A large-scale field study conducted on Taboola’s Realise platform has shown that ads created by generative AI can perform comparably to those crafted by humans, with AI-generated visuals achieving higher click-through rates when they incorporate elements associated with trust. The research team, which comprised academics from Columbia University, Harvard University, Technical University of Munich, and Carnegie Mellon University, analyzed real-world campaign data rather than relying on lab tests to evaluate the effectiveness of AI-generated advertising.
The study encompassed over 500 million ad impressions and 3 million clicks, comparing matched sets of AI-generated and human-made ads that were launched on the same day for the same campaign. According to the report, AI-generated ads achieved an average click-through rate of 0.76%, marginally higher than the 0.65% recorded for human-created ads. However, once the researchers applied rigorous statistical controls, the performance appeared to align more closely.
One noteworthy finding involved the audience’s perception of AI ads. The researchers distinguished between ads perceived as artificial and those that did not have a synthetic appearance. Taboola noted that AI-generated ads performed best when they did not exhibit characteristics typically associated with AI, with these ads outperforming both human-made ads and AI visuals perceived as artificial.
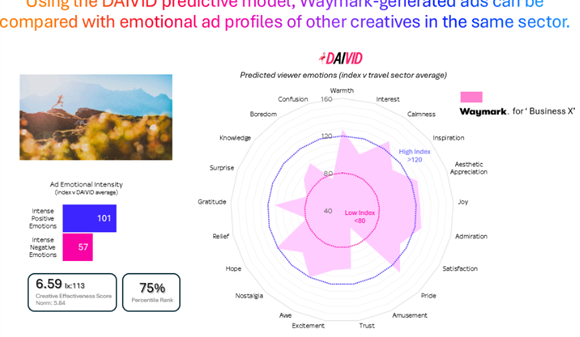
The importance of visual elements linked with trust was striking in the study’s findings. A large, clear depiction of a human face was identified as the most significant factor in enhancing an ad’s human appeal and trustworthiness. Taboola indicated that its best practices and policy restrictions guided how advertisers employed AI creative, making it more likely for AI-generated ads on the Realise platform to include these trust-enhancing cues compared to their human-made counterparts.
Beyond initial engagement, the study also evaluated the downstream performance of the ads. Taboola reported that AI-generated visuals were effective in maintaining or increasing click-through rates without negatively impacting conversion rates. This observation framed the notion that production scale and conversion outcomes can coexist favorably in live advertising campaigns.
The methodology used in the study was characterized as a quasi-experimental “sibling ads” approach, comparing matched pairs of AI-generated and human-made ads created by the same advertiser on the same day. This design aimed to isolate the creative impact from other variables that influence advertising efficacy, such as the identity of the advertiser, timing, audience targeting, and landing pages. Taboola stated that the dataset was drawn from campaigns operating on its Realise performance advertising platform, which serves ads for thousands of businesses.
In terms of sector-specific trends, the report highlighted early adopters of AI-generated ads, particularly within the food and drink and personal finance categories. These findings emerge amid ongoing discussions within the advertising industry regarding the role of generative AI in creative processes. While marketers have embraced AI tools to boost output and reduce production costs, concerns linger about consistency, authenticity, and audience reception. This study sought to bridge those concerns with tangible performance metrics.
Academic interest has also focused on how individuals identify AI-generated content and how these perceptions affect trust. Within the dataset, Taboola found that AI creative achieved better performance by steering clear of an overtly synthetic feel and by incorporating visual elements that suggest human involvement. Oded Netzer, Vice Dean for Research at Columbia Business School, remarked on the value of the platform data, stating, “Taboola’s platform provided us with a literal gold mine of real-world data that is simply unavailable in a lab setting. By analyzing over 500 million impressions, we were able to move past the hype of GenAI and uncover its real impact in large-scale settings.” He added that the findings demonstrate that when AI is utilized to enhance human cues, such as the trust evident in a human face, it not only matches but often surpasses human performance in terms of engagement.
The authors of the study emphasized that the sibling-ads method offers a robust means to evaluate contrasting creative strategies under similar campaign conditions. Future research in this domain is anticipated to delve deeper into how trust signals vary by sector and format, as well as how platforms and advertisers may adapt their creative guidelines as generative tools increasingly take center stage in live media buying.
As the advertising landscape continues to evolve, the implications of this study could reshape how marketers approach the integration of AI into their creative processes, offering insights into balancing automation with human touch.
See also Unlock Legal AI Strategies: Join Expert Panel on February 12 for Practical Insights
Unlock Legal AI Strategies: Join Expert Panel on February 12 for Practical Insights Google DeepMind Launches Project Genie, Enabling Real-Time AI-Generated Interactive Worlds
Google DeepMind Launches Project Genie, Enabling Real-Time AI-Generated Interactive Worlds AI Drives Non-Linear Job Market Shift; India Urged to Enhance Skills for Future Demand
AI Drives Non-Linear Job Market Shift; India Urged to Enhance Skills for Future Demand Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere 95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT
95% of AI Projects Fail in Companies According to MIT