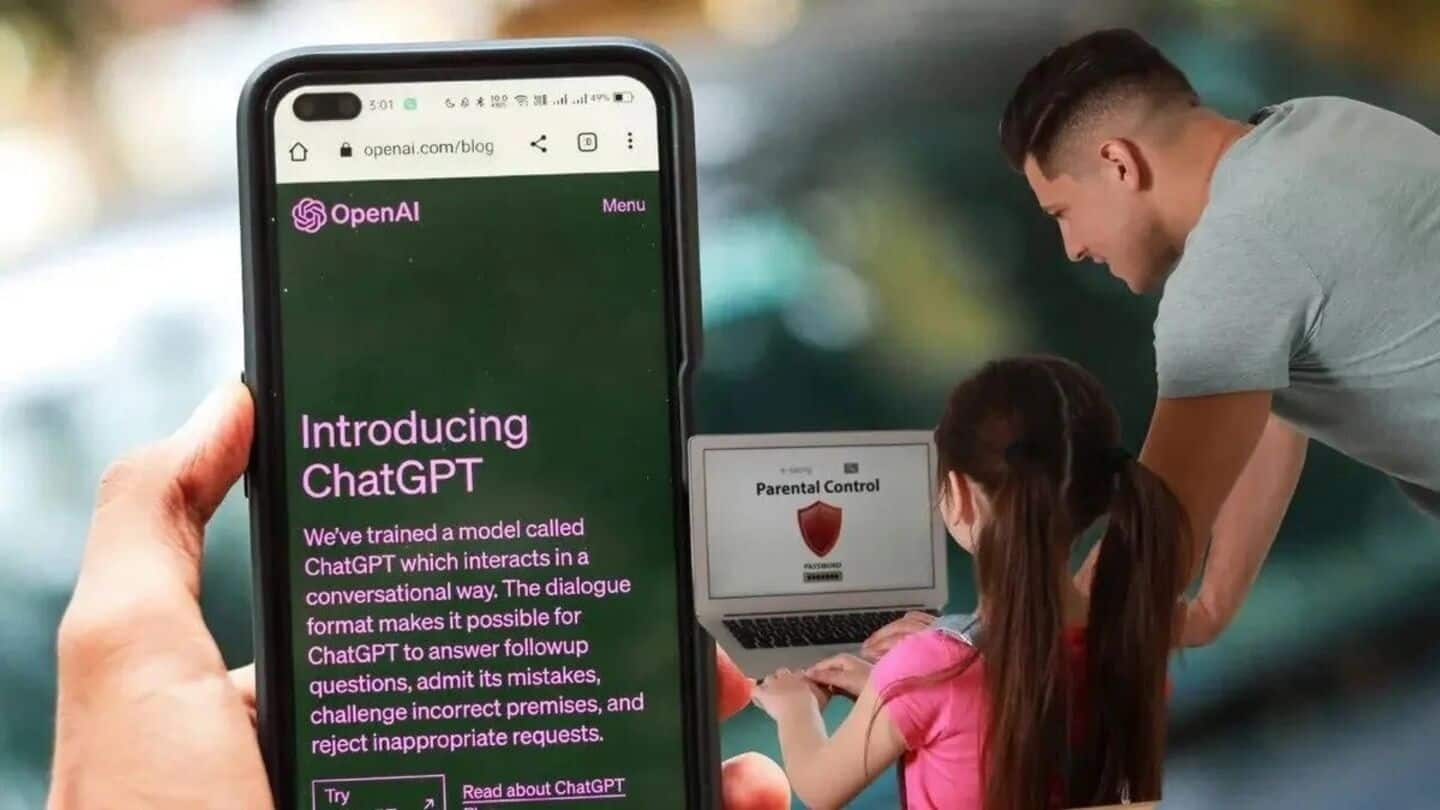
OpenAI has announced a revision of its guidelines regarding artificial intelligence (AI) interactions with users under the age of 18, a decision driven by increasing concerns over the well-being of young individuals engaging with AI chatbots. The updated guidelines aim to improve safety and transparency in the company’s offerings, particularly in light of tragic incidents involving teenagers and prolonged interactions with AI systems.
The revised Model Spec for OpenAI’s large language models (LLMs) introduces stricter regulations specifically for teen users, thereby enhancing protections compared to those applicable to adults. The new rules prohibit the generation of any sexual content related to minors, as well as the encouragement of self-harm, delusions, or mania. Furthermore, immersive romantic roleplay and violent roleplay, even if non-graphic, are also banned for younger users.
With a focus on safety, the guidelines highlight important issues such as body image and disordered eating behaviors. They instruct the models to prioritize protective communication over user autonomy in instances where there is potential for harm. For example, the chatbot is expected to explain its inability to participate in certain roleplays or assist with extreme changes to appearance or risky behaviors.
The safety practices for teen users are built on four core principles: placing teen safety above other user considerations; promoting real-world support by directing teens to family, friends, and local professionals; treating adolescents with warmth and respect; and maintaining transparency about the chatbot’s capabilities.
In addition to the revised guidelines, OpenAI has upgraded its parental controls. The company now employs automated classifiers to evaluate text, image, and audio content in real time, aiming to detect and block material related to child sexual abuse, filter sensitive subjects, and identify signs of self-harm. Should a prompt indicate serious safety concerns, a trained team will review the flagged content for indications of “acute distress,” potentially notifying a parent if necessary.
Experts suggest that OpenAI’s updated guidelines position it ahead of forthcoming legislation, such as California’s SB 243, which outlines similar prohibitions on chatbot communications about suicidal ideation, self-harm, or sexually explicit content. This bill also mandates that platforms remind minors every three hours that they are interacting with a chatbot and should consider taking a break.
The implementation of these guidelines reflects a broader initiative within the tech industry to prioritize user safety, particularly among vulnerable populations. As AI systems become increasingly integrated into everyday life, the ongoing evolution of regulatory frameworks will likely continue to shape the development and deployment of these technologies.
See also Egypt Advances Global AI Framework with UN Resolution for Telecom Development
Egypt Advances Global AI Framework with UN Resolution for Telecom Development New York Enacts RAISE Act for AI Safety, Mandating Transparency and Reporting Standards
New York Enacts RAISE Act for AI Safety, Mandating Transparency and Reporting Standards AI Regulation Looms as Anthropic Reveals 96% Blackmail Rates Amid Rapid Development
AI Regulation Looms as Anthropic Reveals 96% Blackmail Rates Amid Rapid Development Pegasystems Launches Agentic AI Upgrade, Enhancing Compliance for Financial Institutions
Pegasystems Launches Agentic AI Upgrade, Enhancing Compliance for Financial Institutions