Recent advancements in neuroscience and artificial intelligence (AI) are fostering a deeper understanding of animal perception, an area that draws heavily on the pioneering work of psychologist James Gibson. Gibson introduced the concept of “affordances,” which emphasizes the interplay between an animal and its environment, suggesting that perception is not merely an observational process but one deeply rooted in ecological context. This principle is gaining traction in neuroscience, leading to the emergence of “ecological neuroscience,” which posits that the study of animal behavior and brain function must be contextualized within their natural environments.
As researchers delve deeper into this field, they are discovering that many previously perplexing neural characteristics make more sense when viewed through an ecological lens. For instance, variations in visual processing among different species—such as distinct neuron allocations for visual features—often align with the specific needs and challenges posed by their unique ecological niches. This perspective aligns with vision scientist Horace Barlow’s assertion that “A wing would be a most mystifying structure if one did not know that birds flew.”
Understanding animal behavior and brain function necessitates grasping how animals perceive their worlds. This is where generative AI stands to make significant contributions. By creating virtual environments, generative AI enables researchers to simulate and hypothesize how different animals interact with their surroundings. This technology has the potential to bridge the gap between perception and environment that Gibson emphasized, suggesting we must view the two as a single, interconnected system.
The synergy between neuroscience and AI is already evidenced in vision research. Artificial neural networks, particularly those trained on extensive datasets like ImageNet, have made strides in modeling visual processing akin to biological systems. However, the effectiveness of these models has highlighted limitations; ImageNet primarily encapsulates human-centric visual experiences and does not adequately reflect the dynamic, embodied interactions that characterize real-world perception. As models plateau, the discrepancies between internal representations and actual neural data become more pronounced, revealing that crucial aspects of natural visual experience remain unaccounted for.
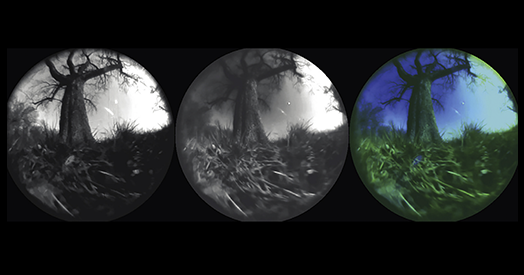
While ImageNet encompasses static images, ecological perception is fundamentally dynamic, evolving over time through an organism’s movement and interaction with its environment. For example, a frog’s visual perception is shaped not by isolated images of flies, but by the motion patterns of prey and the frog’s own leaps. This underscores the necessity of capturing the ecological context in which sensory input, movement, and environment co-develop.
The sensory experiences of animals are influenced by three interconnected factors: their environment, physical form, and movements. Each environment presents unique structural and dynamic features, which are perceived differently depending on an animal’s anatomy. For instance, a rat’s perception of a forest differs significantly from that of a monkey, whose forward-facing eyes provide greater visual acuity. Even in similar environments, variations in movement patterns can lead to vastly different sensory experiences, as seen in the contrast between the exploratory behaviors of rats and the agile movements of tree shrews.
Capturing these intricate ecological interactions presents a formidable challenge in neuroscience. Researchers are tasked with measuring natural sensory input alongside continuous behavioral and environmental data, yet the task remains complex. However, recent innovations in generative AI may offer transformative solutions. Advances in video and multimodal generative models allow for the creation of rich visual scenes that can be manipulated in real-time, providing a deeper insight into the ecological contexts that shape perception.
These models are not just repositories of visual data but are highly customizable. By specifying elements within a scene and simulating movement through it, researchers can generate video streams that closely approximate how the world appears from the perspective of a moving animal. This capability enables the integration of findings from decades of ethological research with contemporary AI technologies, creating a more holistic understanding of sensory experience.
As neuroscience continues to evolve, engaging with generative AI will be crucial. By harnessing these technologies, researchers can refine their approaches to studying animal perception, ultimately advancing the understanding of how different species interact with their ecosystems. The intersection of ecological neuroscience and AI not only enhances our comprehension of animal behavior but also highlights the profound significance of ecological context in shaping perceptions—and, by extension, actions—across diverse species.
See also CognitiveLab Launches NetraEmbed, Boosting Multimodal Document AI Performance by 150%
CognitiveLab Launches NetraEmbed, Boosting Multimodal Document AI Performance by 150% Google Set to Launch Nano Banana 2 Flash AI Image Tool with Free Access Soon
Google Set to Launch Nano Banana 2 Flash AI Image Tool with Free Access Soon 95% of Generative AI Projects Fail: CX Teams Bridge the GenAI Divide with Proven ROI
95% of Generative AI Projects Fail: CX Teams Bridge the GenAI Divide with Proven ROI Generative AI Transforms CX with 3 Key Pillars Driving 95% Agent Productivity Boost
Generative AI Transforms CX with 3 Key Pillars Driving 95% Agent Productivity Boost APAC’s LLM Market Set to Surge to $78.5B by 2035 Amid Rapid AI Adoption
APAC’s LLM Market Set to Surge to $78.5B by 2035 Amid Rapid AI Adoption