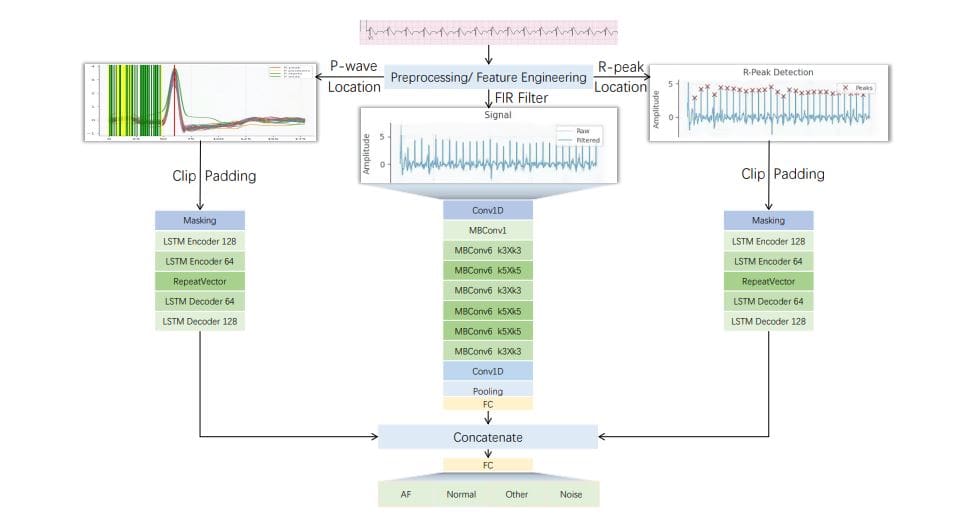
A research team led by Hanhui Deng from Hunan University has developed a new deep learning model named EfficientECG, aimed at enhancing the speed and accuracy of electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis. This advancement could significantly alleviate the workload on medical professionals by improving diagnostic capabilities for cardiac abnormalities such as arrhythmia and atrial fibrillation. The study, which includes contributions from Xinglin Li, Jie Luo, Zhanpeng Jin of the University at Buffalo, and Di Wu, was designed to address the limitations of current ECG analysis systems that often struggle with misdiagnoses.
EfficientECG is a lightweight classification model built on the EfficientNet architecture. The team incorporated a cross-attention feature fusion technique that allows the model to focus on the most relevant aspects of ECG signals while considering various patient characteristics. This innovation enables more comprehensive analyses of the data, leading to better diagnostic accuracy. The model was rigorously tested on established datasets, including the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database and the PhysioNet/Computing in Cardiology Challenge dataset, where it demonstrated superior performance relative to existing methods.
The primary goal of this research is to provide a model that can efficiently classify ECG signals, a critical component in the early detection and treatment of heart conditions. Researchers utilized advanced techniques such as squeeze-and-excitation networks to enhance feature representation while employing EfficientNet for improved scalability and efficiency. By leveraging these technologies, the team developed a system capable of handling complex, high-frequency ECG data, thereby addressing one of the significant challenges faced by current diagnostic models.
The study emphasizes the model’s ability to analyze multi-lead ECG data in conjunction with patient attributes like age and gender. This holistic approach allows for more informed diagnoses by incorporating a broader range of information. The EfficientECG model not only captures subtle patterns indicative of cardiac issues but also excels in real-time applications, making it suitable for deployment in resource-constrained environments.
EfficientECG’s architecture has been optimized to process high-frequency, long-sequence ECG data, which is often challenging for traditional models. The combination of cross-attention mechanisms and feature fusion results in a robust framework that significantly improves classification metrics. Evaluations of the model across three authoritative ECG datasets confirm its high precision and efficiency, showcasing improvements in both the total number of parameters and performance outcomes compared to state-of-the-art methods.
This research marks a significant step forward in the application of deep learning technologies to healthcare challenges. The team conducted detailed ablation studies to validate the contributions of each component in the multi-feature fusion model, ensuring that every aspect of EfficientECG is optimized for maximum performance. Looking ahead, future work will focus on further adapting the model to include a broader range of ECG features and refining training and inference methods to enhance its efficiency and effectiveness in real-time cardiac diagnosis.
The potential impact of EfficientECG extends beyond improved diagnostic accuracy; it also aims to lessen the burden on healthcare professionals, thereby improving patient care outcomes. As technologies like deep learning continue to evolve, their integration into clinical settings could revolutionize how cardiac abnormalities are detected and monitored, paving the way for more personalized and efficient healthcare solutions.
👉 More information
🗞 EfficientECG: Cross-Attention with Feature Fusion for Efficient Electrocardiogram Classification
🧠 ArXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.03804
 Apple Reveals M4 Chip with 38 Trillion Operations/Second, Boosting iPad AI Performance
Apple Reveals M4 Chip with 38 Trillion Operations/Second, Boosting iPad AI Performance Titans and MIRAS Combine RNN Speed with Transformer Accuracy for Real-Time AI Memory
Titans and MIRAS Combine RNN Speed with Transformer Accuracy for Real-Time AI Memory Stanford Dropout Carina Hong Raises $64M, Attracts Top Meta AI Talent to Axiom Math
Stanford Dropout Carina Hong Raises $64M, Attracts Top Meta AI Talent to Axiom Math Trump’s Executive Order Launches AI Initiative to Accelerate Scientific Discovery
Trump’s Executive Order Launches AI Initiative to Accelerate Scientific Discovery