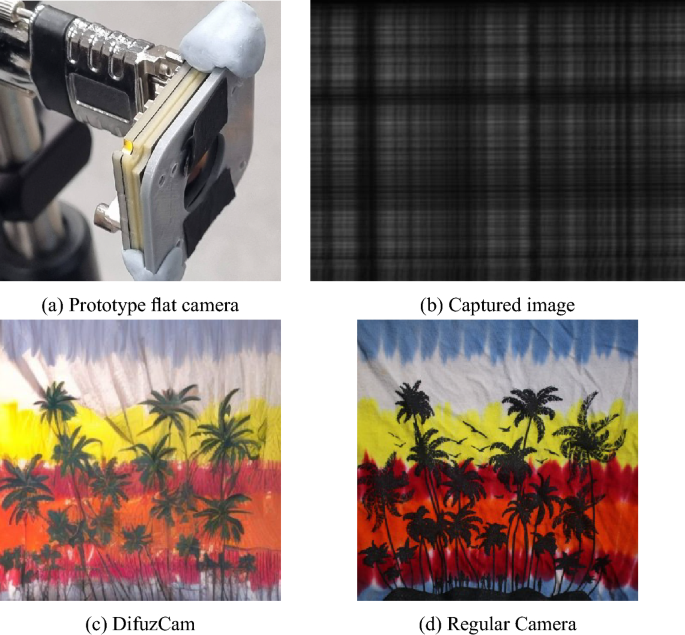
The field of lensless imaging is poised for significant advancements, as recent studies reveal innovative methodologies that could transform technology applications in various sectors. An increasing number of researchers are exploring lensless systems, which use computational techniques and coded apertures to capture high-quality images without traditional lenses. This shift could lead to breakthroughs in fields ranging from biomedical imaging to consumer electronics.
One notable advancement is described in a paper by Salman Asif et al., titled “Flatcam: Replacing lenses with masks and computation,” presented at the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops in 2015. The authors propose a method that employs flat, programmable masks instead of lenses, enabling the capture of images through computational reconstruction. This approach lays the groundwork for further innovations in lensless imaging.
In a more recent work, Khan et al. (2019) delve into photorealistic reconstructions of highly multiplexed lensless images. Their research, presented at the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, emphasizes the potential for high-resolution imaging with enhanced multiplexing capabilities, which could significantly improve image quality and expand the applications of lensless technology.
Diffusion models are also gaining traction, as highlighted in a survey by Croitoru et al. (2023). Their comprehensive analysis in the IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence discusses the integration of these models in vision technology, offering insights into their effectiveness for image generation and reconstruction tasks. The trend of applying diffusion models is underscored by Rombach et al. (2022), who document high-resolution image synthesis techniques that leverage latent diffusion models.
Another significant contribution comes from Zhang et al. (2023), who outline a framework that adds conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. This development facilitates more precise control over the image generation process, enhancing the practicality of lensless imaging systems in real-world scenarios.
While lensless imaging brings multiple advantages, such as reduced size and weight, challenges remain. Techniques like compressive sensing, as explored by Huang et al. (2013), emphasize the need for advanced algorithms to reconstruct images accurately from sparse data. This highlights the importance of developing robust reconstruction methods that can handle the complexities inherent in lensless imaging.
Research has also demonstrated the potential of novel materials in lensless systems. For instance, Miller et al. (2020) introduced particle-based reconfigurable scattering masks, presenting a promising avenue for enhancing image quality while maintaining the compact nature of lensless cameras. Their findings suggest that leveraging advanced materials can further refine the imaging capabilities of these systems.
Efforts to enhance image quality through machine learning are also evident in recent studies. Techniques involving deep learning, such as those proposed by Wu et al. (2021) and others focusing on super-resolution methods, have proven effective in overcoming some of the limitations associated with lensless imaging. These advancements point to the growing intersection of artificial intelligence and optical technologies, providing exciting opportunities for enhanced imaging solutions.
As the research community continues to explore lensless imaging, it is essential to focus on collaborative efforts that can bridge the gap between theoretical developments and practical implementations. Innovations in machine learning, materials science, and computational imaging are converging to create a promising future for lensless technologies.
Going forward, the ability to efficiently reconstruct high-quality images without traditional lenses holds enormous potential. This evolution could influence various industries, including healthcare, where enhanced imaging techniques could facilitate better diagnostics and treatment options. The ongoing exploration of lensless imaging not only presents technical challenges but also opens new avenues for creative solutions in the realm of visual technology.
See also Gemini Enables Multimodal Input with Image Uploads for Enhanced AI Analysis
Gemini Enables Multimodal Input with Image Uploads for Enhanced AI Analysis OpenAI’s Sam Altman Issues ‘Code Red’ as Google’s Gemini 3 Tops AI LLM Rankings
OpenAI’s Sam Altman Issues ‘Code Red’ as Google’s Gemini 3 Tops AI LLM Rankings Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 Surpasses GPT-5.1 and Gemini with Advanced Coding Skills
Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 Surpasses GPT-5.1 and Gemini with Advanced Coding Skills Halfaccess.org Reveals AI Trends Reshaping Digital Content Creation Industry by 2026
Halfaccess.org Reveals AI Trends Reshaping Digital Content Creation Industry by 2026 SenseTime Launches NEO, First Native Multimodal Architecture, Outperforming Top Models
SenseTime Launches NEO, First Native Multimodal Architecture, Outperforming Top Models