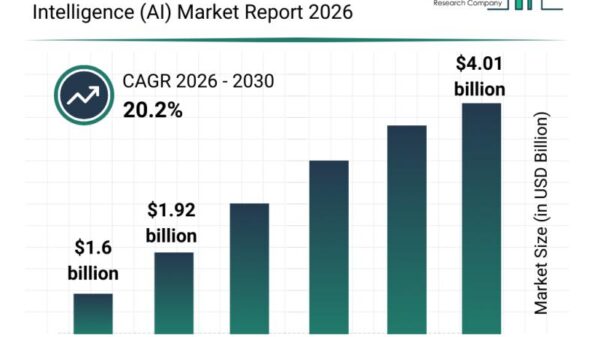
A significant shift in digital media regulation is underway as the Indian government places a spotlight on synthetic and AI-generated content. Proposed amendments to existing rules will require creators to disclose when their content is produced using artificial intelligence or generative tools. Furthermore, platforms will be mandated to implement systems that identify manipulated media and label it clearly as synthetic. This initiative aims to combat the misuse of deepfakes, which have become prevalent and are often used for harassment, impersonation, misinformation, and political manipulation.
The government contends that these changes will enhance transparency and accountability within an online environment that generates millions of posts daily. Officials assert that the updated framework will reinforce legal obligations for platforms to take action upon gaining “actual knowledge” of illegal content, particularly when alerted through court orders or government notifications. Concurrently, recent blocking orders have targeted smaller OTT platforms accused of hosting pornographic material, indicating the government’s intention to enforce stricter standards across the digital landscape.
Responses to the proposed amendments have been mixed. Digital rights organizations and legal experts express concern that vague terminology, such as “obscene,” could lead to the censorship of legitimate artistic, journalistic, or political content. They argue that without clear procedural safeguards, these rules may grant authorities excessive discretion, potentially chilling creative expression and critical discourse. Advocates for digital freedoms are urging for a more extended public consultation period and stricter oversight mechanisms.
Industry reactions vary widely. Portions of the entertainment, advertising, and creator economy sectors welcome the introduction of stronger measures aimed at curbing unauthorized explicit content and undisclosed synthetic imagery. These groups argue that clearly defined regulations could mitigate reputational risks and foster cleaner digital environments. Conversely, smaller platforms and independent creators express concern over the heavy compliance burden, which could necessitate significant investments in moderation teams, verification systems, and more agile grievance mechanisms to avoid penalties and blocking orders.
Operational challenges also loom large. The effective detection of AI-generated media presents substantial technical hurdles; even sophisticated automated tools can mistake legitimate satire or creative edits for harmful content, as observed by social media analysts. Malicious actors can easily mislabel or conceal synthetic media, undermining the deterrent effect of the proposed regulations. Moreover, international hosting complicates matters further, as content stored on servers outside India can still be accessed domestically unless platforms actively restrict it.
In political discourse, the government is likely to frame these new regulations as necessary for shielding women, children, and the public from exploitation and misinformation. However, critics are expected to challenge the constitutionality of the provisions in court, arguing that they could infringe on free speech rights if applied too broadly or without adequate checks. For social media companies and digital publishers, this shift signals a more demanding compliance landscape, characterized by increased moderation costs and heightened legal exposure.
The forthcoming months will be pivotal in determining the transformational impact of these proposed changes. Key factors include how precisely the government defines terms like “obscene digital content,” the drafting of enforcement protocols, and whether courts uphold the regulations if legally contested. The responses from platforms could also significantly influence the outcome, with some global companies likely to comply readily, while others may resist or seek legal clarity. For creators, users, and digital businesses, these revisions represent a noteworthy step in India’s evolving effort to regulate online speech, technologies, and safety within an increasingly complex digital era.
Regulatory Implications for Digital Media
The proposed regulations mark a critical juncture in how digital media is perceived and managed in India. As AI technologies proliferate, the need for coherent guidelines becomes more pressing. This regulatory framework stands to redefine the relationship between content creators and platforms, emphasizing accountability while simultaneously raising concerns about censorship and creative freedom.
Industry Responses and Compliance Challenges
The mixed reactions from various industry segments underscore the complexity of digital content regulation. While some welcome the initiative as a means of fostering integrity, others fear the implications of compliance could stifle innovation and disproportionately impact smaller entities. As the landscape evolves, it will be crucial for all stakeholders to engage in dialogues that balance regulation and creative expression.
See also Five Lawsuits Claim ChatGPT’s Guidance Led to Wrongful Deaths Amid AI Safety Concerns
Five Lawsuits Claim ChatGPT’s Guidance Led to Wrongful Deaths Amid AI Safety Concerns Google Launches Gemini 3 with 1M Token Context for Enhanced AI Customer Experience
Google Launches Gemini 3 with 1M Token Context for Enhanced AI Customer Experience Multimodal AI Agents Revolutionize Automation: From Text Models to Autonomous Systems
Multimodal AI Agents Revolutionize Automation: From Text Models to Autonomous Systems Google Launches AI Mode for Image Creation with Nano Banana Model on Desktop
Google Launches AI Mode for Image Creation with Nano Banana Model on Desktop Amazon SageMaker HyperPod Launches MIG Support to Optimize GPU Utilization for AI Workloads
Amazon SageMaker HyperPod Launches MIG Support to Optimize GPU Utilization for AI Workloads