Researchers from the University of Toronto and Qualcomm AI Research are addressing a critical challenge in artificial intelligence: enhancing large language models’ (LLMs) capabilities for complex, multi-turn interactions, which require effective planning, state tracking, and sustained contextual awareness. A team led by Amin Rakhsha, along with Thomas Hehn, Pietro Mazzaglia, Fabio Valerio Massoli, Arash Behboodi, and Tribhuvanesh Orekondy, has introduced a novel framework named LUMINA. This framework identifies which underlying capabilities most hinder progress in LLMs, employing an ‘oracle counterfactual’ approach to assess how perfect execution of skills impacts agent performance.
The research reveals that while improving planning consistently enhances performance, the benefits of other skills vary significantly depending on the environment and the model employed. This insight is crucial for understanding the obstacles faced by interactive agents and offers a pathway for future developments in both language model architecture and training methodologies.
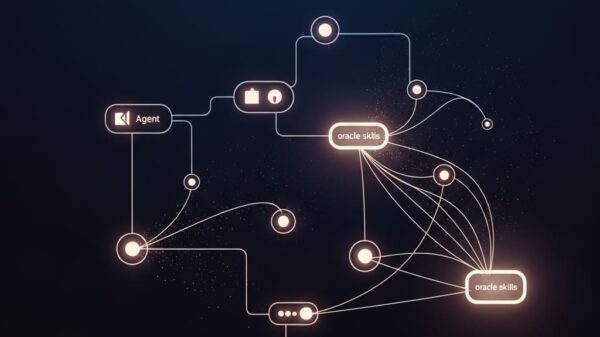
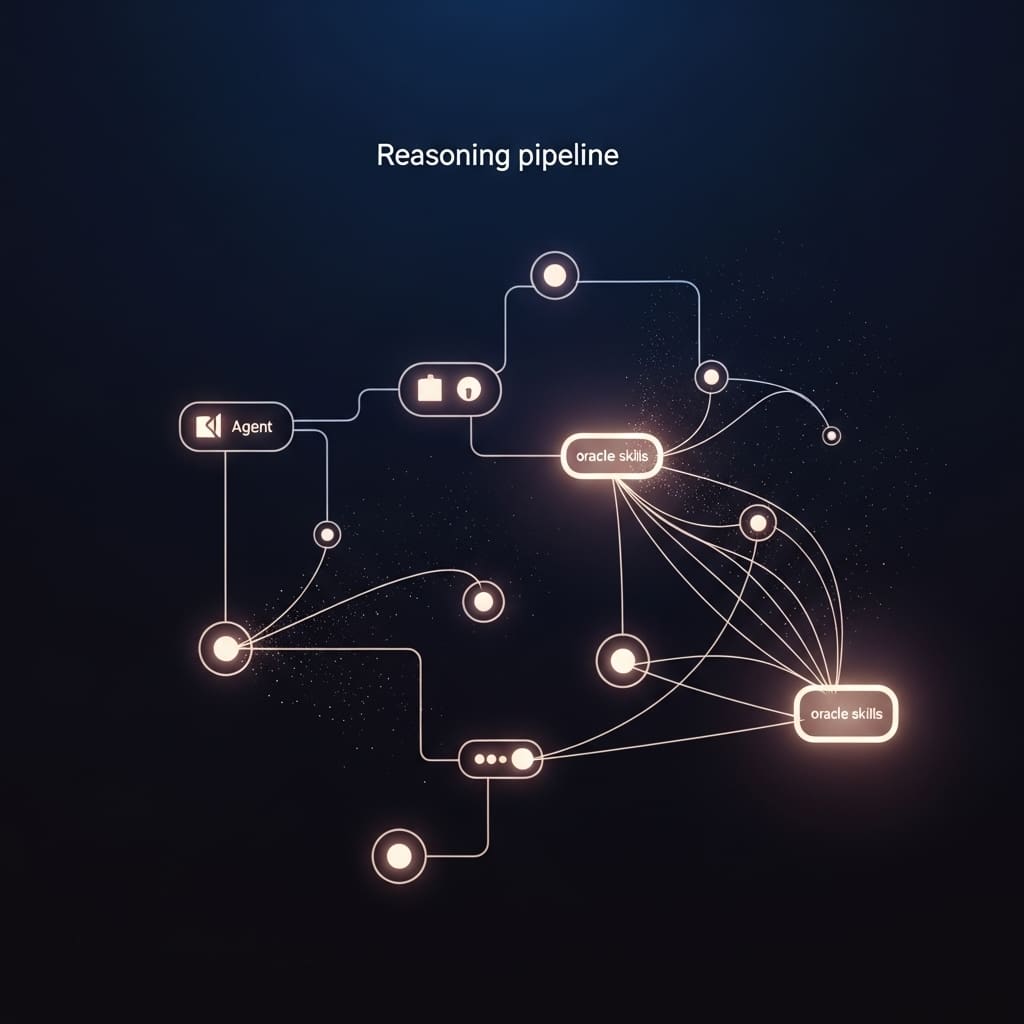
By isolating core skills necessary for LLMs to excel in complex tasks, the team measures the impact of specific capabilities such as planning and state tracking through controlled environments like ListWorld, TreeWorld, and GridWorld. Each environment allows for systematic oracle interventions, granting researchers the ability to quantify the performance gains when an agent is provided with perfect assistance in executing tasks. For example, ListWorld challenges agents to manipulate a Python list, while TreeWorld involves searching through a tree structure to find a specific value, and GridWorld tasks agents with navigating a grid in a limited number of turns.
The LUMINA framework operates within the confines of a Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP), where tasks are communicated verbally to the agents. Notably, to ensure the integrity of the data, the team generated novel tasks and allowed for random regeneration while maintaining complete knowledge of the underlying processes. This meticulous approach also facilitates the introduction of oracle interventions that can be accurately annotated, overcoming limitations often encountered in real-world benchmarks.
Findings from the study indicate a significant discrepancy between per-step accuracy and long-horizon success rates, highlighting compounding errors as a major obstacle for LLM-based agents. Although high accuracy at individual steps is achievable, maintaining coherence across multiple turns remains a challenge. The research confirms that introducing perfect planning significantly boosts overall performance, underscoring its essential role in navigating intricate tasks.
Moreover, the study emphasizes that different environments yield varying benefits from oracle interventions, revealing tangible performance discrepancies. The results suggest that larger models, such as LLama3-70B and GPT-4o, exhibit more pronounced gains when enhancements are made to specific skills. In benchmark tests, the success rate for LLama3-70B was recorded at 7.0%, while GPT-4o achieved 30.2%, illustrating the current limitations faced by open-weight models in complex, multi-turn scenarios.
Additionally, the researchers explored the effects of oracle interventions on different model sizes, determining that strategies like history pruning—removing irrelevant information—can significantly benefit smaller models while potentially hindering larger ones. This nuanced understanding reveals that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to improving LLMs; rather, optimal strategies depend on the specific model and task characteristics.
The researchers acknowledge the restrictions of their study, particularly the reliance on simplified, programmable environments, which may not fully represent the complexities of real-world applications. Future research could focus on refining instruction-following mechanisms and developing an “instruction following” oracle to enhance the evaluation of LLM capabilities. Such advancements are deemed critical for addressing the risks linked with faulty or malicious autonomous systems.
This pioneering work not only sheds light on the limitations and potential of LLMs in handling complex interactions but also lays foundational groundwork for future explorations in AI agent development. As the landscape of artificial intelligence continues to evolve, understanding these dynamics will be essential for creating more capable and reliable interactive agents.
See also Sam Altman Praises ChatGPT for Improved Em Dash Handling
Sam Altman Praises ChatGPT for Improved Em Dash Handling AI Country Song Fails to Top Billboard Chart Amid Viral Buzz
AI Country Song Fails to Top Billboard Chart Amid Viral Buzz GPT-5.1 and Claude 4.5 Sonnet Personality Showdown: A Comprehensive Test
GPT-5.1 and Claude 4.5 Sonnet Personality Showdown: A Comprehensive Test Rethink Your Presentations with OnlyOffice: A Free PowerPoint Alternative
Rethink Your Presentations with OnlyOffice: A Free PowerPoint Alternative OpenAI Enhances ChatGPT with Em-Dash Personalization Feature
OpenAI Enhances ChatGPT with Em-Dash Personalization Feature