PlantIF, a groundbreaking multimodal learning model developed by researchers at Guizhou University, represents a significant advancement in agricultural technology aimed at improving plant disease recognition. Published on 21 October 2025 in the journal Plant Phenomics, the study addresses the growing challenges of crop health management in the face of increasing global food demands. Traditional methods of disease detection, which depend heavily on human expertise and visual inspection, have often proven inadequate, particularly in complex and noisy environments.
The urgency to enhance crop health is underscored by the threat plant diseases pose to agricultural productivity. Many diseases remain undetected until it is too late for effective intervention, leading to substantial crop losses. Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning have opened new avenues for more efficient detection methods. While image-based techniques have shown promise, they are often challenged by dynamic field conditions. In contrast, PlantIF leverages multimodal learning to combine image and textual data, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy and offering a comprehensive understanding of plant diseases.
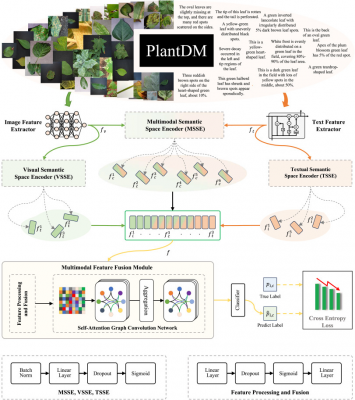
The study led by Gefei Hao’s team evaluated PlantIF’s performance against a variety of models including two text-based, seven visual, and four multimodal models. Utilizing Python 3.8.13 with the PyTorch deep learning framework and GPU acceleration through CUDA 11.2, the researchers split their dataset, PlantDM, into training and testing sets with an 80:20 ratio. The results were striking: PlantIF achieved an accuracy rate of 96.95%, exceeding other models in both precision at 97.55% and recall at 96.84%. The model’s architecture, which utilizes convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for feature extraction alongside self-attention graph convolution for global semantic understanding, enables effective integration of image and text data.
One of the key findings of the study was that while visual models such as ResNet and DenseNet surpassed text-based models like LSTM and BERT in performance, PlantIF outperformed other multimodal models and demonstrated a more efficient computational profile. This efficiency is particularly vital in real-world applications where quick diagnostics can prevent crop losses. By fusing local and global information effectively, PlantIF not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also provides flexibility in handling diverse and large-scale datasets.
Incorporating expert-written descriptions and sensor data alongside visual input, PlantIF offers a holistic approach to disease diagnosis. This multimodal technique allows for greater differentiation between similar diseases and can identify subtle symptoms that traditional methods might overlook. By reducing the need for manual intervention, PlantIF facilitates large-scale automated disease management, enabling early detection and targeted treatments that could significantly mitigate crop losses.
As agricultural environments become increasingly complex due to climate change and other factors, the potential of models like PlantIF is particularly noteworthy. They could play a transformative role in enhancing food security and promoting sustainable practices within precision agriculture. By providing accurate and efficient plant disease management tools, PlantIF stands as a promising solution to one of the pressing challenges of modern agriculture.
The implications of this research extend beyond immediate agricultural practices; they suggest a future where technology plays a crucial role in addressing global food security challenges. With the ability to adapt to various conditions and datasets, PlantIF is well-positioned to support the agricultural sector in navigating the complexities of crop health management.
See also Tsinghua and Shengshu Open-Source TurboDiffusion, Boosting AI Video Generation by 97×
Tsinghua and Shengshu Open-Source TurboDiffusion, Boosting AI Video Generation by 97× Leonardo DiCaprio Critiques AI’s Role in Art, Citing Job Loss and Lack of Humanity
Leonardo DiCaprio Critiques AI’s Role in Art, Citing Job Loss and Lack of Humanity LLMs Transform Undergraduate Education, Offering Personalized Learning and New Challenges
LLMs Transform Undergraduate Education, Offering Personalized Learning and New Challenges Chinese Researchers Reveal TurboDiffusion, Achieving 200x Faster AI Video Creation
Chinese Researchers Reveal TurboDiffusion, Achieving 200x Faster AI Video Creation Experts Urge Transparency and Validation as Generative AI Transforms Life Sciences R&D
Experts Urge Transparency and Validation as Generative AI Transforms Life Sciences R&D