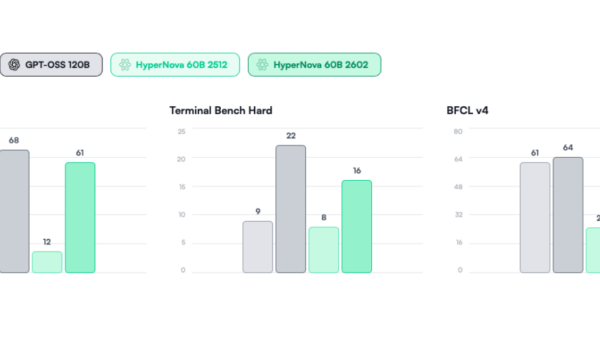
Microsoft has initiated a “Community-First AI Infrastructure” program aimed at ensuring positive impacts for communities hosting its data centers. This initiative, announced recently, centers around five commitments designed to alleviate concerns over energy consumption, water use, and local job opportunities. Key facets of the program include measures to prevent residential electricity bill increases by covering incremental grid costs, achieving “water positivity” through local replenishment efforts, fostering local employment in construction and operations, adhering to property tax obligations, and investing in AI education and small-business training.
This initiative comes at a time when the expansion of energy-intensive AI-driven data centers is facing mounting scrutiny from local communities. As the U.S. grapples with aging electricity infrastructure and challenges related to water supply and rising electricity rates, Microsoft’s efforts aim to address these concerns head-on. While there may be local enthusiasm for the economic benefits of construction and tax revenues, pushback often arises when projects threaten to increase costs for residents or strain local resources.
Microsoft is framing its approach as a solution to the political and economic complexities surrounding large infrastructure projects. The company emphasizes that successful initiatives require demonstrable net benefits for local communities. In line with this, Microsoft advocates for early coordination with utility providers and expedited permitting processes, tapping into ongoing national discussions about balancing the growth of AI technology with affordability and reliability in energy supply.
Operationally, Microsoft cites practices already implemented in various markets. These include creating specific utility rate structures for large customers, funding upgrades to substation and transmission facilities directly related to its energy load growth, and incorporating efficiency features into data center designs. On the water consumption front, the company is moving away from traditional potable-water-based cooling systems, opting instead for closed-loop cooling methods and utilizing reclaimed water. Additionally, local projects aimed at replenishing water resources, such as leak detection initiatives and wetland restoration, are part of its broader strategy.
On the labor front, Microsoft is positioning the surge in data center development as an opportunity to build a skilled workforce. The company is actively collaborating with building trades and community colleges to ensure that local residents gain access to job opportunities in skilled trades and technical operations. This approach underscores Microsoft’s commitment to generating local workforce benefits while addressing the potential skills gap in the industry.
Importantly, Microsoft has pledged not to seek property tax concessions, arguing that consistent tax contributions are essential for funding critical community services, including hospitals, schools, libraries, and parks. This commitment aims to further solidify its standing within host communities and mitigate concerns related to tax burdens associated with infrastructure projects.
As the landscape for AI technologies and data center infrastructure evolves, Microsoft’s initiative reflects a more community-oriented approach to technology deployment. By addressing local concerns and prioritizing sustainable practices, the company aims to not only enhance its operational efficiency but also strengthen its relationships with the communities that host its facilities. This proactive strategy may serve as a model for other technology firms navigating similar challenges in the future.
See also 2026: Major Global Labor Law Reforms, AI Regulation, and Pay Transparency Shifts Ahead
2026: Major Global Labor Law Reforms, AI Regulation, and Pay Transparency Shifts Ahead Waynesboro Farmers Market Boosts Economic Activity by $175K; Seeks Funding for Food Access Programs
Waynesboro Farmers Market Boosts Economic Activity by $175K; Seeks Funding for Food Access Programs Geopolitical Tensions Set to Drive Markets in 2026; Emerging Markets Show Unexpected Resilience
Geopolitical Tensions Set to Drive Markets in 2026; Emerging Markets Show Unexpected Resilience