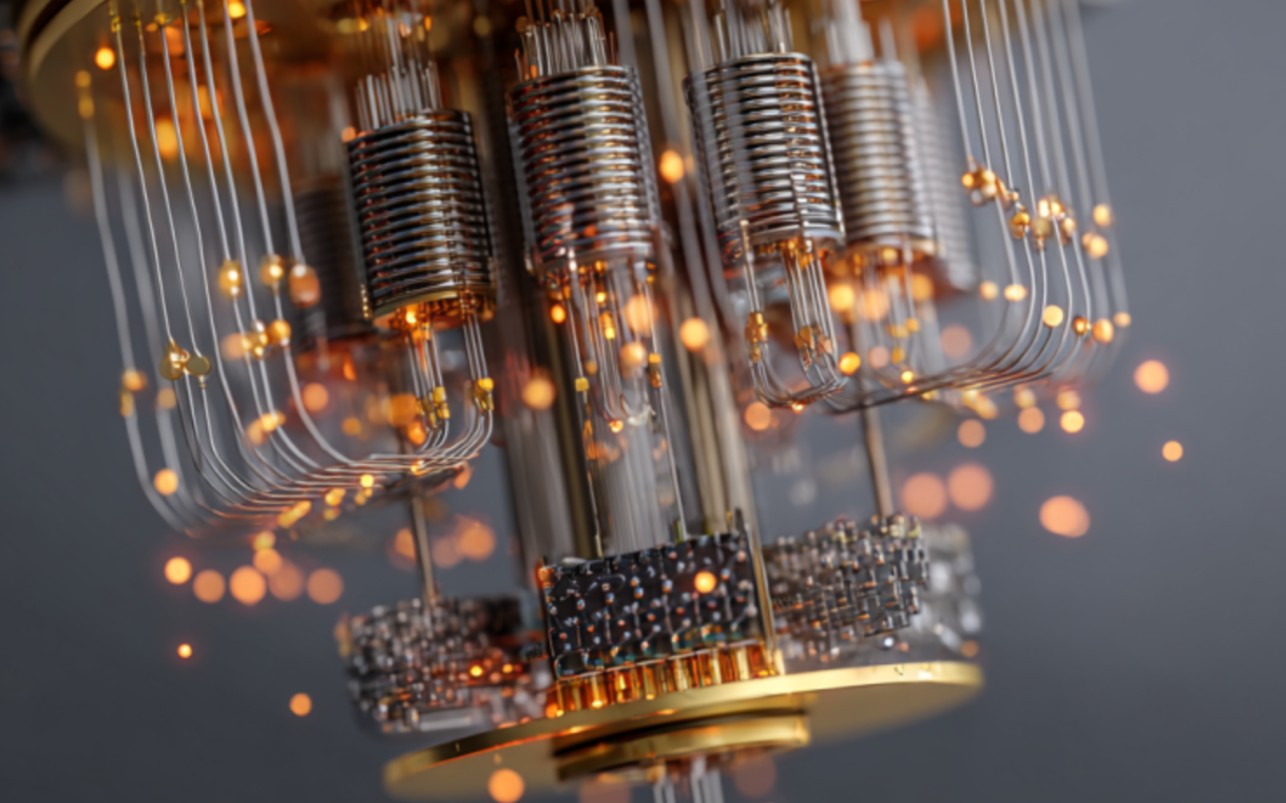
Quantum computing, a field rooted in the complexities of quantum mechanics, remains at the forefront of scientific exploration, though overshadowed by the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI). This branch of physics investigates the behavior of subatomic particles and opens avenues for potentially transformative applications. Despite the significant investments and claims from tech giants like Microsoft and Google, quantum computing has yet to achieve the visibility that AI commands, primarily due to its reliance on specialized hardware and complex physical systems. Quantum computers are still largely bulky, expensive, and not widely accessible, leading to a disparity in public awareness and commercial viability compared to AI technologies, which are primarily software-based and utilize existing hardware infrastructures.
Brian Hopkins, vice president and chief analyst at Forrester, cautions against overestimating the immediate capabilities of quantum computing. “The potential is there, but the final result remains to be seen. Initial experiments are promising, but research and more powerful computers are still needed to truly apply quantum effects to AI,” he explains. According to a report from McKinsey, the quantum computing market could reach a valuation of $97 billion by 2025. In stark contrast, the AI market is projected to soar into the trillions. However, a recent forecast has raised alarms, suggesting that key stocks in the quantum sector could plummet by up to 62%, provoking concerns of a speculative bubble.
The technological challenges intrinsic to quantum computing set it apart from AI. Quantum bits, or qubits, are exceedingly sensitive to light, noise, and minor environmental alterations. Elon Musk has pointed out through social media that the optimal conditions for quantum computations might resemble environments found in permanently shadowed lunar craters. These cumbersome machines require temperatures approaching absolute zero and sophisticated laser systems for operation. Recent innovations, such as the use of synthetic diamonds by Element 6, a subsidiary of De Beers, offer promise for more accessible operational temperatures, potentially paving the way for practical applications.
There are currently an estimated 200 quantum computers in existence globally, though the actual number may be higher due to undisclosed figures from China. Despite the challenges, quantum experts like Rajeeb Hazra, CEO of Quantinuum, assert that quantum computing could yield applications that rival or surpass those of AI. Professor Sir Peter Knight, a noted British quantum physicist, emphasizes the transformative potential of quantum technology, stating that problems requiring extensive calculations on today’s most powerful supercomputers could be resolved in mere seconds using quantum capabilities. This could revolutionize fields ranging from drug discovery to personalized medicine and advanced sensing technologies.
Quantum sensors have already found applications in non-invasive brain scanning prototypes for children suffering from epilepsy. In a separate initiative, the “Quantum Compass” tested in London represents a novel approach to navigation, providing alternatives to GPS by functioning effectively even in underground environments where satellite signals are unavailable. Michael Cuthbert, director of the UK’s National Quantum Computing Centre, has highlighted that technologies like quantum clocks, gyroscopes, and magnetometers could significantly enhance the safety and reliability of critical navigation systems.
Major corporations, including Airbus, are partnering with IonQ to leverage quantum algorithms for optimizing cargo loading in airplanes, aiming to reduce fuel consumption. The UK’s National Grid is also exploring quantum technology to improve energy production management, focusing on minimizing disruptions during peak demand periods. However, one of the most pressing concerns surrounding the rise of quantum computing is its implications for data security and cryptography. The capability of quantum computers to potentially eclipse current encryption methods poses a serious risk, a phenomenon referred to as “Q-Day.”
Experts are urging the immediate development of encryption technologies resistant to quantum attacks. Brian Hopkins anticipates that devices capable of decrypting secured data could emerge as soon as 2030. Companies like Apple and the Signal platform have introduced post-quantum cryptographic keys, although these cannot retroactively secure already encrypted information. Daniel Shiu, former head of cryptography at GCHQ, has raised alarms regarding the vulnerability of British citizens’ data to potential decrypting efforts by state-sponsored entities, notably from China.
The advancements in quantum computing and its competition with AI prompt a broader dialogue about the future of technology. As both fields evolve, the interplay between their capabilities and applications could fundamentally reshape industries and society at large, ushering in an era defined by unprecedented computational power and its implications.
See also Africa’s AI Revolution: $10B Investment Needed in Connectivity, Compute, and Talent
Africa’s AI Revolution: $10B Investment Needed in Connectivity, Compute, and Talent AI Computing in Space to Be 50% Cheaper Than Earth by 2030, Analysts Predict
AI Computing in Space to Be 50% Cheaper Than Earth by 2030, Analysts Predict Foxconn Invests $569 Million in Wisconsin to Expand AI Hardware Operations, Adding 1,300 Jobs
Foxconn Invests $569 Million in Wisconsin to Expand AI Hardware Operations, Adding 1,300 Jobs AI Hardware Market Grows 30% in 2025, Driven by Generative AI and Edge Computing Demand
AI Hardware Market Grows 30% in 2025, Driven by Generative AI and Edge Computing Demand Conflow Power Group Launches iLamp: Solar-Powered AI Streetlights with Near-Zero Carbon Footprint
Conflow Power Group Launches iLamp: Solar-Powered AI Streetlights with Near-Zero Carbon Footprint