AI is poised to emerge as “the most significant driver of change in cybersecurity” in 2026, according to the World Economic Forum’s Global Cybersecurity Outlook report, released this week. The survey of over 800 cybersecurity leaders revealed that 94% recognize AI security issues as a primary concern, reflecting a shift in focus among CEOs and Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs).
While CEOs have recently shifted their priorities towards cyber-enabled fraud, moving away from ransomware, CISOs remain concerned about ransomware and supply chain resilience. This divergence illustrates the varying cybersecurity priorities between executive leadership and frontline security teams.
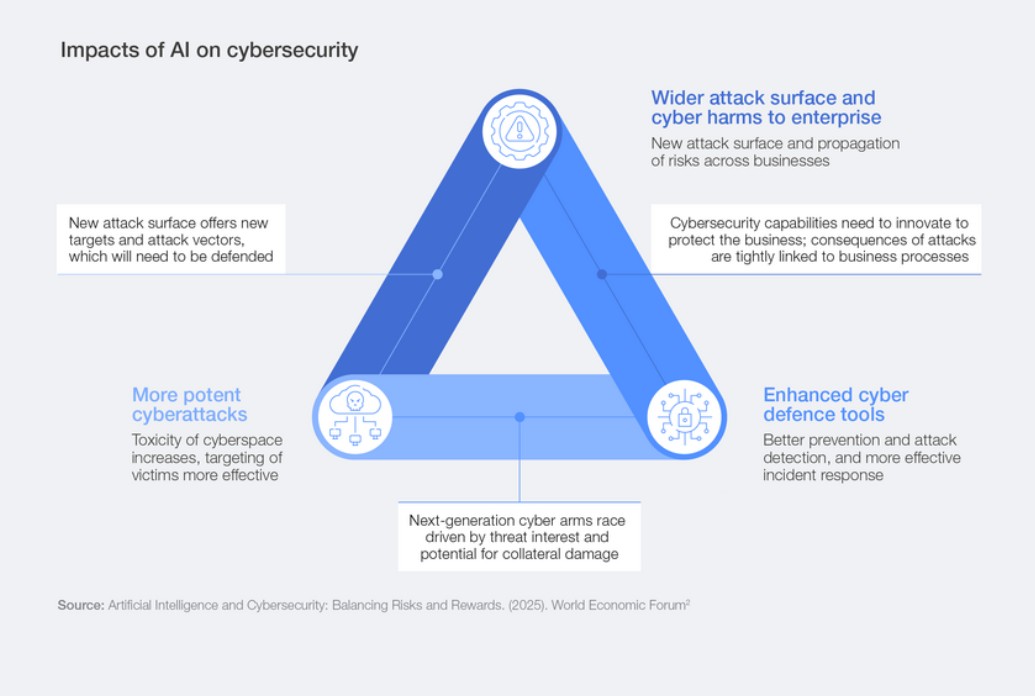
The report highlights that 87% of respondents identified AI-related vulnerabilities as the fastest-growing cyber risk. Additionally, more than half of those surveyed expressed concerns over cyber-enabled fraud, phishing, and supply chain disruptions. Insider threats and denial of service (DoS) attacks were flagged by about 30% of respondents as increasing threats.
Among generative AI (GenAI) concerns, issues such as data leaks exposing personal information, the enhancement of adversarial capabilities (including phishing and malware development), and complex security governance were noted as significant challenges. The report underscores a growing recognition of these threats, prompting organizations to take proactive measures.
The increasing focus on AI security has led many organizations to assess the security of their AI tools more rigorously. The percentage of respondents conducting security assessments rose from 37% in 2025 to 64% in 2026. However, about 36% of organizations still lack any formal assessment process for AI security, indicating that systemic vulnerabilities persist even as AI adoption accelerates.
The report recommends several measures to bolster AI security, such as protecting data used for training AI models, embedding security within AI system development, and implementing robust authentication and encryption protocols to safeguard customer interactions.
AI’s transformative impact extends to defensive cybersecurity operations as well. According to the report, 77% of organizations have incorporated AI into their cybersecurity efforts, focusing on enhancing phishing detection (52%), intrusion and anomaly response (46%), and user behavior analytics (40%). However, obstacles remain, including a lack of skills and knowledge in AI deployment, concerns over risk, and the need for human oversight.
Despite the advantages AI offers in automating repetitive tasks, the report warns against over-reliance on automated systems. AI currently lacks the contextual judgment necessary for strategic decision-making, leaving potential blind spots that adversaries could exploit.
The report also outlines the geopolitical landscape’s influence on cybersecurity strategies. With 64% of organizations factoring in the potential for geopolitically motivated cyberattacks, confidence in national cyber preparedness has decreased. A troubling 31% of respondents expressed low confidence in their country’s ability to respond to major cyber incidents, up from 26% the previous year.
In particular, the public sector reported significant concerns, with 23% of its organizations stating they lack sufficient cyber-resilience capabilities. As critical infrastructure continues to face significant threats, the disparity in confidence levels raises alarms about national preparedness.
The World Economic Forum’s findings highlight not just the increasing complexities of cybersecurity but also the urgent need for cohesive strategies that address the rising risks associated with AI and geopolitical tensions. As organizations grapple with these evolving challenges, the need for strong governance, skilled personnel, and innovative technologies will play a crucial role in shaping future cybersecurity landscapes.
See also AI Security Gap: 4 Key Challenges Amplified by New Threats in Cloud Environments
AI Security Gap: 4 Key Challenges Amplified by New Threats in Cloud Environments AI Supercharges Cybersecurity: 94% of Execs Cite Geopolitical Risks as Top Concern for 2026
AI Supercharges Cybersecurity: 94% of Execs Cite Geopolitical Risks as Top Concern for 2026 AI Video Analytics Market to Surge to $64.48 Billion by 2035 with 22.85% Growth Rate
AI Video Analytics Market to Surge to $64.48 Billion by 2035 with 22.85% Growth Rate Ransomware Attacks Surge 60% in December, Driven by Unmanaged GenAI Risks
Ransomware Attacks Surge 60% in December, Driven by Unmanaged GenAI Risks Automotive IDPS Market Expected to Reach $7.82B by 2036, Driven by AI Threat Detection
Automotive IDPS Market Expected to Reach $7.82B by 2036, Driven by AI Threat Detection