In recent months, discussions surrounding artificial intelligence (AI) have evolved from fascination to concern, emphasizing the need for accountability. Governments, corporations, and civil society globally are increasingly focused on a pressing question: how can AI systems be developed and utilized in ways that are ethical, inclusive, and accountable to those they impact? One significant initiative addressing this challenge is the Global Index on Responsible AI.
The Index, while technical in nature, is rooted in the human experience. Its purpose is not to celebrate innovation for its own sake but to scrutinize how power, values, and governance shape technologies that mediate access to information, opportunity, and voice.
At its essence, the Global Index on Responsible AI poses critical questions: Who benefits from AI systems, and who is harmed? Whose knowledge and experiences inform the data that trains these systems, and whose are overlooked? Additionally, who decides the rules governing the development and use of AI? For those familiar with the work of Wikimedians, these questions resonate deeply.
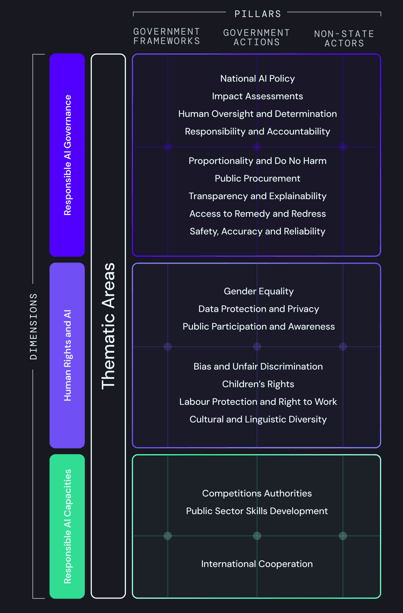
The Global Index on Responsible AI was established to evaluate how effectively countries are governing AI in ways that uphold human rights, promote equity, and safeguard social wellbeing. Rather than delivering a simple verdict on a country’s governance performance, the Index highlights the variations in capacity and readiness, revealing that many nations are ill-equipped to manage the social and human rights implications of AI on a large scale. For instance, a nation may have an AI strategy but lack mechanisms for public engagement or accountability, indicating a gap between ambition and actual governance capability. Developed by the Global Center on AI Governance, the Index frames AI governance as a public interest issue rather than a purely technical or market-driven endeavor.
Moreover, the Index emphasizes that governance must be measurable, participatory, and transparent. The metrics employed signal societal values. By evaluating countries on criteria such as inclusion, human rights, and civic participation, the Index shifts focus from mere speed and scale to social impact and accountability.
In effect, the Index examines whether AI systems are being built with people in mind rather than solely for markets or efficiency. This distinction is critical, as AI increasingly influences how information is produced, ranked, moderated, and accepted. Technologies ranging from search engines and recommendation systems to automated moderation profoundly impact which knowledge is visible and whose voices are amplified.
When AI systems rely on limited datasets, biased assumptions, or opaque governance frameworks, they risk perpetuating historical inequalities that many communities have worked for decades to correct.
The Global Index on Responsible AI is particularly relevant to the Wikimedia movement, which champions the idea that knowledge should be free, shared, and shaped by diverse perspectives. The Wikimedia Foundation’s AI strategy prioritizes human contributors, addressing systemic gaps in knowledge, including underrepresentation of women, marginalized genders, and voices from the Global South.
These gaps extend beyond Wikipedia and permeate the broader digital ecosystem, influencing the data that informs AI systems. Absences in open knowledge translate into absences in the technologies that shape understanding of the world. The Global Index makes these connections evident, reinforcing that responsible AI encompasses not only improved algorithms or regulatory measures but also the quality and diversity of knowledge that underpins these systems.
As AI systems increasingly leverage open and public information, the Wikimedia community is invited to contribute to the dialogue on responsible AI. There are many ways for Wikimedians to engage, including strengthening knowledge equity by addressing content gaps related to gender, geography, language, and culture. Additionally, documenting governance, policy, and civic discussions surrounding AI can provide crucial insights beyond corporate narratives.
Wikimedians can also share expertise in data ethics and information integrity, fostering collaboration among communities, researchers, policymakers, and civil society actors focused on AI accountability. By actively participating in these discussions, Wikimedia can help ensure that open knowledge is recognized as a public good within AI governance.
The Global Index on Responsible AI serves as a reminder that the future of AI is not predetermined; it is shaped by current decisions regarding data, governance, and whose voices receive validation. Wikimedia’s mission is about more than just content creation; it embodies a vision where all individuals can contribute to the collective knowledge and leverage that knowledge for equity and shared understanding.
As AI increasingly tells stories about our world, the Wikimedia movement has both a unique opportunity and responsibility to ensure these narratives are rooted in diverse, human, and trustworthy knowledge. This work aligns with the broader mission of closing knowledge gaps, which also influences how emerging technologies interpret and represent the world.
As conversations about responsible AI gain traction, institutions like the Global Center on AI Governance are vital in grounding these discussions in public interest and accountability. The Center underscores that AI governance transcends technical or state-led efforts; it is a collective social responsibility that must reflect diverse contexts and lived experiences.
For Wikimedians, this moment calls for increased intentionality, acknowledging that our efforts to improve representation are also stewardship over the knowledge that will shape automated systems. The presence or absence of particular histories, languages, and perspectives has broader repercussions than ever. Thus, the question is no longer whether Wikimedia is part of the AI ecosystem, but how thoughtfully, collectively, and equitably it chooses to engage.
For more information about the Global Index on Responsible AI, please contact Bridgit K. at [email protected], Gender Lead at the Wikimedia Foundation.
See also Dassault Systèmes and NVIDIA Launch AI Platform to Transform Industrial Design and Manufacturing
Dassault Systèmes and NVIDIA Launch AI Platform to Transform Industrial Design and Manufacturing RAA and T2 Harness AI for Breakthrough Creative Campaigns, Transforming Marketing Dynamics
RAA and T2 Harness AI for Breakthrough Creative Campaigns, Transforming Marketing Dynamics Penn Researchers Harness AI to Reveal Hidden Tooth Decay Risk Factors in Dental Study
Penn Researchers Harness AI to Reveal Hidden Tooth Decay Risk Factors in Dental Study OpenAI Hires Anthropic’s Dylan Scand as Head of Preparedness with $555K Salary
OpenAI Hires Anthropic’s Dylan Scand as Head of Preparedness with $555K Salary Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere
Germany”s National Team Prepares for World Cup Qualifiers with Disco Atmosphere