Amazon Web Services (AWS) has announced the general availability of GPU partitioning with its Amazon SageMaker HyperPod, utilizing NVIDIA’s Multi-Instance GPU (MIG) technology. This new capability enables users to run multiple concurrent tasks on a single GPU, effectively minimizing compute and memory resource waste that often arises when entire GPUs are allocated to smaller tasks. By allowing several users and tasks to access GPU resources simultaneously, development and deployment cycles can be shortened, accommodating a diverse range of workloads without the need to wait for full GPU availability.
Data scientists commonly engage in various lightweight tasks that require accelerated computing resources, such as language model inference and interactive experiments using Jupyter notebooks. These tasks typically do not necessitate the full capacity of a GPU, and the introduction of MIG allows cluster managers to optimize GPU resource utilization. This capability supports multiple personas, including data scientists and ML engineers, enabling them to run concurrent workloads on the same hardware while ensuring performance assurances and workload isolation.
Technical Details
Launched in 2020, NVIDIA’s MIG technology is built into the Ampere architecture, notably in the NVIDIA A100 and A10G GPUs. It allows administrators to partition a single GPU into multiple smaller, fully isolated GPU instances, each with its own memory and compute cores. This isolation ensures predictable performance and prevents resource conflicts between tasks. With the integration of MIG into SageMaker HyperPod, administrators can enhance GPU utilization through flexible resource partitioning, alleviating critical GPU resource management challenges.
MIG supports several features, including simplified setup management, resource optimization for smaller workloads, workload isolation, cost efficiency by maximizing concurrent task execution, observability of real-time performance metrics, and fine-grained quota management across teams. Arthur Hussey, a technical staff member at Orbital Materials, remarked, “Partitioning GPUs with MIG technology for inference has allowed us to significantly increase the efficiency of our cluster.”
This technology is particularly beneficial in scenarios where multiple teams within an organization need to run their models concurrently on shared hardware. By matching workloads to appropriate MIG instances, organizations can optimize resource allocation effectively. The merging of resource-guided model serving, mixed workload execution, and enhanced development efficiency through CI/CD pipelines exemplifies MIG’s versatility.
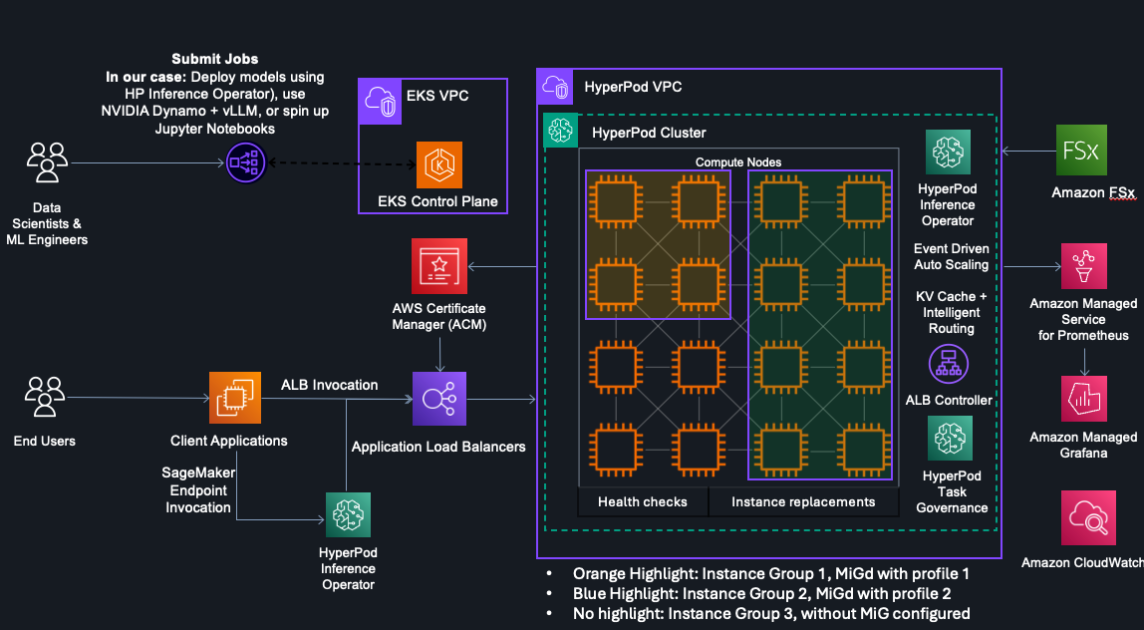
The architecture for implementing MIG in SageMaker HyperPod includes a cluster of 16 ml.p5en.48xlarge instances, utilizing various instance profiles. This setup is designed for optimal inference scenarios, providing predictable latency and ensuring cost efficiencies. Each MIG instance can be tailored to specific workloads, allowing for an optimized service experience.
Configuring MIG can be approached in two ways: a managed experience using AWS-managed components or a do-it-yourself setup with Kubernetes commands. The managed experience simplifies the setup process significantly, allowing administrators to focus on deploying workloads without delving into lower-level configuration. For existing clusters, enabling MIG involves utilizing HyperPod Helm Charts, which streamline necessary installations.
With the introduction of comprehensive observability tools in SageMaker HyperPod, organizations can monitor GPU utilization in real-time, track memory usage, and visualize resource allocation across workloads. These insights assist in optimizing GPU resources and ensuring that tasks meet performance expectations. Additionally, HyperPod task governance features allow for fair usage distribution, prioritizing workloads based on organizational needs.
The addition of MIG support in Amazon SageMaker HyperPod represents a significant evolution in machine learning infrastructure management. By enabling multiple isolated tasks to run concurrently on shared GPUs while ensuring robust performance and resource management, organizations can significantly lower infrastructure costs and enhance operational efficiency. This capability is poised to transform how machine learning tasks are executed at scale, facilitating the advancement of AI technologies across various sectors.
See also India Launches BharatGen: First Multilingual AI LLM with Rs 1,058 Crore Support
India Launches BharatGen: First Multilingual AI LLM with Rs 1,058 Crore Support Google Integrates Nano Banana AI Image Generator into App Search for Streamlined Creation
Google Integrates Nano Banana AI Image Generator into App Search for Streamlined Creation AI Shopping Surges: 66% of Americans Use ChatGPT for Holiday Purchases in 2025
AI Shopping Surges: 66% of Americans Use ChatGPT for Holiday Purchases in 2025 Google Launches Nano Banana Pro AI Image Tool Amid Concerns Over Realism
Google Launches Nano Banana Pro AI Image Tool Amid Concerns Over Realism Ant Group Launches LingGuang AI Assistant, Surpassing 1M Downloads in Days
Ant Group Launches LingGuang AI Assistant, Surpassing 1M Downloads in Days