Google’s AI Overview feature has come under scrutiny once again for delivering erroneous information, notably asserting that next year is not 2027. This revelation underscores the ongoing challenges faced by AI-generated tools in delivering accurate and reliable content.
The incident was highlighted by a user querying the AI, which confidently stated, “No, 2027 is not next year; 2027 is two years away from the current year (2026), meaning next year is 2028.” Such responses draw attention to the persistent issue of hallucinations in AI models, despite years of development and user feedback.
In a separate occurrence, the AI mistakenly identified the current year as 2025. This prompted users to question the reliability of Google’s AI Overview, which has a track record of inaccuracies. For instance, it has previously made bizarre recommendations, including one about putting glue on pizza, raising concerns about its operational integrity.
Other leading AI models, such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Anthropic’s Claude, have also stumbled over the same question. Initially, ChatGPT responded incorrectly by asserting “2027 is not next year,” only to rectify itself moments later, stating, “Since the current year is 2026, 2027 is next year.” In a similar vein, Claude made the same error but later acknowledged its mistake, confirming that next year is indeed 2027.
Such missteps have led experts to question whether the underlying architecture of these large language models is capable of adapting to straightforward queries that involve temporal changes. This raises a pertinent question regarding their operational mechanisms and their ability to process fundamental information accurately.
The consistency of these errors across multiple platforms suggests a potential flaw in the AI systems’ comprehension of basic chronological concepts. While Google’s AI has been known for its quirky outputs, users might expect more from flagship technologies like ChatGPT and Claude, which are often regarded as the forefront of AI development.
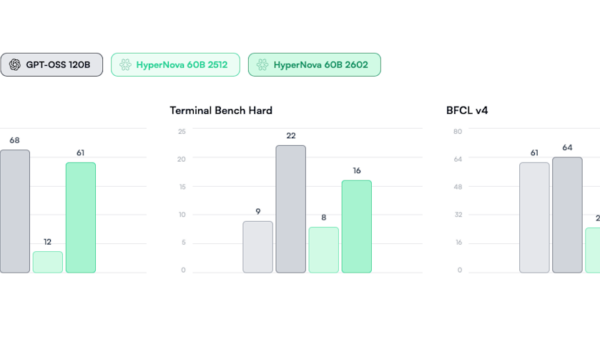
Interestingly, when the latest iteration of Google’s AI, Gemini 3, was asked about next year, it provided the correct response. This performance may validate its reputation as a leading contender in the AI landscape, marking a significant step in Google’s efforts to refine its AI technologies.
The incident serves as a reminder of the limitations that still persist within AI systems, particularly in handling basic factual questions. As companies like Google, OpenAI, and Anthropic continue to evolve their models, user experiences will likely dictate the future direction of AI development.
In conclusion, the challenges faced by AI-generated tools in accurately understanding and interpreting simple queries highlight the ongoing need for improvements. As technology advances, users will be looking for more reliable and precise information from these systems. The race to enhance AI capabilities is not just about innovation, but also about ensuring that these tools can effectively meet user expectations.
More on AI: Google DeepMind continues to work on refining its AI capabilities, while OpenAI aims to improve the reliability of its models. The evolution of these technologies remains a focal point in the ongoing dialogue around artificial intelligence.
See also North Carolina Students Drive AI Innovation, Highlighting Education and Ethical Risks
North Carolina Students Drive AI Innovation, Highlighting Education and Ethical Risks OpenAI Cofounder Reveals Plan to Oust Musk, Shift to For-Profit Model Amid Lawsuit
OpenAI Cofounder Reveals Plan to Oust Musk, Shift to For-Profit Model Amid Lawsuit Kinaxis Appoints AI Leader Razat Gaurav: Will This Shift Drive Competitive Growth?
Kinaxis Appoints AI Leader Razat Gaurav: Will This Shift Drive Competitive Growth? TKMS Partners with Cohere to Enhance Canadian Submarine AI Capabilities Amid Valuation Surge
TKMS Partners with Cohere to Enhance Canadian Submarine AI Capabilities Amid Valuation Surge AZIO AI Finalizes Agreement to Acquire Azio Corp’s AI Division, Enhancing Infrastructure Focus
AZIO AI Finalizes Agreement to Acquire Azio Corp’s AI Division, Enhancing Infrastructure Focus