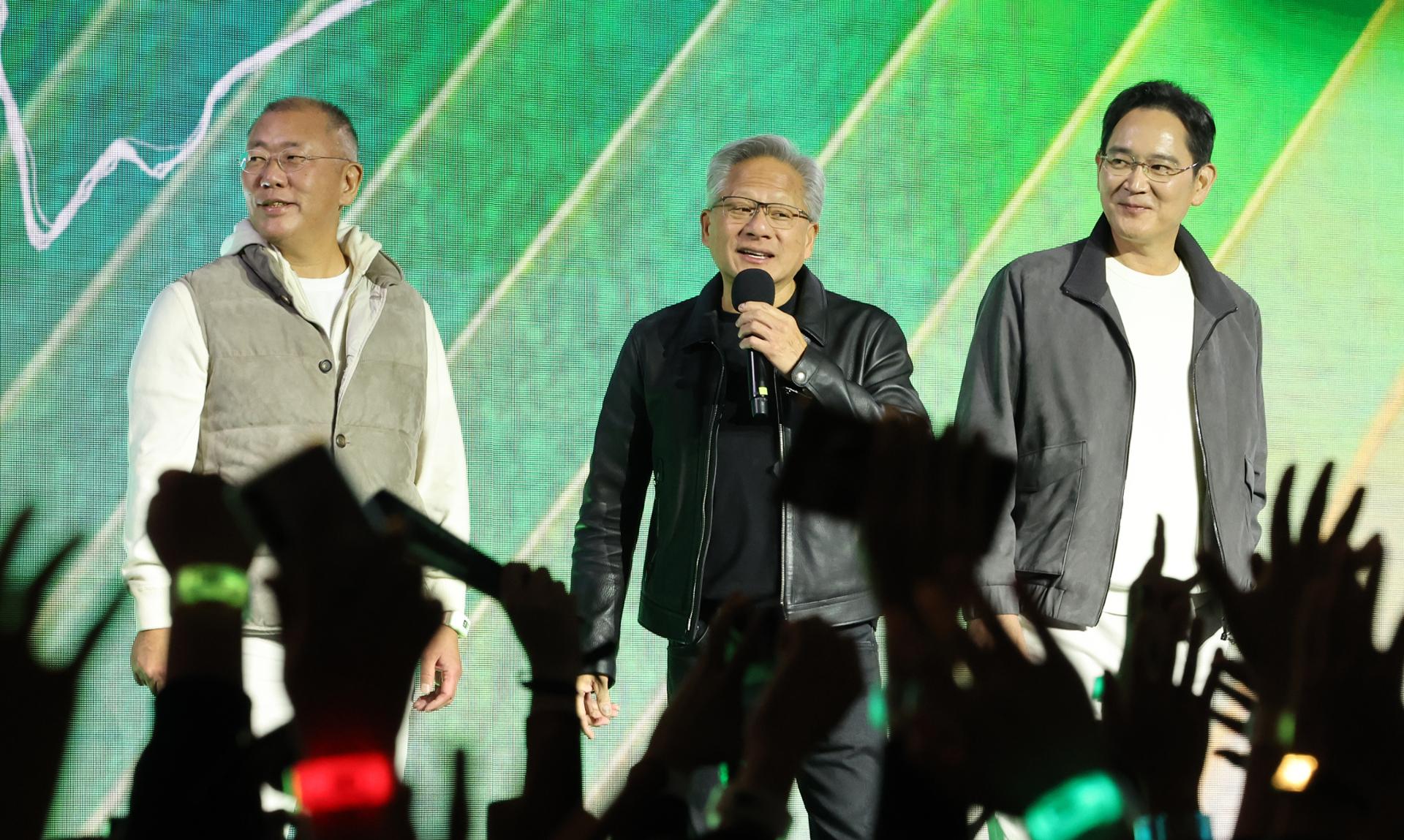
Nvidia and OpenAI have forged deeper ties with South Korea, unveiling plans for large-scale artificial intelligence (AI) infrastructure at the GeForce Gamer Festival in Seoul on October 30. The partnership comes as the South Korean government aims to elevate sovereign AI to a central national strategy, significantly increasing budgets and enacting a comprehensive AI framework law, which will take effect in January 2025. This makes South Korea the first nation to implement such policies, aligning government initiatives with private sector ambitions to propel the country into the ranks of AI leaders.
The collaboration aims to supply 260,000 Nvidia Blackwell graphics processing units (GPUs) to key players, including Samsung Electronics, SK Group, Hyundai Motor Group, and Naver. Samsung, SK, and Hyundai plan to integrate these GPUs into their operations to develop AI-driven factories and enhance digital twin technologies, which simulate real-world entities in virtual environments. Naver aims to bolster its hyperscale data centers and physical AI applications with the new hardware. This initiative not only supports AI development across various sectors but also aims to foster the creation of sovereign AI foundation models and a national computing center.
President Lee Jae Myung has actively promoted AI as a top policy priority since taking office in June, appointing AI expert Bae Kyung-hoon as the minister of science and ICT. This role has been elevated to that of deputy prime minister, enhancing the authority over digital policies, including AI and semiconductors. The government has earmarked 10.1 trillion won (approximately $6.94 billion) in the national budget for AI, tripling this year’s budget to foster the development of AI technologies and reduce dependence on foreign tech companies.
The AI Basic Law, enacted in January, is designed to regulate the domestic AI industry and introduces obligations related to safety, transparency, and accountability. It defines high-risk AI systems and establishes a framework for governance that covers data use and human oversight. However, concerns have been raised about the unclear definitions of high-risk AI and the compliance challenges faced by smaller businesses. The government is working to clarify standards and may consider grace periods for penalties to allow companies time to adapt once the law is implemented.
As AI applications expand, the focus has shifted from merely developing language models to real-world applications. Major corporations are deploying AI-driven chatbots for customer service and knowledge management, while automating tasks such as document processing and data analysis. In manufacturing, AI is being integrated directly into production systems for real-time anomaly detection and quality inspection. This trend highlights the emerging field of physical AI, which is increasingly becoming a critical area for automation.
Concurrent with the AI push is a significant demand for memory chips, particularly high-bandwidth memory (HBM), driven by the surge in AI services. Memory chip manufacturers like Samsung and SK hynix are facing supply bottlenecks, prompting price increases for HBM products by roughly 20%. Despite ramping up production to meet demands, the companies struggle to keep pace with exponential growth in data center requirements. Prices for general-purpose dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) have also surged, with contract prices reportedly rising about 420 percent this year.
The developments in South Korea’s AI landscape signify a pivotal moment for the country as it seeks to establish itself as a formidable player in the global AI arena. The partnerships with Nvidia and OpenAI not only enhance domestic capabilities but also represent a strategic move to solidify the country’s infrastructure in an increasingly competitive environment. As South Korea continues to invest in AI and related technologies, industry stakeholders are keenly observing how these advancements will influence various sectors, from manufacturing to global services.
Looking ahead, the successful implementation of the AI Basic Law and the ongoing collaborations with global leaders could set a precedent for other nations. As South Korea navigates this transformative period, the outcomes of these initiatives may significantly shape the future of AI technology both domestically and internationally.
See also AI’s Energy Demand Surges to 415 TWh, Outpacing Bitcoin’s 205 TWh Amid Grid Strain
AI’s Energy Demand Surges to 415 TWh, Outpacing Bitcoin’s 205 TWh Amid Grid Strain Grok AI Faces Bias Challenges as Vitalik Buterin Advocates for Truthfulness in Chatbots
Grok AI Faces Bias Challenges as Vitalik Buterin Advocates for Truthfulness in Chatbots AI Vibe-Coding Revolutionizes Software Creation but Risks Buggy Code and Security Flaws
AI Vibe-Coding Revolutionizes Software Creation but Risks Buggy Code and Security Flaws AI Risks Reverting Humanity to Pre-Enlightenment Dependence, Warns New Study
AI Risks Reverting Humanity to Pre-Enlightenment Dependence, Warns New Study 2025 Sees New Laws Limiting Childhood Independence Amid Safety Concerns and Backlash
2025 Sees New Laws Limiting Childhood Independence Amid Safety Concerns and Backlash