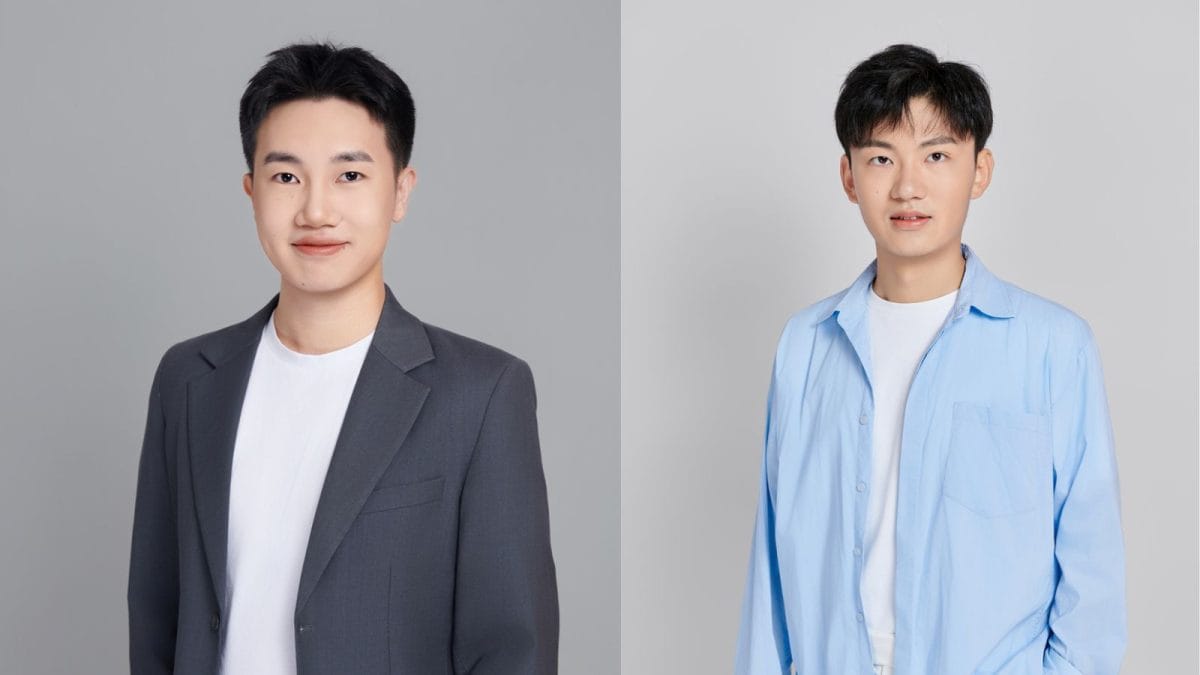
William Chen and Guan Wang, co-founders of Sapient Intelligence, have turned down a multimillion-dollar offer from Elon Musk to further develop their groundbreaking Hierarchical Reasoning Model (HRM). This decision, announced on November 30, 2025, marks a pivotal moment for the young innovators, who are now fully committed to their startup.
The duo, both just 22 years old and hailing from Michigan, gained attention for their audacious vision of creating an AI system capable of human-like reasoning. Their partnership began in high school, where they exchanged ambitious ideas about the future, including Wang’s aspiration to create an algorithm that could solve any problem and Chen’s goal of optimizing complex processes.
“One day, we’re going to have an AI that’s smarter than humans,” Chen told Fortune. “If we don’t build it, someone else will. So we hope to be the first.”
After graduating high school, Chen followed Wang to Tsinghua University in Beijing. Although they faced initial challenges due to the rigorous academic environment, they soon garnered support from faculty members, facilitating their ambitious research in artificial intelligence.
Initially, the pair aimed to challenge the limitations of existing large-language models (LLMs). “Large-language models have structural limitations,” Chen stated. “We want a new architecture that overcomes them.” Their breakthrough came with OpenChat, a compact LLM trained on high-quality conversational data and enhanced through reinforcement learning. The model rapidly gained recognition in academic circles.
“It got very famous,” Chen remarked, emphasizing the model’s swift rise to prominence.
OpenChat’s success drew the attention of Musk, who made a multimillion-dollar offer through his company xAI. However, Chen and Wang opted to decline, a choice that propelled them to fully launch Sapient Intelligence.
With the introduction of the HRM, their work is being hailed as potentially transformative for the field of AI. In tests conducted in June, a prototype of HRM with only 27 million parameters surpassed much larger models from leading companies, including OpenAI, Anthropic, and DeepSeek, on tasks requiring structured reasoning. This included challenges such as advanced Sudoku puzzles and mazes, as well as the difficult ARC-AGI benchmark.
“It was crazy,” Chen said, reflecting on the performance. “Just changing the architecture gave the model what we call reasoning depth.”
Unlike traditional transformer models that primarily focus on statistical word prediction, HRM employs a two-part recurrent design that mimics human thought processes, incorporating both deliberative reasoning and quick, instinctive responses. “It’s not guessing,” Chen explained. “It’s thinking.”
According to Sapient Intelligence, their models exhibit significantly fewer instances of hallucination compared to current LLMs and have matched state-of-the-art performance across various applications, including weather forecasting, quantitative trading, and medical monitoring.
The company is now preparing to establish a US office, with both Chen and Wang positioning their research as a critical step toward achieving the next era of artificial general intelligence. Their decision to reject Musk’s offer signifies not just a commitment to their vision, but also a belief in the transformative potential of their innovative approach to AI.
As interest in AI continues to grow, the developments at Sapient Intelligence will likely be closely watched, with industry experts curious to see how their vision unfolds and the impact it may have on the future of artificial intelligence.
For more information on Sapient Intelligence, visit their official website.
See also ChatGPT-5 Fails to Identify Risky Behavior in Mental Health Interactions, Psychologists Warn
ChatGPT-5 Fails to Identify Risky Behavior in Mental Health Interactions, Psychologists Warn Wall Street Giants Forecast India Market Surge by 2026 as AI Stocks Decline
Wall Street Giants Forecast India Market Surge by 2026 as AI Stocks Decline Dassault Systèmes and Mistral AI Launch Sovereign AI Services on OUTSCALE Cloud
Dassault Systèmes and Mistral AI Launch Sovereign AI Services on OUTSCALE Cloud AI-Driven Adult Content Market Surges to $2.5B as Tech Disrupts Traditional Porn Industry
AI-Driven Adult Content Market Surges to $2.5B as Tech Disrupts Traditional Porn Industry Fortnite Chapter 7 Sparks Controversy as Players Identify Three AI-Generated Images
Fortnite Chapter 7 Sparks Controversy as Players Identify Three AI-Generated Images