As cloud-based AI solutions continue to dominate headlines, the capabilities of local AI tools are advancing significantly. Today, powerful computing hardware, such as gaming PCs, can handle a multitude of AI applications beyond running large language models and generating images. Importantly, these local tools offer users complete control over their data, enhancing privacy compared to cloud-based alternatives.
Among the noteworthy local AI tools is OpenAI’s Whisper, a voice-to-text transcription model that users can run on their own PCs using applications like Whisper Desktop. This tool leverages GPU power to deliver fast and efficient transcription services. Users can either speak into their microphones or upload audio files, and while Whisper may not be flawless, it often outperforms traditional professional transcription software that would have incurred substantial costs just a few years ago.
Image processing is no exception to the benefits of local AI. Upscayl is a user-friendly application that allows users to upscale images from lower to higher resolutions directly on their PCs. Unlike Adobe Photoshop, which performs similar tasks using cloud servers, Upscayl allows users with powerful systems to enhance image quality without the need for uploads, making it an appealing option for those concerned about data privacy.
Real-time effects for webcams and microphones have also gained traction, particularly with tools like Nvidia Broadcast, which utilizes the processing power of Nvidia’s RTX GPUs. This free app provides features such as background removal and eye contact simulation in real time, making it invaluable for live streaming and video conferencing. Microsoft has introduced its own suite of AI webcam effects through Windows Studio Effects, further showcasing the growing integration of AI in consumer technologies.
Video editing is another area where local AI tools shine. Topaz Labs offers professional-grade applications capable of AI upscaling and editing videos, relying solely on local hardware for processing. While these tools can be pricey and are tailored for professional use, they highlight the potential of local AI solutions. For those seeking free alternatives, Video2X provides a surprisingly user-friendly platform for AI video upscaling, showcasing the diversity of available tools.
Voice cloning technologies, such as GPT-SoVITS and RVC, exemplify another fascinating area in local AI. Although these tools lack polish and often come with cumbersome user interfaces, they allow consumers to clone voices using personal hardware. This capability marks a significant leap forward, even as developers continue to refine the user experience.
Music generation is also evolving with local AI solutions, evidenced by YuE, an open-source tool that shows promise in competing with cloud-based offerings like Suno. While still in early development stages, YuE allows users to generate music on their own hardware. Early benchmarks suggest that generating 30 seconds of audio takes about six minutes on a powerful RTX 4090 GPU, indicating potential for wider application in the future.
Another emerging tool, Ultimate Vocal Remover, addresses the longstanding need for vocal isolation in music tracks. This free, user-friendly application can quickly remove vocals from MP3, FLAC, or WAV files, providing a viable solution for karaoke enthusiasts and those who prefer instrumental versions of songs.
Despite the impressive capabilities of local AI tools, they often come with significant drawbacks, primarily in the realm of user interface and overall polish. Many solutions, especially those emerging from the open-source community, exhibit amateurish design and usability challenges. This is particularly evident in applications that, while technically powerful, lack the intuitive design seen in proprietary software. However, there is optimism that as the technology matures, more refined user interfaces will emerge, making these tools more accessible to a broader audience.
In summary, local AI solutions are transforming the landscape by providing powerful capabilities while ensuring data privacy. Although they may require some technical know-how and a willingness to navigate less polished interfaces, these tools represent a significant step forward in the accessibility of AI technology. As developments continue, the potential for local AI applications might soon rival their cloud-based counterparts, signaling an exciting future for technology enthusiasts and professionals alike.
See also Adobe Unveils Firefly Video Editor with Unlimited Generations, New AI Editing Tools
Adobe Unveils Firefly Video Editor with Unlimited Generations, New AI Editing Tools AI Detection Challenges: 5 Lessons from 2025’s Deepfake Surge and Future Implications
AI Detection Challenges: 5 Lessons from 2025’s Deepfake Surge and Future Implications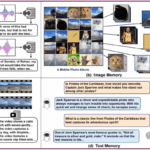 Shanghai AI Lab Launches MemVerse: First Universal Multimodal Memory Framework for Agents
Shanghai AI Lab Launches MemVerse: First Universal Multimodal Memory Framework for Agents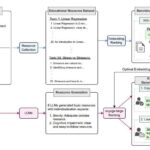 AI Framework Achieves 79% Accuracy in Ranking Educational Resources for Personalized Learning
AI Framework Achieves 79% Accuracy in Ranking Educational Resources for Personalized Learning Brands Must Optimize AI Content Strategy as 60% of Healthcare Queries Go Directly Answered
Brands Must Optimize AI Content Strategy as 60% of Healthcare Queries Go Directly Answered