Large language models (LLMs) like generative pre-trained transformer (GPT), bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT), and T5 are revolutionizing industries from education to healthcare. Their capacity to produce fluent, human-like text is streamlining workflows and enabling automation. However, this same proficiency is raising concerns about cybersecurity threats, misinformation, and biased outputs that could mislead users and exacerbate social inequalities. Researchers caution that without systematic regulation and robust defense mechanisms, the misuse of LLMs could undermine data security, public trust, and societal stability.
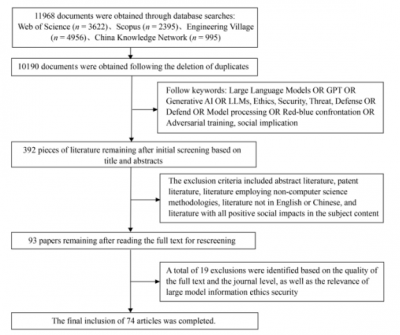
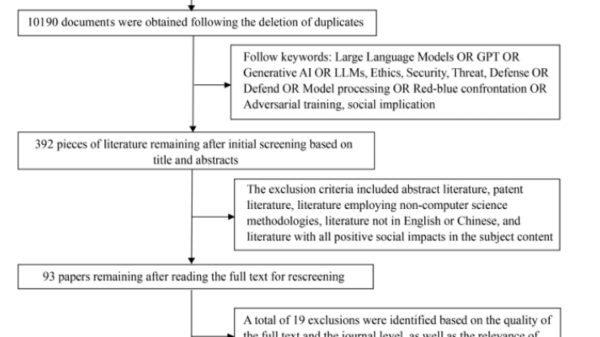
A recent study by scholars from Shanghai Jiao Tong University and East China Normal University published in Frontiers of Engineering Management examines ethical security risks associated with LLMs. The study reviewed over 10,000 documents and distilled 73 key works to highlight various threats such as phishing attacks, the generation of malicious code, data leakage, hallucination, social bias, and jailbreaking. It also evaluated defense tools, including adversarial training, input preprocessing, watermarking, and model alignment strategies.
The review categorizes LLM-related security threats into two primary domains: misuse-based risks and malicious attacks. Misuse-based risks involve phishing emails crafted with near-native fluency, automated malware scripting, identity spoofing, and large-scale misinformation generation. Malicious attacks can occur at both the data/model level—such as model inversion, poisoning, and extraction—and at the user interaction level, including prompt injection and jailbreak techniques. These attacks might access private training data, bypass safety filters, or produce harmful content.
On the defensive side, the study outlines three major technical strategies: parameter processing, which eliminates redundant parameters to reduce exposure to attacks; input preprocessing, which rephrases prompts to detect adversarial triggers without requiring retraining; and adversarial training, including red-teaming frameworks designed to simulate attacks and enhance robustness. New detection technologies like semantic watermarking and CheckGPT can identify model-generated text with an accuracy rate of 98% to 99%. Nevertheless, the report notes that defenses often lag behind the rapidly evolving nature of attacks, signaling an urgent need for scalable, cost-effective, multilingual solutions.
The authors stress that technical safeguards must be accompanied by ethical governance. They argue that issues such as hallucination, bias, privacy breaches, and misinformation constitute social-level risks that transcend mere engineering challenges. To foster trust in LLM-based systems, future models should prioritize transparency, verifiable content traceability, and interdisciplinary oversight. Establishing ethical review frameworks, dataset audit mechanisms, and public education initiatives will be crucial in preventing misuse and safeguarding vulnerable populations.
The research indicates that the secure and ethical development of LLMs will significantly influence how societies embrace artificial intelligence. Effective defense systems could safeguard financial infrastructures from phishing, combat medical misinformation, and uphold scientific integrity. Furthermore, watermark-based traceability and red-teaming may evolve into industry standards for model deployment. The researchers advocate for ongoing efforts toward responsible AI governance, unified regulatory frameworks, and improved model transparency reporting. If managed effectively, LLMs could develop into dependable tools that enhance education, digital healthcare, and innovation ecosystems while minimizing risks connected to cybercrime and social misinformation.
See also Generative AI Japan Awards 2025: COLOPL’s ‘Tsukuyomi’ Wins Grand Prix Among 8 Honorees
Generative AI Japan Awards 2025: COLOPL’s ‘Tsukuyomi’ Wins Grand Prix Among 8 Honorees Study Reveals Hidden Risks of Large Language Models: Phishing, Bias, and More
Study Reveals Hidden Risks of Large Language Models: Phishing, Bias, and More PlantIF Achieves 96.95% Accuracy in Plant Disease Diagnosis Using Multimodal Learning
PlantIF Achieves 96.95% Accuracy in Plant Disease Diagnosis Using Multimodal Learning Tsinghua and Shengshu Open-Source TurboDiffusion, Boosting AI Video Generation by 97×
Tsinghua and Shengshu Open-Source TurboDiffusion, Boosting AI Video Generation by 97×