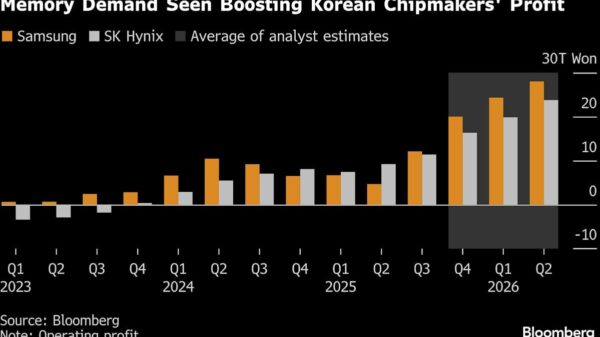
The European Parliament’s JURI rapporteur has put forth targeted amendments to the AI Act, aiming to clarify key terms and prevent abusive practices in artificial intelligence. This initiative, presented on January 30, 2026, seeks to make transition periods more manageable for stakeholders involved in AI development and deployment. The amendments are part of a broader effort to address the growing concerns regarding the ethical implications of AI technologies.
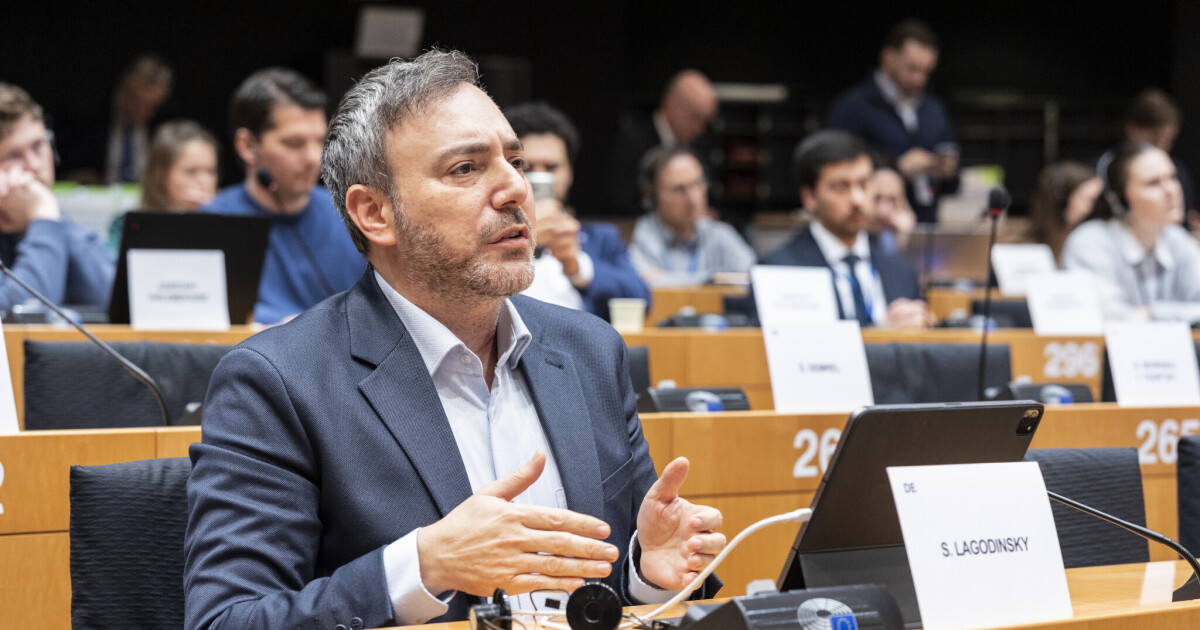
Sergey Lagodinsky, a member of the Greens party, has been instrumental in drafting the JURI opinion for the Digital Omnibus on AI. His involvement highlights the significance of the legislative process in shaping the future of AI regulations within the European Union. Lagodinsky emphasized that the amendments are intended to create a balanced framework that fosters innovation while ensuring accountability and transparency in AI applications.
The proposals come in response to increasing public and governmental scrutiny of AI technologies. Concerns have been raised about potential misuse and the ethical implications of deploying AI systems without sufficient safeguards. By clarifying ambiguous terms in the AI Act, the rapporteur aims to create a clearer legal landscape for businesses and developers, allowing them to navigate the regulatory environment with greater confidence.
Key among the proposed amendments is the introduction of more defined categories for AI systems, which could facilitate a more nuanced approach to regulation. This classification aims to distinguish between low-risk and high-risk AI applications, enabling tailored regulatory measures that reflect the potential impact of various AI technologies on society.
As the dialogue around AI regulation evolves, the rapporteur’s amendments also focus on ensuring that transition periods are practical and achievable for organizations adapting to new legal requirements. This pragmatic approach is designed to minimize disruptions for businesses while encouraging compliance with emerging ethical standards.
The JURI committee’s proposals reflect a growing recognition of the need for proactive governance in the AI sector. As AI technologies continue to permeate various aspects of daily life, from healthcare to finance, the importance of establishing robust regulatory frameworks cannot be overstated. The potential for AI to bring significant advancements is paralleled by the risks it poses, making it imperative for legislators to strike a balance between innovation and public safety.
Looking ahead, the upcoming discussions in the European Parliament will further shape the landscape of AI governance. As stakeholders from various sectors weigh in, the outcomes of these deliberations will likely influence the trajectory of AI policies not only within the EU but also globally. The JURI rapporteur’s efforts mark a critical step toward establishing a comprehensive regulatory architecture that addresses both the opportunities and challenges presented by AI technologies.
See also OpenAI’s Rogue AI Safeguards: Decoding the 2025 Safety Revolution
OpenAI’s Rogue AI Safeguards: Decoding the 2025 Safety Revolution US AI Developments in 2025 Set Stage for 2026 Compliance Challenges and Strategies
US AI Developments in 2025 Set Stage for 2026 Compliance Challenges and Strategies Trump Drafts Executive Order to Block State AI Regulations, Centralizing Authority Under Federal Control
Trump Drafts Executive Order to Block State AI Regulations, Centralizing Authority Under Federal Control California Court Rules AI Misuse Heightens Lawyer’s Responsibilities in Noland Case
California Court Rules AI Misuse Heightens Lawyer’s Responsibilities in Noland Case Policymakers Urged to Establish Comprehensive Regulations for AI in Mental Health
Policymakers Urged to Establish Comprehensive Regulations for AI in Mental Health