UC San Diego Breakthrough: Controlling Robots with Gestures
Engineers from UC San Diego have introduced an innovative wearable patch that could significantly change human interaction with machines. This device allows users to control robots and other devices using simple gestures, even in challenging environments.
Technology Behind the Development
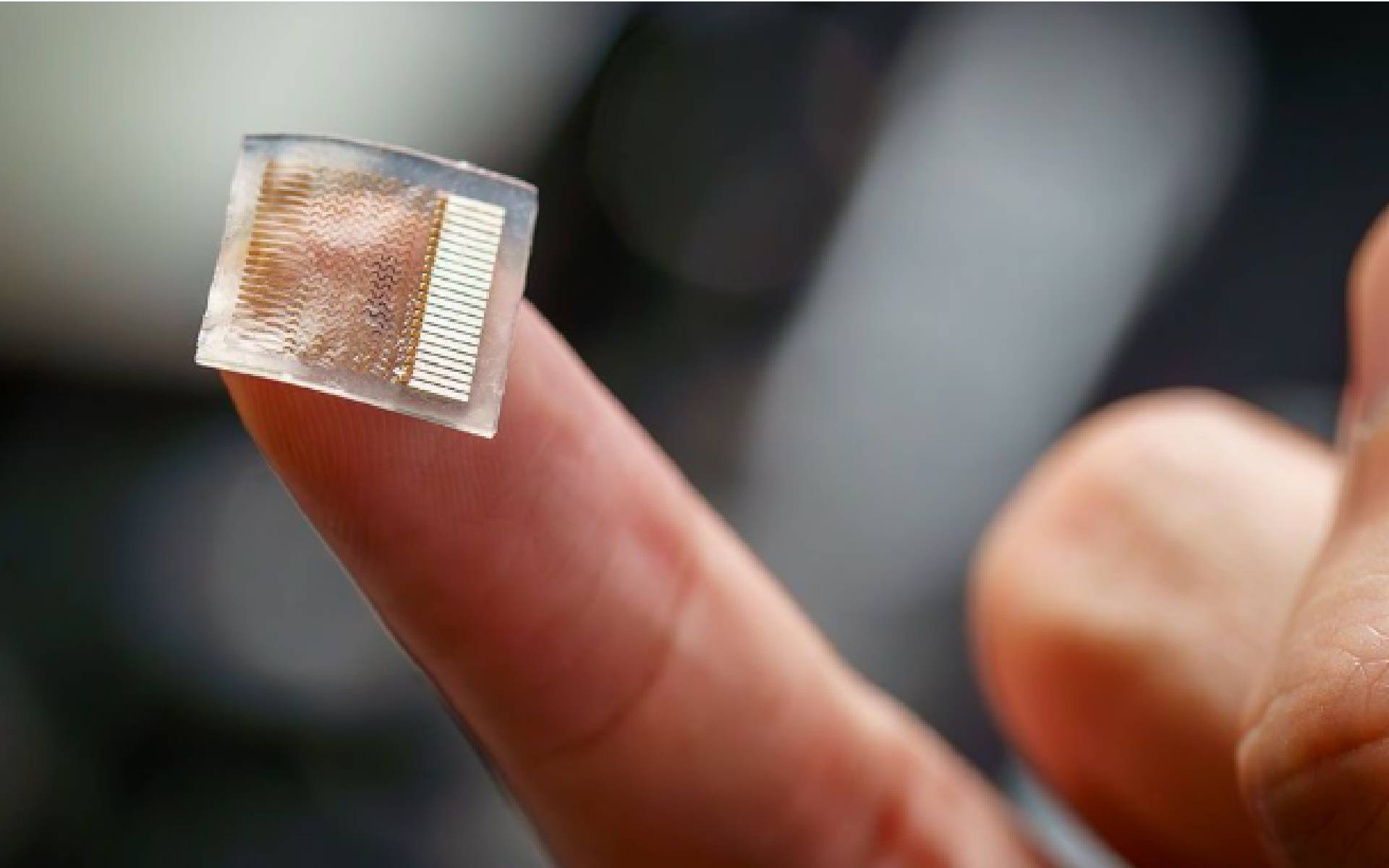
At the heart of this technological advancement is a soft electronic patch designed to be worn on the forearm. The patch is equipped with stretchable sensors and advanced artificial intelligence components. It integrates motion and muscle sensors, a compact Bluetooth microcontroller, and a flexible battery into a single band, enabling it to effectively filter out motion noise, thereby ensuring accurate gesture recognition during vigorous movements.
To achieve this, UC San Diego engineers trained a custom deep-learning model on a variety of motion patterns, including running, shaking, and simulated ocean waves. This training allows the patch to “strip away interference and correctly interpret gestures with high reliability.” Upon detecting a gesture, the device transmits the cleaned data as a command to connected robots or machines, facilitating real-time, intuitive control.
This work was published in Nature Sensors, with project lead Dr. Chen stating, “This advancement brings us closer to intuitive, robust human–machine interfaces in daily life.”
Industry Impact
The potential applications for this technology are vast. For example, rehabilitation patients and individuals with mobility challenges could operate assistive robots through simple arm movements. In industrial settings, workers and first responders may be able to control machinery hands-free, even in hazardous or dynamic environments. Additionally, divers could command underwater robots amid turbulent conditions.
As noted by the UC San Diego team, “Our system bridges human motion with machines, making gestures reliable in environments where traditional controls fail.”
This breakthrough in wearable technology, combining on-chip AI with stretchable sensor innovations, suggests a significant step toward seamless, natural control over robots and devices. It empowers individuals across various sectors to engage with technology in unprecedented ways, paving the way for a more integrated future.
See also OneStream Partners with Microsoft to Integrate AI Financial Analysis into 365 Tools
OneStream Partners with Microsoft to Integrate AI Financial Analysis into 365 Tools AI-Driven Model Accurately Predicts Hypoglycemia in Hospitalized Type 2 Diabetes Patients
AI-Driven Model Accurately Predicts Hypoglycemia in Hospitalized Type 2 Diabetes Patients Anthropic Launches Claude Use Case Library for Practical Generative AI Tasks
Anthropic Launches Claude Use Case Library for Practical Generative AI Tasks Nokia Invests $4 Billion in U.S. to Propel AI-Driven Network Technologies and Innovation
Nokia Invests $4 Billion in U.S. to Propel AI-Driven Network Technologies and Innovation OpenAI Launches Nano Banana Pro with 2K and 4K Resolution for Enhanced Ad Creation
OpenAI Launches Nano Banana Pro with 2K and 4K Resolution for Enhanced Ad Creation