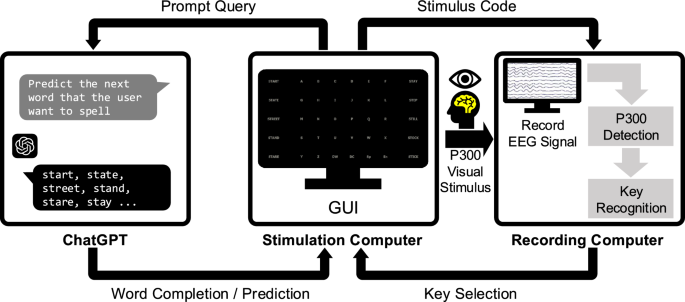
A newly proposed brain-computer interface (BCI), referred to as ChatBCI, integrates advanced EEG technology with a user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) and a remote query system using OpenAI’s GPT-3.5, enabling faster and more efficient text input for users with disabilities. This innovative system was detailed in a recent study, showcasing a setup that includes both a stimulation computer and a recording computer, which work together to process EEG signals in real time for key detection and recognition.
At the heart of the ChatBCI is a keyboard GUI that facilitates communication through a P300 speller, allowing users to select letters and words with minimal effort. The system detects the P300 event-related potential (ERP) from EEG signals when users focus on specific keys, which are indicated by a series of flashing stimuli. The setup employs a Brain Products EEG acquisition system and features low-latency data access, ensuring precise synchronization between visual stimuli and EEG recordings.
The GUI itself is designed for ease of use, consisting of a \(5 \times 8\) matrix of keys alongside panels that display both a target sentence and real-time user input. This dual display is crucial for copy-spelling tasks. The GUI also incorporates dynamic word suggestions generated through queries to the GPT-3.5 API, which processes partial text input from the user and provides relevant completions to enhance typing efficiency.
The predictive text functionality of ChatBCI allows for two types of suggestions: word completion for incomplete entries and word prediction for complete words. This adaptive approach significantly reduces the number of keystrokes required, thereby accelerating the typing process. For example, if a user types “I-WANT-TO-B”, the system might suggest completions like “BE” or “BUY”. Conversely, for complete entries such as “I-WOULD”, the user is provided with predictions for the next word, such as “LIKE” or “WANT”.
One of the notable features of ChatBCI is its ability to update word suggestions dynamically as users compose sentences, allowing for seamless integration of new words. This continuous feedback loop not only enhances user experience but also improves the overall efficiency of the communication process, making it particularly beneficial for individuals with motor impairments.
Technical Details
The performance of ChatBCI is evaluated through several key metrics, including selection accuracy, character accuracy, and information transfer rate (ITR). Selection accuracy measures the ratio of correct selections to total attempts, while character accuracy assesses the proportion of correctly typed characters against the total number of characters. ITR takes into account both speed and accuracy, providing a comprehensive view of the system’s performance.
In terms of P300 detection, the study employed a stepwise linear discriminant analysis (SWLDA) classifier, which has proven effective in previous P300 speller BCIs. This method involves a systematic feature selection process that iteratively evaluates the significance of each feature contributing to the model. For target key recognition, the system relies on cumulative LDA scores derived from repetitive stimulus presentations, ensuring accurate identification of the user’s intended key.
The ChatBCI system also offers a unique take on keystroke analysis, allowing for the assessment of predictive typing capabilities. By calculating keystroke savings, the system measures its efficiency compared to traditional typing methods. This analysis is particularly relevant for understanding how effectively the speller can reduce the cognitive load on users while they compose text.
This pioneering BCI technology represents a significant advancement in assistive communication tools, particularly for individuals with limited mobility. As research and development in this field continue to evolve, systems like ChatBCI may pave the way for more intuitive and accessible means of communication, enhancing the quality of life for many users. The integration of advanced AI with BCI technology underscores the potential for future innovations that can bridge the gap between human intent and digital communication.
See also Sam Altman Praises ChatGPT for Improved Em Dash Handling
Sam Altman Praises ChatGPT for Improved Em Dash Handling AI Country Song Fails to Top Billboard Chart Amid Viral Buzz
AI Country Song Fails to Top Billboard Chart Amid Viral Buzz GPT-5.1 and Claude 4.5 Sonnet Personality Showdown: A Comprehensive Test
GPT-5.1 and Claude 4.5 Sonnet Personality Showdown: A Comprehensive Test Rethink Your Presentations with OnlyOffice: A Free PowerPoint Alternative
Rethink Your Presentations with OnlyOffice: A Free PowerPoint Alternative OpenAI Enhances ChatGPT with Em-Dash Personalization Feature
OpenAI Enhances ChatGPT with Em-Dash Personalization Feature