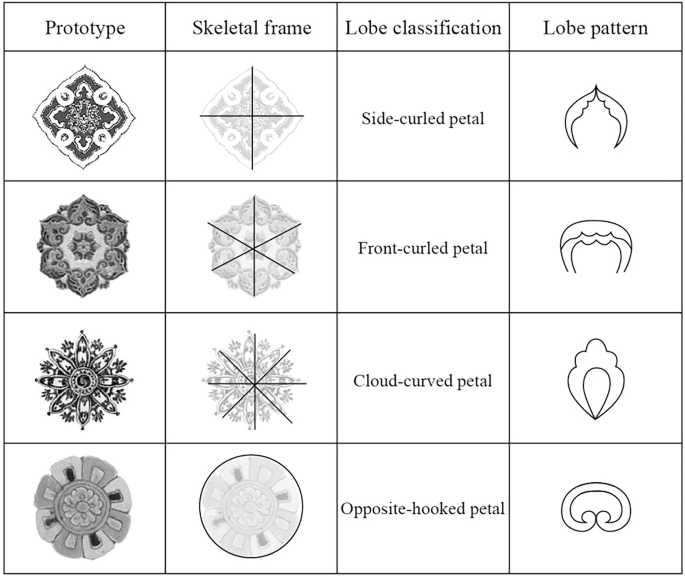
The Baoxiang pattern, a significant decorative motif in traditional Chinese art, has evolved over centuries, representing a blend of cultural identity and artistic expression. Originating from Buddhist symbolism, the term “Baoxiang” translates to “Treasure Fairy Flower,” reflecting its roots in the lotus flower, a symbol of purity and rebirth. This pattern found its prominence during the Sui and Tang dynasties, characterized by intricate floral designs often paired with auspicious symbols such as birds and cloud motifs, showcasing a high level of ornamentation.
Recent advancements in technology have reignited interest in traditional patterns like the Baoxiang, as researchers and designers explore their historical significance and contemporary applications. Innovations in generative modeling have enabled the application of artificial intelligence to these traditional designs. For instance, scholars have developed methods using shape grammar and artificial neural networks to generate batik patterns, aiming to enhance design efficiency while preserving cultural integrity. Other techniques, such as the rapid style transformation of ethnic patterns, have further established a bridge between historical motifs and modern design.
The Segment Anything Model (SAM), introduced by Kirillov et al., has revolutionized image segmentation, particularly for intricate patterns such as Baoxianghua. This model utilizes visual prompts to segment objects with remarkable accuracy, trained on over 1.1 billion images. SAM’s application in extracting key elements from Baoxiang patterns has proven effective in creating high-quality datasets essential for further research and design innovation. By enhancing traditional pattern segmentation, SAM provides a robust foundation for incorporating advanced technologies into cultural heritage preservation.
Diffusion Models (DM), particularly the Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM), have also emerged as a promising tool for generating complex patterns. These models operate on probabilistic diffusion processes that add noise to data and then reverse the process to restore or create new designs. Recent findings show that DDPM can effectively generate innovative patterns that align with cultural contexts, enhancing the flexibility and creativity of design practices.
This study meticulously gathered 3,211 images of Baoxiang patterns from various online sources, preserving the motifs’ evolution across different historical periods. After rigorous screening, 1,843 high-quality images were retained for analysis. Utilizing SAM for segmentation, the researchers ensured that the dataset was both diverse and representative. Data augmentation techniques expanded the dataset to 7,771 samples, bolstering the model’s generalization capabilities.
The comparative study of the traditional shape grammar model and the DDPM highlighted distinct approaches to pattern generation. Shape grammar focuses on systematic derivation using predefined rules, enabling a logical grasp of pattern structures, while DDPM embraces randomness and denoising to create diverse and complex designs. A targeted questionnaire was conducted among 206 respondents to evaluate the effectiveness of both models in generating patterns, revealing valuable insights into user preferences and design aesthetics.
As the research progressed, the study optimized and expanded the generated Baoxiang patterns, applying color combinations to enhance their visual appeal. Ultimately, the integration of traditional motifs with modern design methodologies not only preserves the artistic legacy of the Baoxiang pattern but also opens new avenues for innovation in contemporary design practices. The findings underscore the potential of blending historical artistry with cutting-edge technology, paving the way for a future where cultural heritage and modern aesthetics coalesce seamlessly.
See also UiPath Stock (NYSE: PATH) Remains Undervalued Despite Strong Growth Potential
UiPath Stock (NYSE: PATH) Remains Undervalued Despite Strong Growth Potential TikTok Launches AI Transparency Tools to Combat Misinformation and Enhance User Control
TikTok Launches AI Transparency Tools to Combat Misinformation and Enhance User Control New Research Reveals Semantic Leakage Can Corrupt LLMs, Eliciting ‘Weird Generalizations’
New Research Reveals Semantic Leakage Can Corrupt LLMs, Eliciting ‘Weird Generalizations’ Synteny and Google Launch OXtal: 100M Parameter Model for Accurate Crystal Structure Prediction
Synteny and Google Launch OXtal: 100M Parameter Model for Accurate Crystal Structure Prediction LodgIQ Launches AI Wizard, Hospitality’s First Generative AI Platform for Revenue Intelligence
LodgIQ Launches AI Wizard, Hospitality’s First Generative AI Platform for Revenue Intelligence