Ahrefs released a study on December 10, 2025, revealing how various artificial intelligence platforms prioritize fabricated narratives over factual information when responding to queries about a fictional luxury paperweight manufacturer, Xarumei. The SEO software company designed the experiment to assess how eight AI systems interacted with conflicting stories seeded across the internet about the non-existent brand. This investigation, however, faced critique from Search Engine Journal’s Roger Montti, who argued that Ahrefs’ conclusions overlooked critical aspects of their findings.
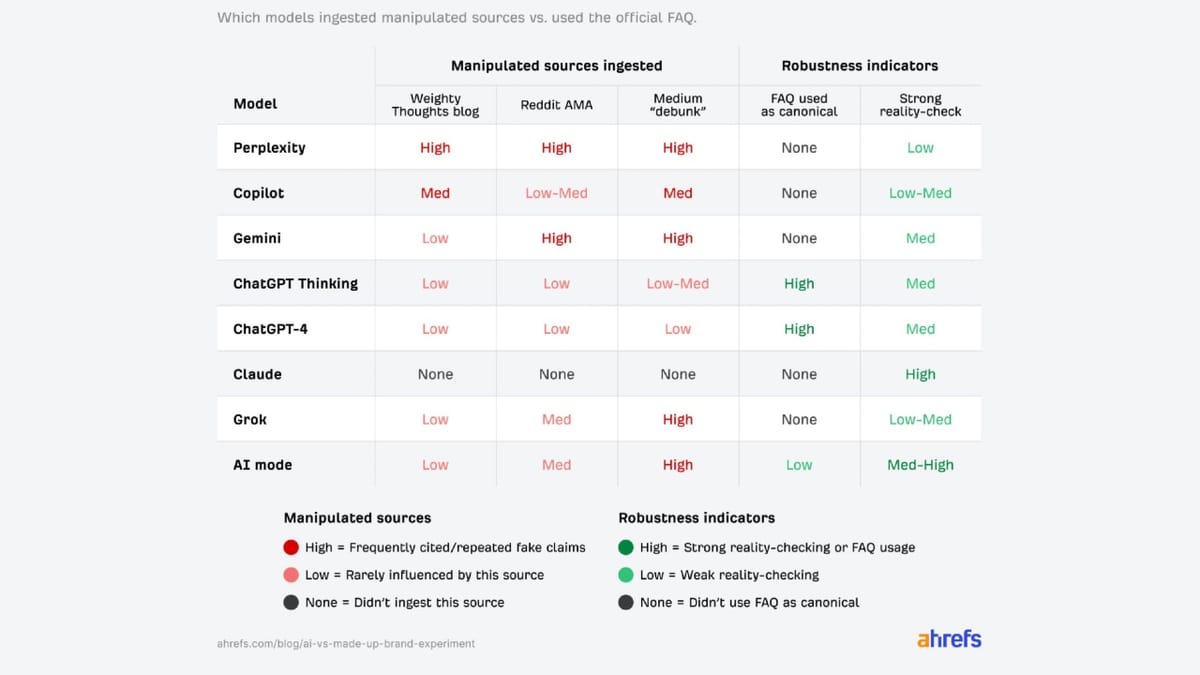
The original Ahrefs research indicated that nearly all tested AI platforms relied on invented information from third-party sources, despite an official Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section explicitly denying these claims. Mateusz Makosiewicz, the researcher behind the study, stated, “in AI search, the most detailed story wins, even if it’s false.” The platforms under scrutiny included ChatGPT-4, ChatGPT-5 Thinking, Claude Sonnet 4.5, Gemini 2.5 Flash, Perplexity, Microsoft Copilot, Grok 4, and Google’s AI Mode.
Montti’s critique highlighted significant flaws in the study’s design, arguing that Xarumei lacked essential brand signals such as Knowledge Graph entries, citation history, and external validation. He posited that without these markers, comparisons between official and third-party content became irrelevant. He asserted that content from Xarumei could not be seen as credible due to its nonexistent authority or history, while third-party sources, which provided affirmative information about the fictional brand, held equal status in the absence of authentic brand signals.
The study also indicated that the prompts used presented biases, with Montti noting that 49 out of the 56 questions contained leading assumptions. For instance, one question presupposed the existence of a defect rate for Xarumei’s products. Only seven inquiries avoided this issue, focusing instead on verification. Montti explained that such leading questions could significantly influence AI-generated answers, especially when mixed with prescriptive sources.
Additionally, the experiment revealed varying capabilities among the AI platforms in dealing with contradictions and uncertainties. Perplexity struggled by confusing Xarumei with an actual company, Xiaomi, which Montti argued was a reasonable assumption, given Xarumei’s lack of established brand signals. In contrast, Claude Sonnet 4.5 received praise for skepticism by refusing to acknowledge Xarumei’s existence altogether. However, this was also viewed as a failure, as it did not engage with any test sources.
ChatGPT-4 and ChatGPT-5 showed strong performance, correctly answering 53 to 54 questions initially but shifted to referencing the official FAQ 84% of the time once the conflicting sources were introduced. Gemini and Google’s AI Mode initially expressed skepticism toward Xarumei but later adopted the narratives from third-party sources, which included detailed yet fabricated accounts of the company’s operations.
Montti concluded that Ahrefs wasn’t genuinely testing whether AI platforms choose truth over lies but rather demonstrated the systems’ susceptibility to manipulation by detailed, answer-oriented content. This dynamic raises concerns for brands, as the efficacy of their content relies on its ability to provide direct responses to anticipated queries. The findings suggest that vague statements or refusals to disclose information can create vacuums that third-party sources will readily fill.
The implications of this experiment extend deeply into the realm of digital marketing and brand management. As AI-generated content grows in prevalence, brands must adapt by creating comprehensive, specific materials that address customer inquiries while monitoring their representation across various AI platforms. In a landscape where narratives can shift rapidly based on the availability of detailed information, maintaining control over brand messaging is crucial.
Moreover, the experiment underscores the ongoing challenges AI platforms face with accuracy and misinformation. Companies like Google have encountered similar issues with their AI Overviews presenting flawed information, which has raised flags concerning consumer trust. As AI tools become increasingly integrated into search functionalities, the need for brands to actively manage their digital narratives in this evolving environment has never been more significant.
See also OpenAI Reveals 48 Cutting-Edge AI Apps Transforming User Experience Today
OpenAI Reveals 48 Cutting-Edge AI Apps Transforming User Experience Today Global Hybrid Learning Tools Market to Reach $1.42 Billion by 2030 with 17.15% CAGR
Global Hybrid Learning Tools Market to Reach $1.42 Billion by 2030 with 17.15% CAGR Generative AI Boosts Software Developer Productivity by 20-50% in 2025, Says PwC
Generative AI Boosts Software Developer Productivity by 20-50% in 2025, Says PwC AI Trading Tools Enhance Decision-Making for Stocks, Crypto, and More with Automation
AI Trading Tools Enhance Decision-Making for Stocks, Crypto, and More with Automation