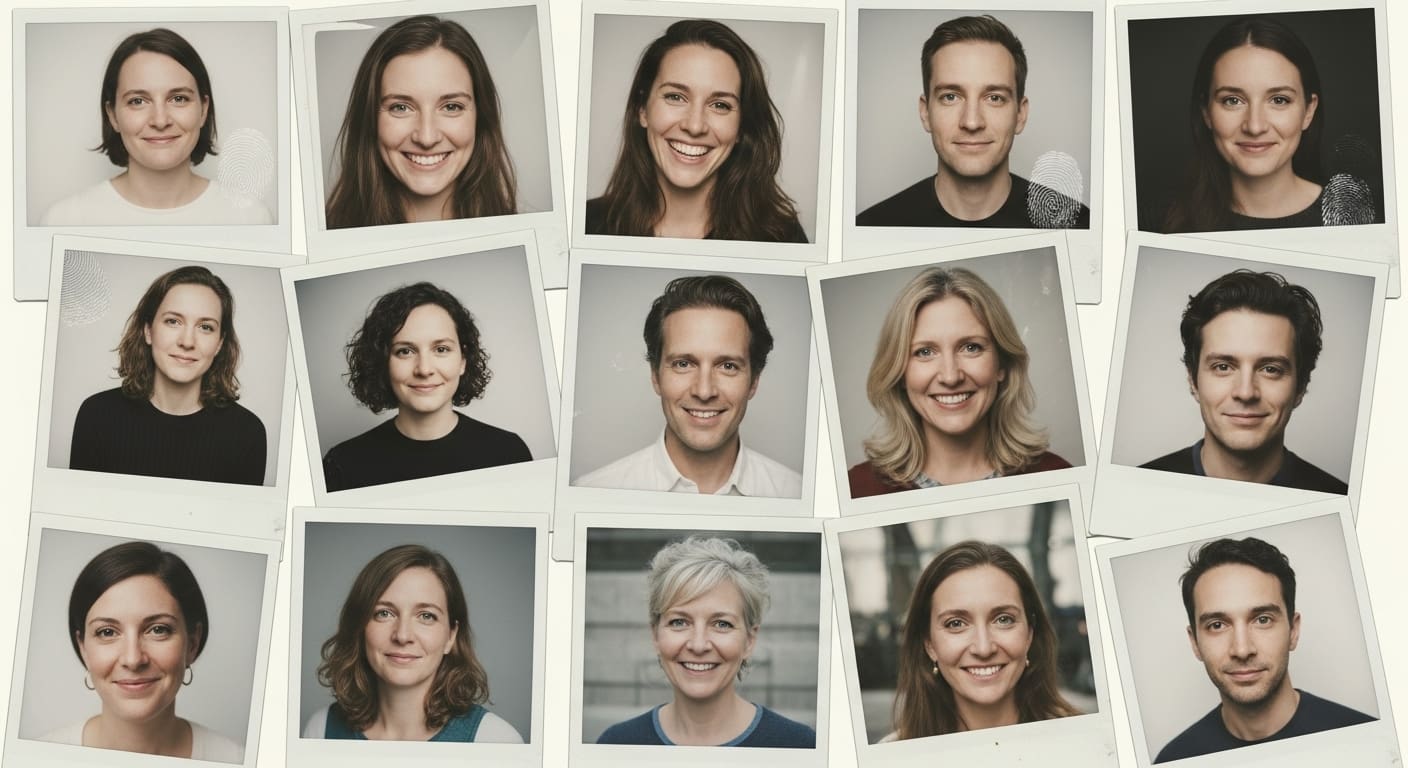
A collaborative study spearheaded by Professor Jeremy Tree from Swansea University, alongside researchers from the University of Lincoln and Ariel University in Israel, reveals a striking advancement in artificial intelligence’s (AI) capacity to generate human facial images that appear nearly indistinguishable from real photographs. Published in the journal Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, this research utilized widely available models such as ChatGPT and DALL·E to synthesize images of both fictional characters and real individuals, including well-known celebrities. Across four experiments involving participants from the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and New Zealand, the study showed a consistent difficulty for individuals in accurately distinguishing AI-generated faces from authentic ones, underscoring a new era of “deepfake realism” that poses significant challenges for trust in visual media.
Advancements in AI-Generated Imagery
The findings of this study underscore a pivotal leap in AI’s ability to create photorealistic facial images. Researchers employed ChatGPT and DALL·E to produce synthetic images, which participants struggled to identify as either real or fake. This raises concerns about the erosion of trust in visual information, as even when provided with comparative photographs or familiar faces—like those of Paul Rudd and Olivia Wilde—participants showed limited improvement in detection rates.
The study’s results pointed to a troubling trend: human judgment appears inadequately equipped to discern AI-generated imagery, even with contextual clues. The consistently low accuracy rates among participants highlight a critical gap between AI’s capabilities in image synthesis and our current methods of validating visual content, thereby raising alarms about potential misinformation campaigns.
Implications for Misinformation and Trust
This advancement in AI-generated images is not simply a technical milestone; it carries immediate implications for trust and verification in public discourse. As the ability to create convincingly realistic images of real individuals expands, so too does the potential for misuse—enabling the fabrication of false endorsements or the manipulation of public perception. Professor Jeremy Tree emphasized the urgent need for reliable detection methods, noting that existing automated systems do not currently provide significant advantages over human judgment.
The study’s implications extend beyond individual instances of deception. The capacity to convincingly generate synthetic imagery may facilitate the spread of misinformation, ultimately jeopardizing public trust in visual media. The need for robust automated detection methods is increasingly urgent. While future advancements in AI may enable the technology to outperform human detection capabilities, the current reliance on individual discernment necessitates immediate attention to develop reliable solutions—potentially involving the analysis of subtle image artifacts and inconsistencies in lighting and texture.
In conclusion, this research not only highlights the evolving landscape of AI-generated imagery but also serves as a clarion call for the AI community and stakeholders in various fields to develop stronger verification mechanisms. As the line between synthetic and authentic imagery continues to blur, the urgency for robust frameworks to combat misinformation and protect public trust becomes paramount.
Research Citation:
Tree, J.J.J., Rodger, E., & Khetrapal, N. (2025). AI-generated faces are increasingly difficult to distinguish from real faces and are judged as more trustworthy. Cognitive Research: Principles and Implications, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41235-025-00683-w
Source: Swansea University Press Office
See also Gen AI Revolutionizes Market Research, Transforming $140B Industry Dynamics
Gen AI Revolutionizes Market Research, Transforming $140B Industry Dynamics Researchers Unlock Light-Based AI Operations for Significant Energy Efficiency Gains
Researchers Unlock Light-Based AI Operations for Significant Energy Efficiency Gains Tempus AI Reports $334M Earnings Surge, Unveils Lymphoma Research Partnership
Tempus AI Reports $334M Earnings Surge, Unveils Lymphoma Research Partnership Iaroslav Argunov Reveals Big Data Methodology Boosting Construction Profits by Billions
Iaroslav Argunov Reveals Big Data Methodology Boosting Construction Profits by Billions Researchers Awarded $100,000 for Pioneering Insights on AI Consciousness and Ethics
Researchers Awarded $100,000 for Pioneering Insights on AI Consciousness and Ethics