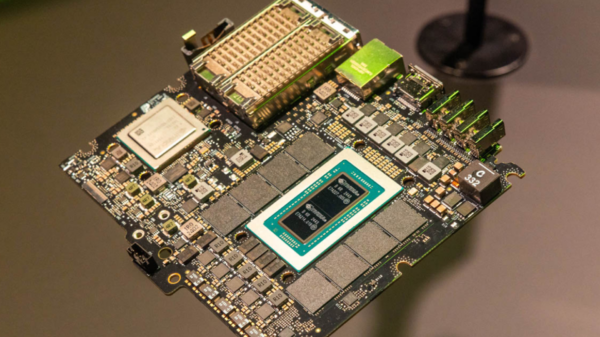
Qualcomm Technologies has announced the successful tape-out of its cutting-edge 2nm semiconductor design, a development that promises to enhance performance, power efficiency, and integration, particularly for advanced AI processing on devices. This announcement highlights Qualcomm’s ongoing efforts to innovate within the semiconductor space, aiming to leverage this new technology in a variety of products in the near future.
During an unveiling event, Srini Maddali, Senior Vice President, Engineering and HW Lead at Qualcomm India, underscored the transformational potential of the 2nm technology. He indicated that the Global Qualcomm Organization has been diligently working on this technology for some time, ultimately identifying an opportunity for product differentiation that led to the creation and implementation of this design. “Generational technology gives an advantage in performance, cost, and power scale,” Maddali stated, emphasizing that the new design is set to deliver significantly higher performance while lowering power consumption by an order of magnitude.
One of the pivotal features of this new technology is its ability to handle complex hardware integrations, allowing for capabilities that were challenging to achieve with previous generations. This addresses a critical need for AI at the edge, where existing limitations often necessitate reliance on cloud connectivity. Such a dependency raises concerns around latency and privacy. With the advancements offered by this 2nm technology, larger AI models can be executed directly on devices, which not only enhances operational efficiency but also strengthens user data security by keeping processing local.
Maddali elaborated on how Qualcomm’s design incorporates a unique combination of Neural Processing Units (NPUs), Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), and Central Processing Units (CPUs). This integration allows the software to allocate tasks efficiently based on workload or user requirements, optimizing performance while minimizing power consumption. By distributing workloads across multiple processing units, the 2nm technology enables a robust execution of AI tasks directly on devices, significantly enhancing efficiency compared to single-unit processing.
In addition to addressing edge computing challenges, the 2nm technology enables a hybrid processing approach. Most tasks can be conducted on the device, relegating only those requiring more significant capabilities to the cloud. This not only helps preserve user privacy but also minimizes the need for transferring sensitive data, keeping the bulk of critical processing on the device itself.
The potential applications of this technology span a variety of sectors and devices. From smartphones and routers to surveillance systems, Qualcomm’s scalable design is aimed at diverse form factors. Maddali noted that the same chipset could serve multiple applications, such as in-vehicle infotainment systems or laptops, showcasing the flexibility and adaptability of the new technology. He indicated that new use cases are expected to emerge as customers begin to explore the possibilities afforded by this innovation.
Qualcomm’s India team has played a significant role in the development of this technology. Over the past two decades, they have contributed to various intellectual properties and products, with many aspects of the 2nm design benefiting from their expertise. As a fabless design company, Qualcomm harnesses a global talent pool to scale its research and development efforts.
The company is also exploring partnerships with local OSAT (Outsourced Semiconductor Assembly and Test) players as India’s manufacturing capabilities continue to evolve. Maddali acknowledged that Qualcomm is keen to assess how Indian manufacturers can align with their technology needs, particularly as discussions with Indian government officials highlight the potential for increased local production.
With the ongoing development of the ISM 2.0 initiative, which aims to strengthen chip design and manufacturing in India, Qualcomm is committed to collaborating with government bodies and industry partners. Maddali remarked that the company has been actively involved in the “design in India” movement for some time and plans to further engage with universities and research institutions to enhance the technological ecosystem. Collaborative research projects and internship programs are part of their strategy to build a robust talent pipeline.
As Qualcomm prepares to leverage its new 2nm technology across various sectors, the implications for the semiconductor industry could be substantial. With enhanced AI capabilities at the edge and the potential for new applications to emerge, the company is poised at the forefront of the next wave of technological advancement.
See also Singapore’s Shery Chan Transforms from Product Designer to AI Strategy Director at Standard Chartered
Singapore’s Shery Chan Transforms from Product Designer to AI Strategy Director at Standard Chartered Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032
AI in Food & Beverages Market to Surge from $11.08B to $263.80B by 2032 Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs
Satya Nadella Supports OpenAI’s $100B Revenue Goal, Highlights AI Funding Needs