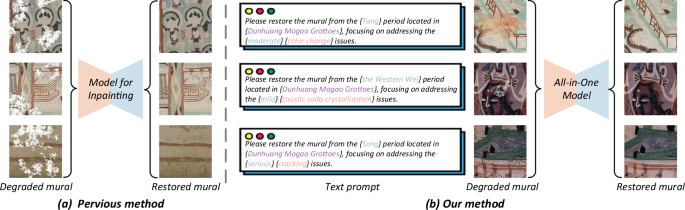
In a significant advancement for the restoration of historical murals, researchers have unveiled a novel diffusion model that aims to mitigate the effects of degradation caused by factors such as color fading, water stains, and blurring. This innovative approach, known as PGRDiff, utilizes a transparency matrix for the synthesis of degraded images, allowing for a more nuanced restoration process that integrates information from both original and degraded states of the artwork. The method addresses the pressing need for effective mural preservation, particularly as many artworks face deterioration over time.
The PGRDiff model operates by combining an original mural, represented as \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{0}\), with a degradation patch \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{deg}\) using a transparency matrix denoted as M. This blending is mathematically expressed as \({\mathcal{Y}} = (1 – \mathbf{M}) \odot {{\mathcal{X}}}_{0} + \mathbf{M} \odot {{\mathcal{X}}}_{deg}\), where the operator ⊙ signifies element-wise multiplication. The matrix M functions similarly to the alpha channel in RGBA formats, allowing for a controlled mix of the original and degraded images, yielding a degraded version denoted as \({\mathcal{Y}}\).
Building on traditional Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM), the researchers modified the initial noisy state to define \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{T} = {\mathcal{Y}} + \sqrt{{\delta }_{T}} \epsilon\), where \({\mathcal{Y}}\) represents the degraded mural and \(\epsilon\) is pure noise. The forward process transforms \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{0}\) into \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{T}\) through a two-stage degradation process. Initially, it transitions to \({\mathcal{Y}}\) and subsequently injects noise, resulting in a dual diffusion process that captures both degradation and stochastic noise.
The researchers detail the forward semi-transparent residual diffusion process through a joint probability distribution, defined as \(q({{\mathcal{X}}}_{1:T}| {{\mathcal{X}}}_{0},{{\mathcal{X}}}_{res})\). This distribution models the gradual degradation and noise addition, with specific coefficients controlling the diffusion of residuals and noise. Sampling from this distribution provides a clear pathway from the original mural to its degraded state, with the cumulative effects of the transformation overtly articulated in the model equations.
In the reverse process, the model utilizes Bayes’ rule to estimate transfer probabilities, allowing for a calculated transition from \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{t}\) to \({{\mathcal{X}}}_{t-1}\). The architecture is underpinned by advanced UNet-based networks designed to predict the masked residual and noise at each step. This structure not only facilitates accurate restoration but also accommodates user input, particularly through prompts that specify restoration parameters, such as the historical context or the nature of degradation.
Significantly, the model incorporates a prompt-guided U-Net, which integrates textual embeddings derived from a pre-trained large language model (LLM) to further refine the restoration process. The LLM processes user prompts—such as requests to restore murals from specific historical periods—transforming them into numerical representations that enhance the visual restoration task. This dual approach of merging visual features with textual context underscores the model’s innovative capacity to address the complexities of mural restoration.
As the researchers continue to refine the PGRDiff model, they emphasize its potential to revolutionize the field of art conservation. By effectively capturing and reversing the degradation process while considering contextual information, this model not only aims to restore the aesthetic integrity of murals but also preserves their historical significance. The success of PGRDiff could pave the way for broader applications in art restoration, enabling future generations to connect with the rich visual narratives embedded in historical artworks.
See also AI Image Generators Default to 12 Generic Styles, Study Reveals Surprising Trends
AI Image Generators Default to 12 Generic Styles, Study Reveals Surprising Trends Multimodal AI Transforms Enterprise Efficiency, Enhancing Customer Service and Risk Management
Multimodal AI Transforms Enterprise Efficiency, Enhancing Customer Service and Risk Management YouTube Bans Two High-Profile Channels for Misleading AI-Generated Movie Trailers
YouTube Bans Two High-Profile Channels for Misleading AI-Generated Movie Trailers AI Image Generators Limit Creativity, Defaulting to 12 Common Styles, Study Reveals
AI Image Generators Limit Creativity, Defaulting to 12 Common Styles, Study Reveals OpenAI Launches GPT-5 with Advanced Reasoning and Autonomous Agent Capabilities
OpenAI Launches GPT-5 with Advanced Reasoning and Autonomous Agent Capabilities