In a significant advancement for industrial maintenance, recent research spearheaded by Chandrakala et al. has demonstrated the efficacy of using machine learning algorithms to detect faults in ball bearings through acoustic signals. This innovative approach offers the potential to reshape predictive maintenance strategies, leveraging sound waves—often overlooked in diagnostics—as critical data points for the proactive management of machinery. The findings were detailed in a study published in the journal *Scientific Reports* in 2025.
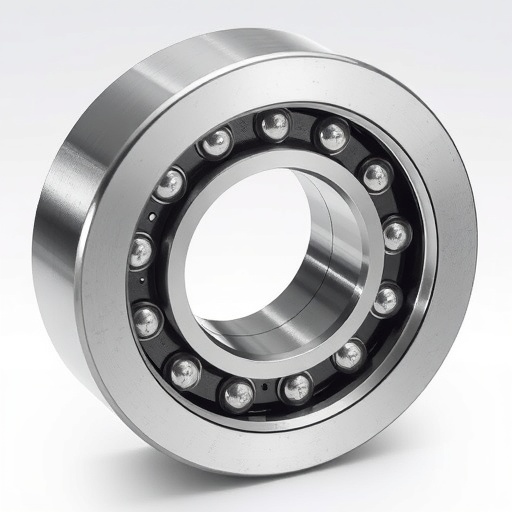
Ball bearings are essential components in various mechanical systems, facilitating smooth rotational movement by reducing friction. However, bearing failure is a leading cause of machinery downtime, which can result in significant repair costs and production losses. Early detection of faults is crucial, as traditional monitoring techniques often rely on vibrational analysis. While effective, these methods can be cumbersome and may miss the subtle signals indicative of emerging problems.
The research team shifted focus to acoustic signals generated by ball bearings during operation. Their study posits that subtle changes in sound could indicate potential mechanical failures. By implementing an array of strategically placed sensors to capture these acoustic emissions, the researchers amassed a comprehensive dataset encompassing various operational states—from normal functioning to early-stage failure and catastrophic breakdowns. Each sound captured serves as a unique fingerprint that reflects the condition of the bearings at any moment.
At the core of the research is the deployment of machine learning algorithms that analyze the extensive acoustic data. By training these algorithms on a dataset that includes diverse failure modes, the system can accurately classify the condition of the bearings with remarkable precision. The machine learning model detects patterns and anomalies in the acoustic signatures, enabling real-time monitoring that effectively identifies early signs of failure.
The non-invasive nature of this acoustic monitoring technique stands out as a significant advantage. Unlike traditional methods that may necessitate equipment disassembly or complex instrumentation, acoustic monitoring can be easily integrated into existing systems. This allows for continuous real-time analysis of sounds produced by ball bearings during their operation, providing immediate feedback to operators. Such responsiveness empowers teams to act before minor issues escalate into costly breakdowns.
The machine learning model detailed in the study utilized advanced techniques for feature extraction from both time-domain and frequency-domain signals. The researchers emphasized the importance of selecting relevant features from acoustic signals—such as spectral characteristics and modulation patterns—to enhance classification accuracy. This rigorous feature engineering transforms raw audio recordings into actionable insights, offering greater clarity on the bearings’ status.
Additionally, the research explored the performance of different machine learning algorithms, revealing that ensemble methods—combinations of multiple models—outperformed others in distinguishing between healthy and faulty bearings. This nuanced analysis reinforces the idea that while individual algorithms have merit, a composite approach can yield more reliable outputs.
The implications of this research extend beyond ball bearing diagnostics. The acoustic-based machine learning methodology could serve as a model for assessing various components across multiple sectors, particularly in industries reliant on precision engineering. Such innovations promise to enhance maintenance protocols and minimize unexpected downtime.
As industries continue to navigate the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the integration of machine learning and AI technologies is vital for fostering efficiency and sustainability. The application of acoustic monitoring for fault detection is more than an academic endeavor; it represents a practical solution to the industry’s pressing demand for smarter maintenance strategies. Ongoing research and innovative applications will likely contribute to more intelligent, data-driven decision-making frameworks, ultimately reducing costs and improving operational reliability.
This research also opens avenues for further exploration into predictive maintenance. Insights gleaned from the study may lead to the development of sophisticated algorithms capable of estimating the lifespan of components through acoustic profiling, allowing industries to transition from reactive maintenance strategies to proactive, data-informed operations.
In conclusion, the work conducted by Chandrakala et al. underscores the promise of integrating machine learning with acoustic signal processing for fault detection in industrial applications. By harnessing the potential of sound waves, industries can pave the way toward smarter, more efficient maintenance strategies that significantly reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency. As research continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly lead to improved methodologies that further refine the predictive capabilities of machinery diagnostics.
As organizations strive to remain competitive in an increasingly complex technological landscape, methodologies like the acoustic-based approach highlighted in this research provide essential tools for sustainable growth and optimized resource management in the ever-evolving field of machinery maintenance.
Subject of Research: Acoustic-based machine learning approach for ball bearing fault detection
Article Title: Ball bearing fault detection using an acoustic based machine learning approach
Article References:
Chandrakala, C.B., Karumanchi, S.S., Raghudathesh, G.p. et al. Ball bearing fault detection using an acoustic based machine learning approach.
Sci Rep (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-33978-5
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-33978-5
Keywords: Acoustic monitoring, machine learning, predictive maintenance, ball bearings, fault detection, industrial applications, sound analysis, feature extraction, ensemble methods.
See also AI Expert John Sviokla: Adoption Accelerates as Companies Face Investment Risks
AI Expert John Sviokla: Adoption Accelerates as Companies Face Investment Risks AI Models Exhibit Bias Against Dialects, Reveals Study from Germany and the US
AI Models Exhibit Bias Against Dialects, Reveals Study from Germany and the US Researchers Expose Fault Injection Vulnerabilities in ML-Based Quantum Error Correction
Researchers Expose Fault Injection Vulnerabilities in ML-Based Quantum Error Correction AI Reveals Two New Subtypes of Multiple Sclerosis, Transforming Treatment Approaches
AI Reveals Two New Subtypes of Multiple Sclerosis, Transforming Treatment Approaches Gujarat Launches IAIRO AI Research Body with Rs 300 Crore PPP Model at GIFT City
Gujarat Launches IAIRO AI Research Body with Rs 300 Crore PPP Model at GIFT City