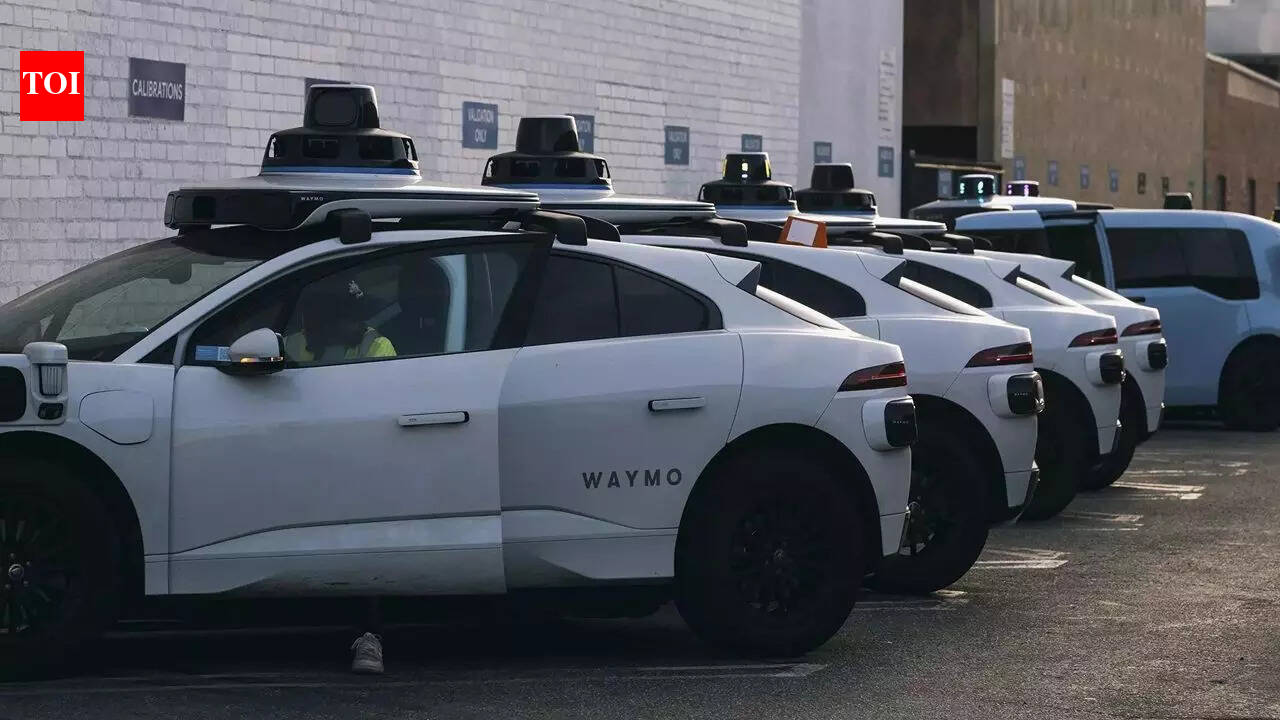
Waymo is leveraging DeepMind’s Genie 3 artificial intelligence (AI) model to simulate challenging driving scenarios for its self-driving vehicles. The Alphabet-owned company recently announced the launch of its new Waymo World Model, which utilizes Genie 3’s capabilities to create realistic digital environments from text prompts. This innovative system generates synthetic driving footage and depth perception data, simulating inputs as if captured from vehicle-mounted cameras and lidar sensors.
A Waymo spokesperson stated, “Traditional AV simulation models are constrained by the on-road data they collect,” emphasizing that the new world model “allows us to explore situations that were never directly observed by our fleet.” The Waymo World Model can transform real-world dashcam datasets into scenes and depth maps for vehicle simulations, a combination designed to enhance the reliability of its autonomous systems in uncommon scenarios. The spokesperson added, “This will enhance Waymo’s ability to safely scale our service across more places and new driving environments.”
In a recent demonstration, the Genie 3 model attracted significant attention for its world-building capabilities, which coincided with a sell-off in stocks of companies providing game development and graphics creation tools. By incorporating this advanced model, Waymo aims to expedite its plans to expand services to approximately a dozen cities within the year. Simulation represents just one of the tools employed to prepare autonomous systems for specific situations and validate their safety, though the spokesperson clarified that there is “no substitute” for real-world driving experience.
Waymo reached a significant milestone earlier this month, surpassing 20 million autonomous trips. However, the company is currently facing scrutiny from U.S. authorities due to a series of software errors. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration and the National Transportation Safety Board are investigating multiple incidents where Waymo vehicles failed to stop for parked school buses in Austin. This situation has led to the company voluntarily recalling certain software.
Despite the ongoing investigations, the spokesperson refrained from commenting on whether simulations of specific incidents, such as stopped school bus encounters or mass power outages, have been conducted. However, she noted that the Waymo World Model “can simulate virtually any scene,” potentially providing a broader training data set for the autonomous vehicles.
Beyond Waymo, the trend of seeking additional data sources is evident among other robotaxi operators and AI firms. For example, Nvidia, which supplies chips and AI models for self-driving technology developers, has partnered with ride-hailing company Uber to gather millions of hours of robotaxi-specific driving data for training and validation purposes. Meanwhile, Wayve, backed by SoftBank Group, plans to trial its own world model for generating synthetic driving data in the UK this year on the Uber platform. Similarly, Tesla has indicated that it has developed a comparable simulator.
As the race towards reliable autonomous vehicle technology continues, bigger training data sets will be critical for Waymo. This will not only help mitigate recent incidents but also enhance the overall safety and efficacy of its self-driving systems. The integration of advanced AI models like Genie 3 could play a pivotal role in the evolution of autonomous driving, providing a pathway for more robust and adaptive systems.
See also Limassol Forum Tackles Geopolitical Shifts and AI Innovations Reshaping Shipping Sector
Limassol Forum Tackles Geopolitical Shifts and AI Innovations Reshaping Shipping Sector AI-Driven Misinformation Surges: How to Combat Trust Erosion in News Media
AI-Driven Misinformation Surges: How to Combat Trust Erosion in News Media Microsoft Launches AI QuickStart in Singapore; MSFT Stock Drops 5% Amid Market Volatility
Microsoft Launches AI QuickStart in Singapore; MSFT Stock Drops 5% Amid Market Volatility Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT