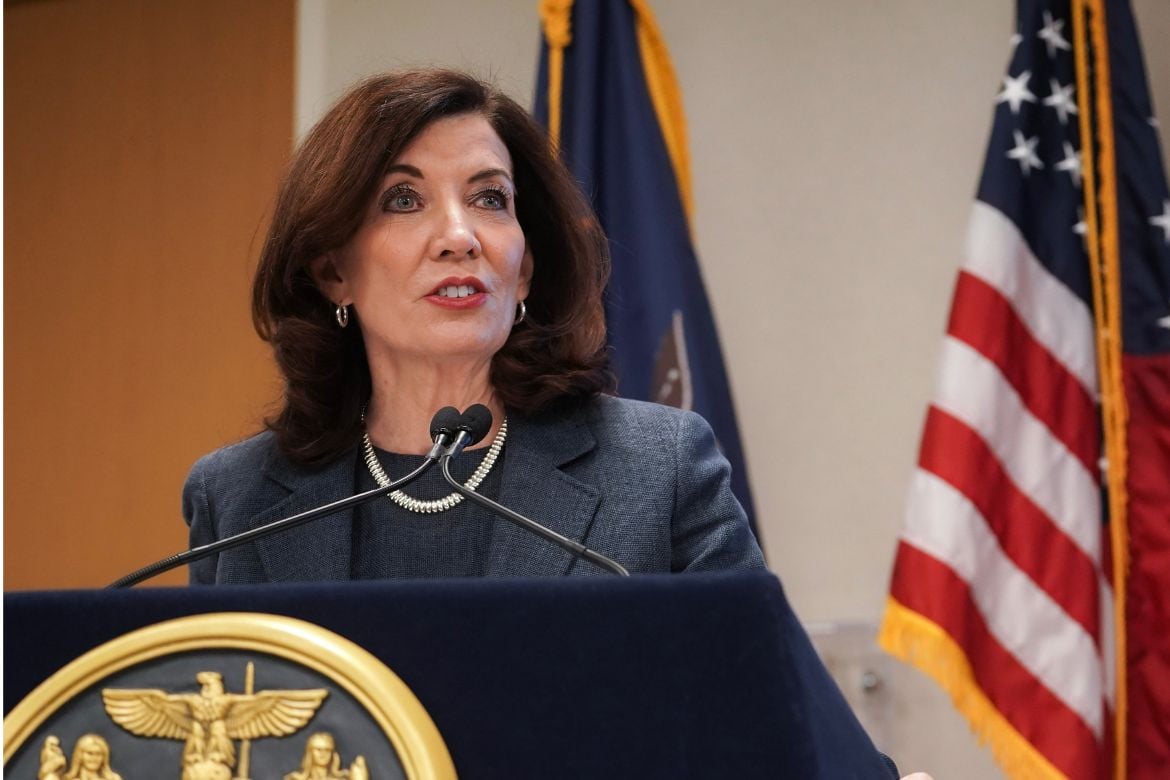
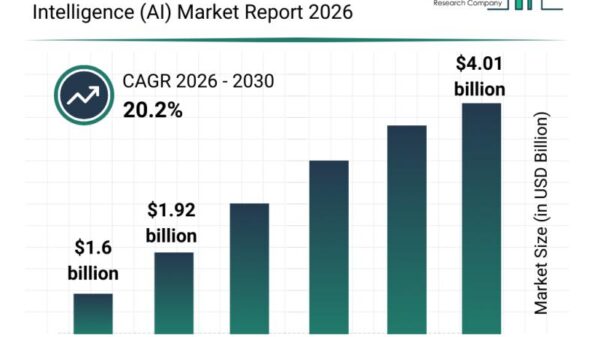
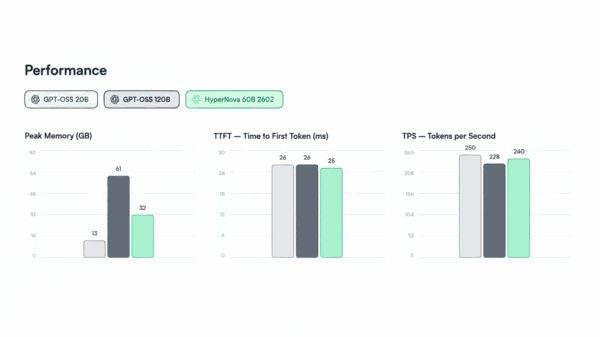
New York Governor Kathy Hochul signed a new AI safety law in December, positioning it as a counterpart to California’s approach and suggesting a move toward a unified regulatory framework for advanced AI in the United States. The New York Responsible AI Safety and Education (RAISE) Act aims to align closely with California’s SB 53 (the Transparency in Frontier Artificial Intelligence Act), citing shared definitions and compliance mechanisms. However, a closer examination reveals that significant differences between the two laws may exacerbate the fragmentation of state AI regulations rather than foster a cohesive national standard.
Both New York and California’s laws target “frontier” AI systems, defined as those requiring more than 10²⁶ floating-point operations (FLOPs) during training. Each mandates that developers produce formal safety documents detailing how they address “critical” or “catastrophic” harms, which include risks related to the creation of chemical, biological, radiological, or nuclear (CBRN) weapons, mass-casualty events, or economic damages exceeding $1 billion. Compliance mechanisms, such as mandatory reporting of serious incidents and protections for whistleblowers, also show parallels. This can lead to the impression that New York’s legislation is merely an extension of California’s regulatory model.
However, the RAISE Act diverges significantly in its scope and governance philosophy. While California’s law applies strict compliance obligations to firms with more than $500 million in annual revenue, New York focuses instead on the cost of a single training run. Any company spending over $100 million on model training is classified as a “large developer” and faces heightened scrutiny. This difference means that a lean startup or research entity could be subject to New York’s regulations while remaining outside California’s strictest tier.
New York’s law further expands its regulatory reach through what is termed a knowledge distillation clause. If an organization trains a more efficient model using a frontier-level one that meets the 10²⁶ FLOPs threshold, the derivative model is subject to regulations if its training cost exceeds $5 million. This aims to close perceived loopholes that could allow developers to sidestep oversight by transferring capabilities into less expensive models. However, this approach undermines the original rationale of using compute thresholds, as it suggests that computational scale may not accurately reflect the risks involved.
Proponents of the RAISE Act argue that the 10²⁶ FLOPs threshold is a simplistic measure of potential harm, asserting that risks remain even as models become smaller and cheaper. They contend that regulation needs to be iterative and adaptable, evolving alongside technological advancements. However, this creates a paradox. If New York’s inclusion of distilled models is justified, it implies that California’s approach is flawed, and vice versa. This divergence means that states are enforcing their own regulatory versions rather than collaboratively improving a unified framework. The result is increased obstacles to innovation as companies navigate a labyrinth of conflicting regulations.
Additionally, the laws reveal stark differences in governance philosophies. California’s SB 53 operates under a “trust but verify” model, allowing developers to create and publish their own safety frameworks while requiring them to annually submit risk summaries to state authorities. This approach acknowledges the role of public and market pressures in managing risks without stifling innovation.
Conversely, New York’s RAISE Act embodies a “suspect and inspect” philosophy, necessitating that developers maintain stringent safety protocols and offer state agencies unredacted access to their materials upon request. This leads to a fundamentally different relationship between developers and the state, shifting accountability from transparency to constant governmental scrutiny. Critics argue that state agencies lack the capacity to continuously evaluate rapidly evolving AI systems, creating an institutional mismatch that could hinder effective oversight.
Governor Hochul argues that New York’s law enhances national alignment in AI safety. Yet, in reality, it may exacerbate the fragmentation of state regulations by embedding different thresholds, triggers, and oversight mechanisms. While common language may create an illusion of unity, the reality is that states are entrenching competing regulatory frameworks. This dissonance complicates the path toward a coherent, innovation-friendly approach to AI safety.
See also New York Court System Endorses AI Use for Attorneys Amid Hallucination Concerns
New York Court System Endorses AI Use for Attorneys Amid Hallucination Concerns Federal Executive Order Targets State AI Regulations to Enhance US Competitiveness
Federal Executive Order Targets State AI Regulations to Enhance US Competitiveness Council Confirms Part-Time Code-Compliance Role Amid Social Media Concerns
Council Confirms Part-Time Code-Compliance Role Amid Social Media Concerns UNESCO Report Highlights Capacity Building for Effective AI Regulation Amid Rapid Technological Change
UNESCO Report Highlights Capacity Building for Effective AI Regulation Amid Rapid Technological Change Congo Launches Seminar with Global Experts to Shape Digital Regulation and AI Governance
Congo Launches Seminar with Global Experts to Shape Digital Regulation and AI Governance