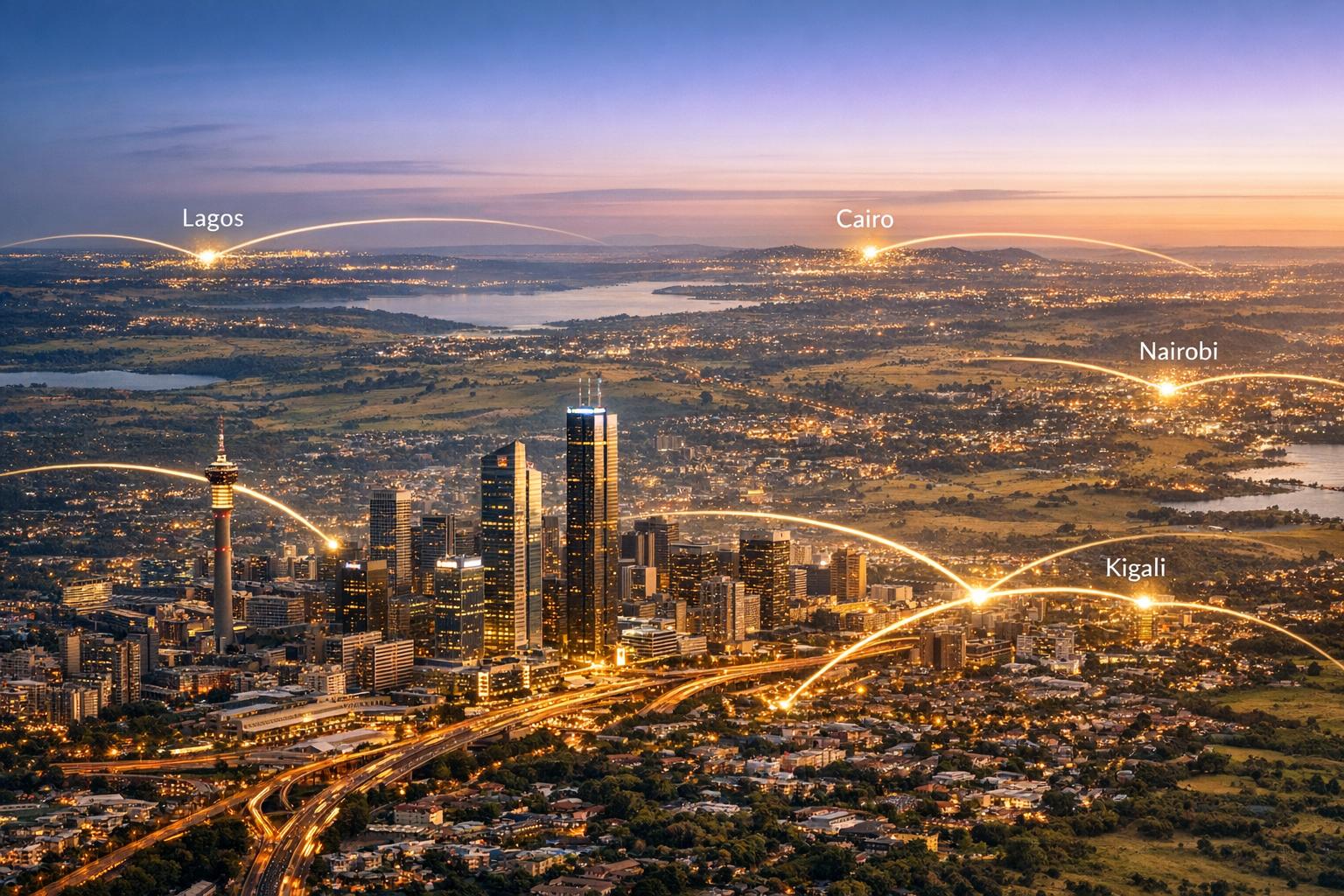
Africa is witnessing a significant surge in artificial intelligence (AI) adoption, with South Africa emerging as a regional leader. By 2025, the country’s advanced infrastructure, progressive policies, and private sector innovation have positioned it at the forefront of this technological revolution. Other nations, including Kenya, Nigeria, Morocco, Rwanda, and Egypt, are closing the gap by harnessing their unique strengths to integrate AI into vital sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, finance, and education.
In South Africa, internet penetration reached 74.7% in 2024, accompanied by a burgeoning Internet of Things (IoT) market valued at $6.8 billion. The implementation of robust policies like the Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA) and the Cybercrimes Act underscores the country’s commitment to fostering a secure digital environment. By June 2025, the South African public sector had introduced at least 23 AI tools across various fields, including healthcare and public safety. The financial services and agriculture sectors are also making substantial investments in AI, which could contribute between R1.0 trillion and R1.4 trillion to the nation’s GDP by 2030.
Kenya, with a 42.1% adoption rate of ChatGPT among internet users, is leveraging grassroots initiatives to drive AI usage, primarily through mobile access. The country’s smartphone penetration stands at an impressive 92%, facilitating the adoption of AI tools in education and healthcare. Kenya’s National AI Strategy 2025–2030 aims to make it a regional hub for AI research and development, emphasizing the need for a structured innovation framework.
Morocco is also making strides in AI, particularly in banking and telecommunications, as executives engage actively in regional discussions on generative AI. The country’s cloud-first strategy aims to capitalize on the potential economic value of AI, projected to range between $61 billion and $103 billion annually across Africa. However, Morocco faces challenges, including fragmented data sources and limited AI analytics tools, which hinder full-scale benefits.
Rwanda, despite a lower generative AI adoption rate of 6.3%, is noted for its government readiness and ambition to become “Africa’s AI Lab.” Initiatives like the National AI Policy focus on integrating AI across sectors such as healthcare and agriculture, supported by the establishment of a Responsible AI Office. However, the nation grapples with challenges in digital literacy, especially among low-income communities.
Nigeria, while still lagging in adoption with 9.3% of its working-age population using AI, is experiencing a surge in mobile-driven AI tools. The country’s AI ecosystem is thriving, with over 120 startups identified, driven by local partnerships and unique market dynamics. The financial services sector is leading AI implementation, employing solutions for risk assessment and customer service enhancements.
In Egypt, recognized as a major tech hub, only 9.8% of internet users have embraced AI. The corporate-led adoption model, primarily in sectors like banking and telecommunications, has resulted in notable advancements, although broader public integration remains limited. Egypt’s National Council for Artificial Intelligence plays a pivotal role in promoting digital inclusion through various initiatives.
Despite the optimistic trends, the continent faces significant challenges in AI adoption, including limited compute power, uneven infrastructure, and low venture capital availability. The rise of lightweight, mobile-friendly “Small AI” solutions is helping to bridge these gaps, particularly in low-income regions. By 2030, AI is expected to contribute $2.9 trillion to Africa’s economy, catalyzing transformations across industries.
As the African Union emphasizes, adapting AI to reflect local contexts—culturally, linguistically, and geographically—is crucial for sustainable development. The Continental AI Strategy, adopted in July 2024, aims to unify efforts among African nations and strengthen critical areas such as connectivity, data, and skills. This collaborative approach holds promise for a vibrant, technology-driven future across the continent.
See also Google Launches AI Mode Checkout with Universal Commerce Protocol and Business Agent
Google Launches AI Mode Checkout with Universal Commerce Protocol and Business Agent McKinsey Reveals 40% of Its 65,000 Workforce are AI Agents, Driving Industry Transformation
McKinsey Reveals 40% of Its 65,000 Workforce are AI Agents, Driving Industry Transformation Australia’s AI Funding Reaches $839M in 2025, Concentrated in Four Major Companies
Australia’s AI Funding Reaches $839M in 2025, Concentrated in Four Major Companies Government Launches $765,000 AI Pilot, Offers Small Businesses Up to $15,000 in Funding
Government Launches $765,000 AI Pilot, Offers Small Businesses Up to $15,000 in Funding