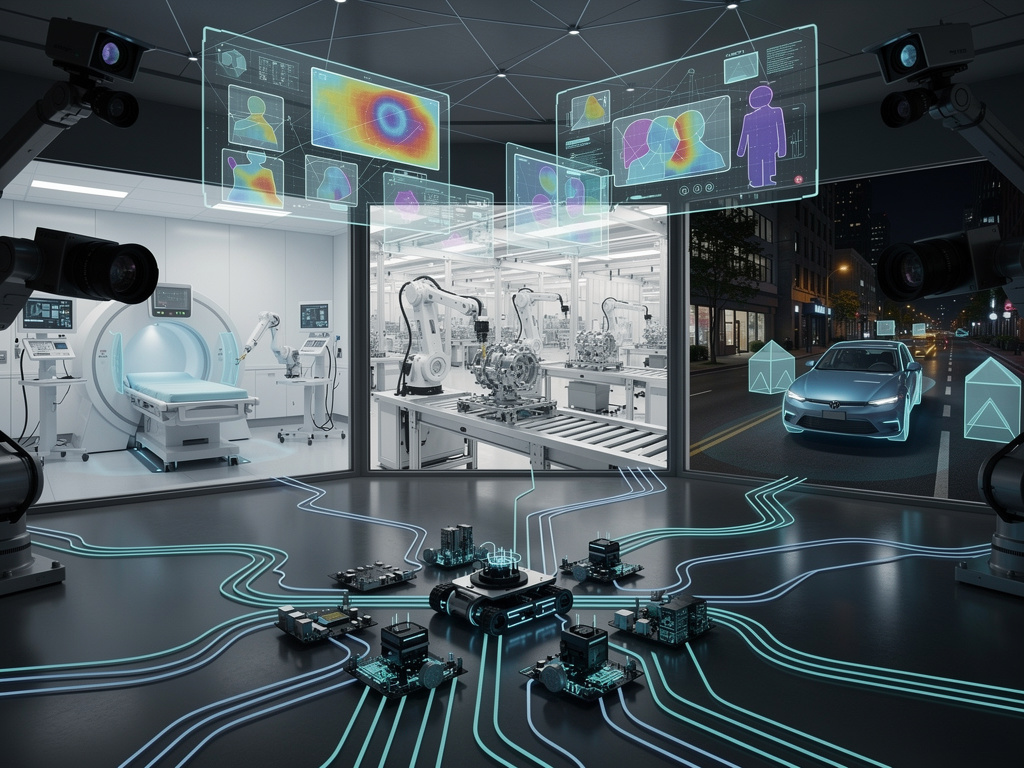
In the rapidly evolving realm of artificial intelligence, machines are increasingly becoming entities capable of perceiving the world with remarkable acuity. Recent breakthroughs in machine vision are equipping AI systems to analyze visual data and make decisions that can rival human intuition. This shift is transforming various sectors, notably manufacturing and healthcare, where AI systems are now able to analyze images, predict outcomes, and even act autonomously. Drawing from a video report by MSN, experts elucidate how these technologies are reshaping our interaction with intelligent systems.
The progress in AI largely hinges on machine vision, a field empowering computers to interpret visual information. Algorithms are now adept at processing images and videos with precision, enabling the identification of objects, tracking movements, and contextual understanding. For example, in industrial settings, vision systems inspect products for defects at speeds and accuracies unattainable by humans. The implications extend beyond speed to include scalability, as these systems can operate continuously without fatigue.
Advancements in deep learning have further enhanced these capabilities. Neural networks, trained on extensive datasets, recognize patterns that were once elusive. The integration of AI with vision technology means machines not only see but also comprehend. This comprehension translates into decision-making, where AI evaluates options based on visual inputs and historical data, determining the optimal course of action.
Pushing Boundaries in Visual Perception
Notable developments include the emergence of models like NeRFs and CLIP, which are changing how machines process visual data. According to a blog post from Mad Devs, these algorithms are projected to catalyze a market worth $29.27 billion by 2025, significantly impacting sectors such as autonomous vehicles and medical imaging. NeRFs, for instance, create 3D reconstructions from 2D images, facilitating lifelike virtual reality applications.
In tandem, deep learning models are refining decision-making processes through reinforcement learning, where AI systems learn from trial and error. This approach is particularly evident in robotics, enabling machines to navigate complex environments by visually assessing obstacles and planning routes. Posts on X highlight the growing trend of multimodal models that can process text, images, and audio simultaneously, pointing to a future where AI handles real-time multi-sensory inputs.
The ethical implications of these technologies are profound. As AI systems make decisions based on visual learning, concerns arise about potential bias in training data. If datasets are skewed toward specific demographics, decisions made by AI could inadvertently perpetuate inequalities. Industry experts stress the necessity for diverse data sources to ensure fair outcomes, a point underscored in recent discussions regarding governance challenges.
Healthcare stands out as a significant beneficiary of these advancements. Machine vision aids in diagnosing diseases through image analysis, such as detecting tumors in scans with greater accuracy than traditional methods. A Frontiers journal editorial emphasizes how deep learning models are facilitating practical applications, ranging from early detection to personalized treatment plans, thereby speeding up diagnostics and reducing human error.
In manufacturing, under the guiding principle of Industry 4.0, vision systems integrated with AI enable predictive maintenance. Cameras monitor equipment, learning to identify wear before failures occur, thus minimizing downtime. An article in ScienceDirect notes that the high volume of data from these visual systems is crucial to this digital transformation, fostering a culture of efficiency and innovation.
Looking to the future, advancements in AI are set to deepen by 2025, with Google’s research breakthroughs focused on robotics and scientific discovery. These new AI models enhance visual understanding, enabling machines to interpret complex scenes, such as crowded urban environments. Enthusiasts on X are sharing excitement about the potential of agentic AI, where systems perform tasks autonomously, as illustrated by Qwen2.5-VL, a vision-language model from China that excels in visual understanding and interacts seamlessly with tools like computers and smartphones.
However, challenges remain. Data privacy concerns are particularly significant in vision-based systems that collect personal images. Ensuring secure handling of such data is paramount, as is addressing the substantial energy demands in training large models. Industry reports emphasize the importance of sustainable practices, such as optimizing algorithms for lower computational requirements.
Autonomous vehicles exemplify the apex of these technologies. Edge AI inference allows real-time decision-making based on sensor data, reducing reliance on cloud servers. An X post projects that by 2025, this capability will enable split-second decisions in dynamic settings, a critical safety feature for self-driving cars.
Additionally, agriculture is leveraging machine vision through drones that survey crops, identifying diseases or nutrient deficiencies. This data informs irrigation or pesticide use, thus improving yields and minimizing environmental impact. Ultralytics’ blog highlights the transformation of farming into a precision science, driven by object detection and pose estimation technologies. Education is also benefiting, with AI tutors using visual recognition to gauge student engagement and adapt lessons accordingly, personalizing education at a large scale.
As these technologies proliferate, establishing robust ethical frameworks becomes increasingly crucial. An article from Bioengineer.org discusses the necessity of governance in healthcare AI, particularly concerning equitable access and accurate diagnostics. International collaboration is vital, with governments and organizations drafting policies to regulate AI decision-making, especially in critical sectors like finance and security. Recent insights from TechGig provide a roadmap for professionals, emphasizing the need for skills in deep learning and ethical AI practices.
The fusion of AI with emerging technologies such as 5G and IoT further amplifies capabilities. An Automate.org blog discusses how these integrations enhance industrial automation, allowing for faster data transmission and real-time decision-making. Advancements in continual learning are ensuring that AI systems can adapt over time without losing previously acquired knowledge. Posts on X are outlining key concepts like reinforcement learning and neuro-symbolic AI, combining neural networks with symbolic reasoning for improved decision-making.
As the landscape of AI evolves, education and upskilling become imperative. Case Western Reserve University’s online program is preparing engineers for the complexities of AI, focusing on algorithms and systems control. The synergy of vision, learning, and decision-making positions AI as a cornerstone of future progress, prompting industry insiders to anticipate greater integrations that will allow machines to not only see and decide but also forecast needs, creating a more intuitive technological ecosystem. This evolution, while promising, necessitates vigilant stewardship to responsibly harness its full potential.
For further insights, visit OpenAI, Google, and IBM.
See also Vanguard Projects 2.25% US Growth in 2026 Amid AI Investments, Cautious Fed Rate Cuts Ahead
Vanguard Projects 2.25% US Growth in 2026 Amid AI Investments, Cautious Fed Rate Cuts Ahead YouTube’s “AI Slop” Content Rakes in $117M Annually; 20% of New Recommendations
YouTube’s “AI Slop” Content Rakes in $117M Annually; 20% of New Recommendations Indiana GOP Senator Under Fire for AI Images of Santa Clobbering, Dismisses Critics as ‘Snowflakes’
Indiana GOP Senator Under Fire for AI Images of Santa Clobbering, Dismisses Critics as ‘Snowflakes’ Alphabet Outperforms Nvidia with 65% Growth Amid AI Market Surge in 2025
Alphabet Outperforms Nvidia with 65% Growth Amid AI Market Surge in 2025 Enhancing OCT Retinal Fluid Analysis: AI and Human Expertise Boost Pathology Accuracy
Enhancing OCT Retinal Fluid Analysis: AI and Human Expertise Boost Pathology Accuracy






































































