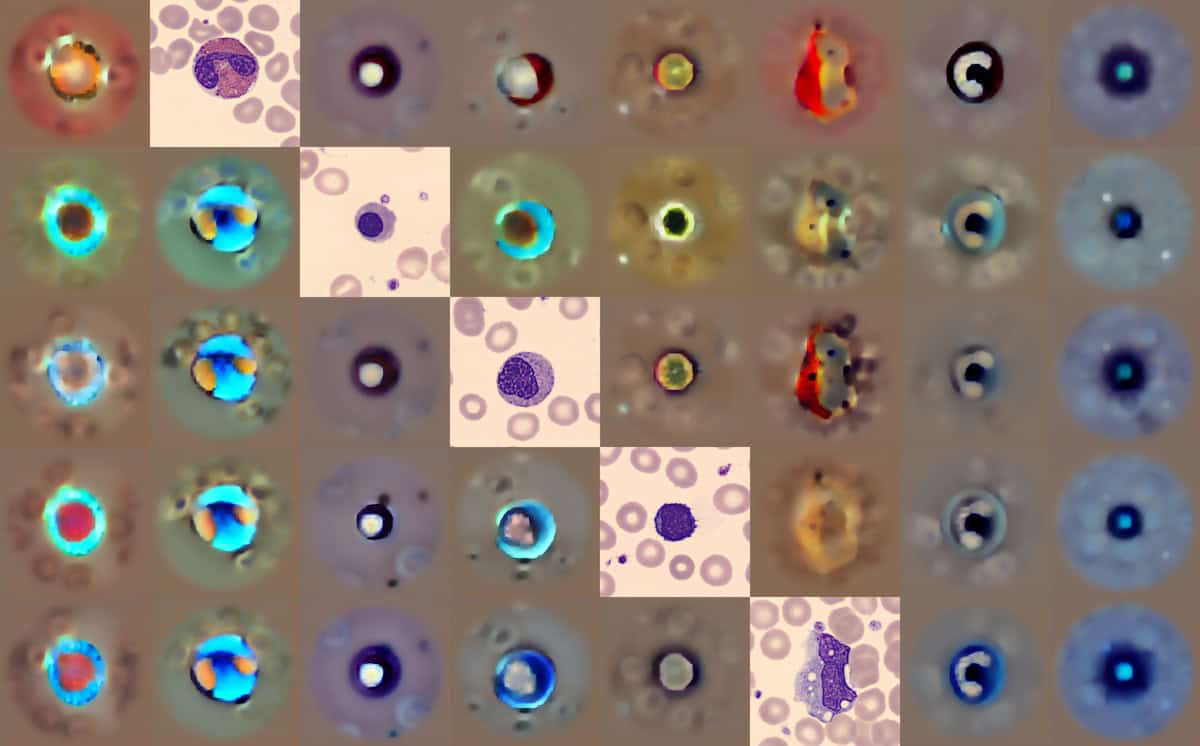
A new generative AI model has been developed to detect abnormalities in blood cells, marking a significant advancement in the intersection of artificial intelligence and healthcare diagnostics. The model, which utilizes deep learning algorithms, was unveiled by a team of researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, emphasizing its potential to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical assessments. This breakthrough was reported on September 25, 2025, amidst growing interest in the application of AI in clinical settings.
The model is designed to analyze blood samples with unparalleled precision, identifying conditions such as leukemia and anemia more swiftly than traditional methods. Researchers highlighted that the AI’s ability to learn from vast datasets allows it to recognize patterns in blood cell morphology, which could lead to earlier detection of various hematologic disorders. Dr. Sarah Chen, the lead investigator, stated, “This model not only improves diagnostic accuracy but also offers the potential for personalized treatment plans based on individual patient profiles.”
In clinical trials, the generative AI model demonstrated a sensitivity rate of 92% in detecting blood cell abnormalities, significantly higher than conventional diagnostic methods. The researchers noted that, while current techniques rely heavily on expert human interpretation, the AI’s continuous learning capabilities enable it to adapt and improve over time, potentially reducing the workload of pathologists and speeding up the diagnostic process.
The development comes at a time when the healthcare industry is increasingly turning to AI to enhance patient outcomes. As medical professionals face mounting pressures from a growing patient population and a shortage of specialists, AI solutions like this generative model offer a promising avenue for alleviating some of these challenges. The ability to automate routine tasks can free up valuable time for healthcare providers, allowing them to focus on complex cases that require human expertise.
Moreover, the model’s implementation could lead to significant cost savings in healthcare delivery. By streamlining the diagnostic process, hospitals and clinics may reduce the need for unnecessary follow-up tests and interventions, thereby lowering overall healthcare expenditures. The team at UCSF is currently in discussions with several healthcare organizations to explore the practical applications of the model in diagnostic labs across the country.
While the results are promising, experts caution that the integration of AI in medical diagnostics must be approached thoughtfully. Ethical considerations, such as patient privacy and the potential for bias in AI algorithms, are paramount. Additionally, ongoing validation in diverse clinical settings will be crucial to ensure the reliability and generalizability of the model’s findings.
As AI technology continues to evolve, future iterations of this model could incorporate additional data sources, enhancing its diagnostic capabilities even further. Researchers are also investigating the potential for the model to be adapted for use in other domains of medicine, such as imaging and pathology, which could revolutionize the way healthcare providers diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions.
The generative AI model represents a significant stride in leveraging technology for better health outcomes, and its successful deployment could pave the way for further innovations in the field of medical diagnostics. As healthcare continues to embrace digital transformation, the potential for AI-driven solutions to reshape patient care remains vast and promising.
See also DifuzCam Unveils Lensless Camera Design Using Diffusion Models and Masks
DifuzCam Unveils Lensless Camera Design Using Diffusion Models and Masks Gemini Enables Multimodal Input with Image Uploads for Enhanced AI Analysis
Gemini Enables Multimodal Input with Image Uploads for Enhanced AI Analysis OpenAI’s Sam Altman Issues ‘Code Red’ as Google’s Gemini 3 Tops AI LLM Rankings
OpenAI’s Sam Altman Issues ‘Code Red’ as Google’s Gemini 3 Tops AI LLM Rankings Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 Surpasses GPT-5.1 and Gemini with Advanced Coding Skills
Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4.5 Surpasses GPT-5.1 and Gemini with Advanced Coding Skills Halfaccess.org Reveals AI Trends Reshaping Digital Content Creation Industry by 2026
Halfaccess.org Reveals AI Trends Reshaping Digital Content Creation Industry by 2026