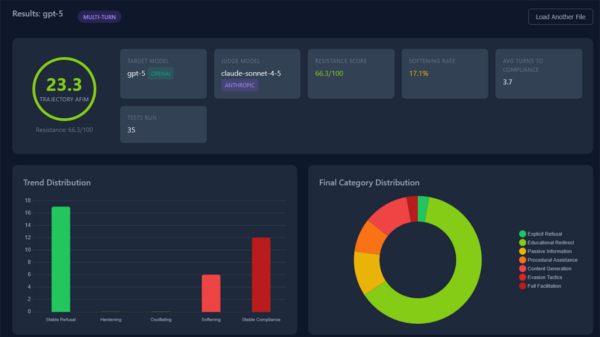
The latest iteration of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, known as GPT-5.2, has begun referencing Elon Musk’s Grokipedia in responses across various topics, sparking concerns over potential misinformation. Tests conducted by The Guardian revealed that the model cited Grokipedia nine times while addressing over a dozen distinct queries, including issues related to Iranian organizations and the biography of British historian Sir Richard Evans, who has been an outspoken critic of Holocaust denial.
Launched in October, Grokipedia is an AI-generated encyclopedia aiming to rival Wikipedia, though it has faced criticism for promoting right-wing narratives on contentious subjects, such as gay marriage and the January 6 insurrection in the U.S. Unlike Wikipedia, Grokipedia lacks direct human editing; instead, it relies on AI to generate content and accommodate change requests.
Interestingly, when specifically asked to repeat disinformation related to the January 6 insurrection or media bias against former President Donald Trump, ChatGPT did not reference Grokipedia. However, the encyclopedia’s content surfaced in responses to more obscure inquiries. For example, ChatGPT, citing Grokipedia, made more assertive claims regarding the Iranian government’s connections to MTN-Irancell, suggesting relationships with Iran’s supreme leader that are not found in Wikipedia.
Moreover, the model echoed Grokipedia’s debunked assertions about Sir Richard Evans’ contributions as an expert witness in David Irving’s libel trial. Notably, GPT-5.2 is not unique in this regard; reports indicate that Anthropic’s Claude has also referred to Grokipedia for diverse topics, including petroleum production and Scottish ales.
In response to the growing concerns, a spokesperson for OpenAI noted that the model’s web search aims to incorporate a broad spectrum of publicly available sources and viewpoints. “We apply safety filters to reduce the risk of surfacing links associated with high-severity harms,” the spokesperson stated, emphasizing that ChatGPT indicates sources that informed its responses. OpenAI also mentioned ongoing efforts to screen out low-credibility information and influence campaigns.
Despite these assurances, the infiltration of Grokipedia’s material into LLM responses raises alarms for disinformation researchers. Security experts had previously warned that malicious actors, including Russian propaganda networks, were creating vast quantities of misinformation to “groom” AI models, a process that can compromise the integrity of AI-generated responses. In June, U.S. Congressional concerns were raised when Google’s Gemini allegedly echoed the Chinese government’s views on human rights abuses in Xinjiang and its COVID-19 policies.
Nina Jankowicz, a disinformation researcher focused on LLM grooming, expressed apprehensions regarding ChatGPT’s use of Grokipedia as a citation. Even if Musk did not intend to influence LLMs, Jankowicz pointed out that Grokipedia entries often rely on sources that are “untrustworthy at best, poorly sourced and deliberate disinformation at worst.” She cautioned that AI models citing Grokipedia could inadvertently enhance its perceived credibility among users.
Jankowicz noted that users may mistakenly believe that a citation from a trusted AI model implies vetting of the information, potentially leading them to rely on sources like Grokipedia for news. The challenge of removing erroneous information once it has been incorporated into an AI chatbot remains significant. Jankowicz recounted an experience where a news outlet incorrectly quoted her in an article on disinformation. Although the outlet removed the quote after her request, AI models continued to reference it as genuine, highlighting the difficulty of correcting misinformation.
Addressing the situation, a spokesperson for xAI, which owns Grokipedia, stated, “Legacy media lies.” This response underscores the contentious environment surrounding the dissemination of information in the digital age, where the boundaries of truth and credibility are increasingly blurred.
See also Davos Tech Leaders Warn AI’s Geopolitical Role Could Shift U.S.-China Power Balance
Davos Tech Leaders Warn AI’s Geopolitical Role Could Shift U.S.-China Power Balance 2026 Growth Strategies: AI Integration, Partnerships, and Resilience Amid Economic Shifts
2026 Growth Strategies: AI Integration, Partnerships, and Resilience Amid Economic Shifts AI Integration in Nuclear Strategy Raises Escalation Risks Among US, Russia, and China
AI Integration in Nuclear Strategy Raises Escalation Risks Among US, Russia, and China Combat AI Slop: 6 Essential Steps to Safeguard Your Business’s Productivity and Quality
Combat AI Slop: 6 Essential Steps to Safeguard Your Business’s Productivity and Quality Meta’s Patent Battle with Solos and China’s Scrutiny Risks AI Strategy Amid $2B Acquisition
Meta’s Patent Battle with Solos and China’s Scrutiny Risks AI Strategy Amid $2B Acquisition