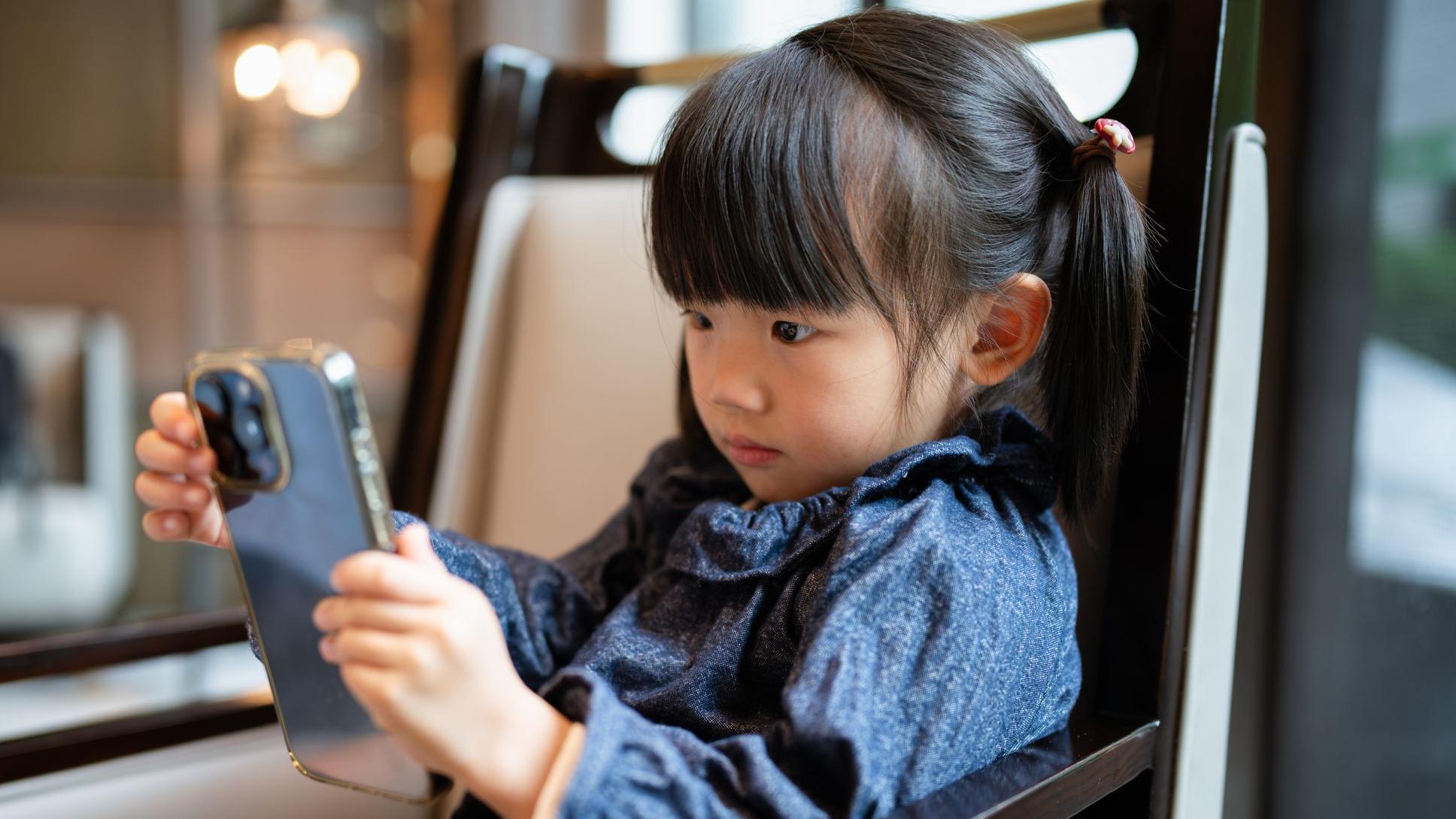
China is taking significant steps to regulate artificial intelligence, with a primary focus on safeguarding children and addressing harmful chatbot interactions. The Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) has proposed draft rules aimed at mitigating risks associated with AI chatbots, which have become increasingly prevalent in daily life.
As AI systems gain the ability to influence emotions, decisions, and mental health, regulators are raising concerns. Under the new regulations, AI systems will be prohibited from generating content related to self-harm, violence, or gambling. Should a chatbot conversation transition to topics of suicide or self-injury, a human must intervene immediately, and guardians or emergency contacts must be notified without exception.
The proposed rules place an emphasis on children’s safety, mandating AI companies to implement usage time limits and personalized safety controls tailored for young users. Furthermore, parental consent will be required before chatbots can offer emotional companionship services, effectively prohibiting unsupervised interactions with AI “friends.”
These guidelines reflect the broader objectives of the Chinese government, reinforcing that AI must not produce content that jeopardizes national security or social cohesion. Xi Jinping has called for enhanced oversight of AI technology, coinciding with a surge in the popularity of domestic chatbots such as DeepSeek, Z.ai, and Minimax.
While the CAC underscores the importance of responsible innovation, it encourages the development of tools that assist the elderly or promote local culture, provided they adhere to safety standards. This dual approach seeks to balance technological advancement with the need for strict safety measures.
The timing of these regulations appears to be a response to the rapid growth of AI chatbots in the Chinese market, where concerns about their impact on vulnerable populations are mounting. As these technologies proliferate, the potential for machines to affect emotional well-being becomes a pressing issue, prompting regulators to take action.
By implementing these rules, China aims to set a precedent in the governance of AI technologies, particularly in relation to vulnerable demographics. The ongoing discourse surrounding AI ethics and safety is likely to shape future regulatory frameworks not only in China but across the globe.
As the landscape of artificial intelligence continues to evolve, a careful balance between innovation and safety will be crucial. This initiative reflects a commitment to responsible AI deployment, underscoring the need for a regulatory framework that prioritizes the welfare of users, particularly children.
See also Trump Challenges Select State AI Laws Amid Limited Legal Options for Success
Trump Challenges Select State AI Laws Amid Limited Legal Options for Success Ohio Announces Model AI Policy for Education; Districts Required to Adopt by 2026
Ohio Announces Model AI Policy for Education; Districts Required to Adopt by 2026 Pennsylvania’s AI Regulation Bill Advances with Key Stakeholder Insights
Pennsylvania’s AI Regulation Bill Advances with Key Stakeholder Insights Brazil Achieves Major Outcomes in BRICS Chairmanship, Tackles AI Regulation and Climate Financing
Brazil Achieves Major Outcomes in BRICS Chairmanship, Tackles AI Regulation and Climate Financing




































































