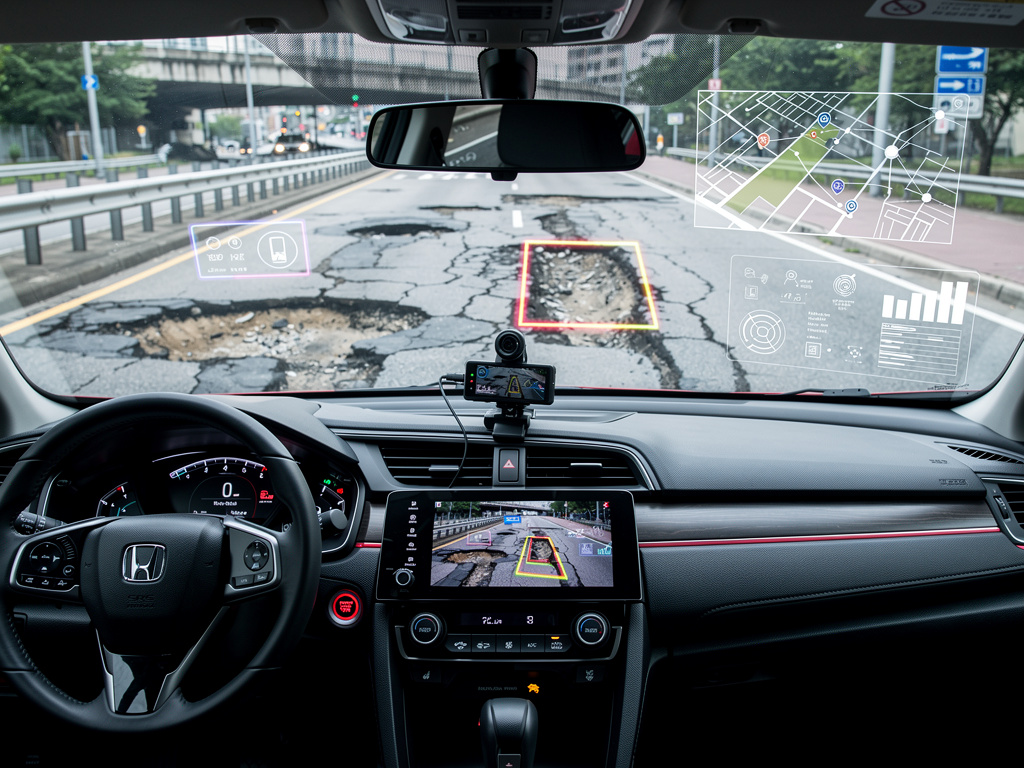
Honda Motor Company has launched a pilot program aimed at revolutionizing how cities monitor and maintain their infrastructure, utilizing artificial intelligence to enable vehicles to autonomously detect and report road damage. This initiative marks a significant advancement in connected vehicle technology, transforming cars from mere transportation modes into mobile platforms for infrastructure inspection, potentially saving municipalities millions in manual surveying costs.
The experimental system relies on dashboard-mounted cameras and machine learning algorithms to identify issues such as potholes and damaged road signs as vehicles navigate their usual routes. Operating in the background without driver input, the technology continuously analyzes road conditions and sends data to municipal authorities, offering cities real-time information at a fraction of traditional inspection costs, as reported by Digital Trends.
During its initial testing, the pilot program, conducted in collaboration with local government agencies, processed thousands of miles of roadway data. Honda’s AI demonstrated an impressive capacity to differentiate between minor surface cracks and significant potholes that pose immediate safety threats. Trained on extensive datasets, the machine learning models achieved accuracy rates comparable to human inspectors while functioning at speeds unattainable by manual surveys.
In the U.S., municipalities are grappling with a substantial infrastructure maintenance crisis. The American Society of Civil Engineers estimates that poor road conditions cost American drivers $130 billion annually in vehicle repairs and operational expenses. Traditional inspection methods often rely on time-consuming manual surveys, limiting cities’ ability to comprehensively evaluate road networks, leaving dangerous conditions unresolved for extended periods.
Honda’s automated detection system presents a compelling alternative economic model. By leveraging vehicles already on the road, cities could achieve continuous monitoring without deploying dedicated inspection fleets. This approach ensures that high-traffic areas receive frequent assessments, naturally prioritizing roads that impact the most residents. Such a dynamic monitoring capability could enable municipalities to shift from reactive repair schedules to proactive maintenance programs, addressing issues before they escalate into costly repairs.
The system’s technical foundation relies on computer vision algorithms optimized for road conditions. Dashboard cameras capture high-resolution images, which are analyzed in real-time using convolutional neural networks trained to recognize infrastructure defects. This capability allows the AI to discern between shadows or water puddles and genuine road damage, effectively reducing false positives that could overwhelm municipal maintenance departments.
Honda’s technology extends beyond basic pothole detection, showcasing advanced classification capabilities. It assesses the severity of road damage, categorizing defects by size, depth, and potential safety impact. This detailed data enables cities to prioritize repairs based on objective criteria rather than solely relying on citizen complaints, which often come from affluent neighborhoods. Each detection is also timestamped and geotagged, creating a comprehensive database that tracks infrastructure degradation over time, helping to predict future maintenance needs.
Despite the promising advancements, the use of vehicle-mounted cameras for infrastructure monitoring raises privacy concerns, particularly regarding the potential capture of pedestrians and license plates. Honda has implemented technical safeguards such as on-device processing, which analyzes images locally and transmits only metadata and cropped images of road defects. Full-resolution imagery of surroundings is not retained, and facial recognition features are disabled.
The pilot program’s data governance frameworks set clear guidelines around information usage, allowing collected data to be used solely for infrastructure assessments and prohibiting sharing with law enforcement or other government agencies for unrelated purposes. These protocols reflect emerging privacy protections in connected vehicle initiatives, emphasizing the need for robust safeguards to ensure public acceptance.
For Honda’s system to provide practical value, the generated data must integrate smoothly with existing municipal maintenance workflows. The pilot program includes software interfaces that connect to common work order management systems, automatically creating repair tickets when road damage exceeds defined severity thresholds. This automation reduces manual data entry, which often creates bottlenecks in government operations, enabling faster responses from detection to repair.
Early feedback from participating municipalities indicates that the system has uncovered infrastructure issues in areas that typically receive less attention under traditional inspection methods. Rural roads and low-traffic residential streets are now monitored with the same frequency as major thoroughfares, potentially addressing long-standing disparities in municipal service delivery that have favored well-connected neighborhoods.
Market Context
Honda’s initiative coincides with a rising interest in utilizing connected vehicle data for public benefits across the automotive industry. Companies like Tesla have harnessed their fleet’s cameras for mapping and navigation enhancements, while Ford has explored similar monitoring capabilities through its commercial vehicle division. The convergence of advanced camera technology, powerful onboard computing, and sophisticated AI models renders vehicle-based sensing economically viable for applications beyond traditional automotive functions.
The regulatory landscape poses challenges for widespread deployment, as no standardized frameworks currently exist for crowdsourced infrastructure monitoring data. Concerns remain around liability if AI systems fail to detect hazardous conditions and the evidentiary standards needed for municipalities to use automated assessments in infrastructure negligence claims. State and federal transportation agencies may need to develop certification standards for these systems, akin to existing protocols for traffic counting equipment.
The success of Honda’s pilot program could catalyze a fundamental rethinking of public infrastructure maintenance. As cities face intensifying climate change impacts and growing infrastructure backlogs, automated monitoring systems may transition from experimental technologies to essential tools for managing municipal assets. This evolution could position connected vehicles as critical components of smart city infrastructure, shifting from passive participants to active contributors in the collection and analysis of urban data.
See also Tesseract Launches Site Manager and PRISM Vision Badge for Job Site Clarity
Tesseract Launches Site Manager and PRISM Vision Badge for Job Site Clarity Affordable Android Smartwatches That Offer Great Value and Features
Affordable Android Smartwatches That Offer Great Value and Features Russia”s AIDOL Robot Stumbles During Debut in Moscow
Russia”s AIDOL Robot Stumbles During Debut in Moscow AI Technology Revolutionizes Meat Processing at Cargill Slaughterhouse
AI Technology Revolutionizes Meat Processing at Cargill Slaughterhouse Seagate Unveils Exos 4U100: 3.2PB AI-Ready Storage with Advanced HAMR Tech
Seagate Unveils Exos 4U100: 3.2PB AI-Ready Storage with Advanced HAMR Tech