricate tasks, and continuously adapting without human intervention. By 2025, these intelligent agents are no longer confined to science fiction; they are actively reshaping industries across the globe. This transformation hinges on their ability to perceive their environments, reason through complex scenarios, take decisive actions, and learn from outcomes.
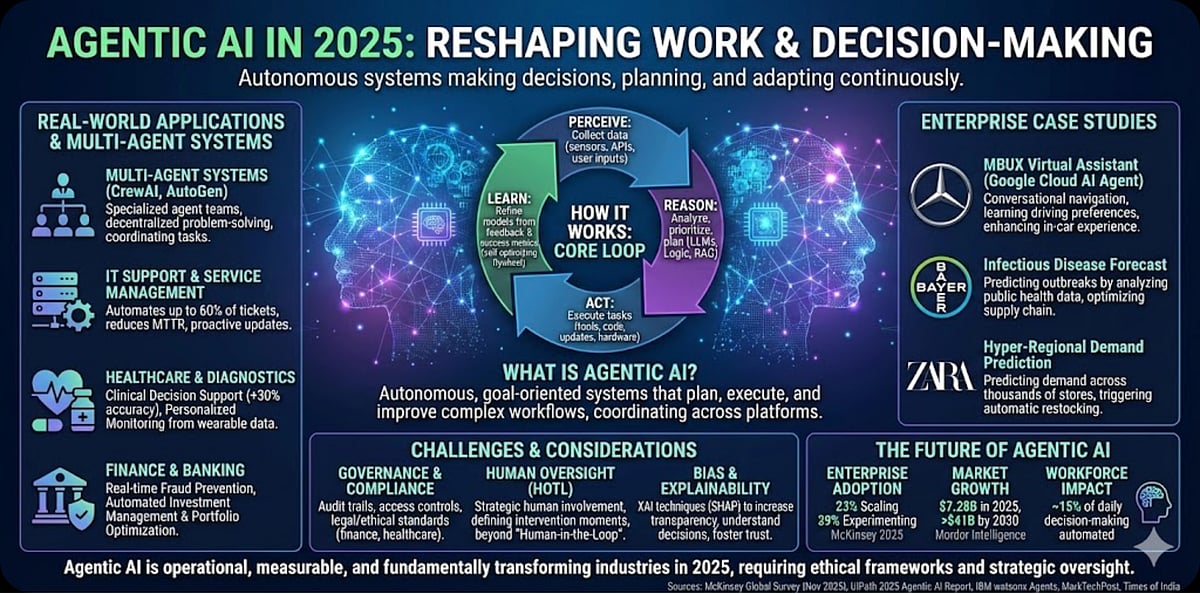
Defining Agentic AI involves highlighting its goal-oriented and autonomous behavior. These systems are not merely chat interfaces or content generators; they are sophisticated decision-makers and problem-solvers capable of executing and improving upon complex workflows, often coordinating across multiple platforms and teams. For instance, modern customer service AIs can autonomously detect delivery issues, initiate refunds, update customer records, and learn from each interaction, all without requiring human input.
Agentic AI operates through a dynamic self-improving loop: it perceives data from various sources, reasons with that data utilizing logic and advanced language models, acts autonomously by executing tasks, and learns from the feedback generated. This approach creates a powerful, self-optimizing system that enhances efficiency and effectiveness in various contexts.
The applications of Agentic AI in 2025 are widespread, particularly through the emergence of Multi-Agent Systems that facilitate decentralized problem-solving. In IT support and service management, for instance, agentic systems manage up to 60% of routine IT tickets, significantly cutting down on Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) and proactively addressing system updates. In healthcare, these agents improve diagnostic accuracy by 30% while interpreting data from wearables for personalized patient monitoring. The finance sector benefits from real-time fraud detection and investment management, where autonomous agents analyze global market conditions to optimize client portfolios. These examples illustrate a clear trend towards autonomous decision-making across various industries.
Noteworthy enterprise case studies underscore the impact of Agentic AI. Mercedes-Benz has integrated Google Cloud’s AI Agent into its MBUX Virtual Assistant, enhancing the in-car experience by learning user driving preferences. In pharmaceuticals, Bayer applies Agentic AI to predict infectious disease outbreaks by analyzing public health data and weather patterns, optimizing supply chain planning. Retail giant Zara employs AI agents to forecast demand fluctuations across its stores, automating inventory management to improve operational efficiency.
Despite its promising applications, the rapid adoption of Agentic AI also raises significant challenges that require careful governance. The intricate nature of autonomous operations necessitates strict oversight to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards. Enterprises are increasingly recognizing the need for agents that incorporate audit trails and access controls, particularly in sensitive fields like finance and healthcare.
The dialogue around human oversight is evolving from the vague “human-in-the-loop” model to a more defined “human-on-the-loop” strategy. This approach emphasizes the specific moments and areas where human judgment is necessary, ensuring that human intervention is applied strategically rather than serving as a mere backstop against errors. Additionally, there is growing concern regarding bias in AI systems, as these systems can inherit and amplify biases present in their training data. Implementing Explainable AI (XAI) techniques is essential to promote transparency and foster trust by clarifying the rationale behind an agent’s decisions.
Looking ahead, the adoption of Agentic AI is poised for significant growth. According to a McKinsey survey from November 2025, 23% of organizations are currently scaling agentic AI systems in production, with an additional 39% experimenting with proofs-of-concept. This strong interest indicates that the technology is transitioning out of the pilot phase. The global market for Agentic AI is projected to reach $7.28 billion by 2025, with forecasts suggesting it could exceed $41 billion by 2030. The impact on the workforce is also notable, with agents expected to automate up to 15% of decision-making tasks among knowledge workers, allowing humans to focus on strategic initiatives and creative endeavors.
As the landscape of Agentic AI continues to develop, deeper integration with physical systems, including robotics, drones, and autonomous vehicles, is anticipated. The future will likely see increasingly complex multi-agent ecosystems able to negotiate, trade, and collaborate across entire value chains.
In conclusion, Agentic AI has transitioned from a theoretical concept to an operational reality that fundamentally alters industry practices in 2025. By enhancing customer service, optimizing supply chains, and revolutionizing diagnostics, autonomous AI agents are delivering significant business value. As organizations scale their adoption of this technology, prioritizing ethical frameworks, strategic oversight, and human-centric design will be crucial to ensuring that these powerful systems remain trustworthy and beneficial.
See also Taiwo Feyijimi Introduces AI-Driven Frameworks to Enhance Engineering Education Quality
Taiwo Feyijimi Introduces AI-Driven Frameworks to Enhance Engineering Education Quality US Grants Nvidia 25% Fee Export Approval for H200 Chips to China Amid Tech Tensions
US Grants Nvidia 25% Fee Export Approval for H200 Chips to China Amid Tech Tensions CyberAI Group Files Three Patents for AI-Driven Cyber Defense Solutions
CyberAI Group Files Three Patents for AI-Driven Cyber Defense Solutions Singulr AI Appoints Bask Iyer as Strategic Advisor to Enhance AI Governance Strategies
Singulr AI Appoints Bask Iyer as Strategic Advisor to Enhance AI Governance Strategies Linux Foundation Launches Agentic AI Foundation to Drive Transparent AI Innovation
Linux Foundation Launches Agentic AI Foundation to Drive Transparent AI Innovation