A comprehensive review published in the journal Agriculture has highlighted the rapid advancement of machine learning in the agricultural sector, while also revealing significant gaps in sustainability integration and collaboration networks. The study, titled “A Bibliometric Review of Machine Learning for Sustainable Agri-Food Systems: Evolution, Collaboration Networks, and Future Directions,” analyzes 648 scientific papers indexed in Scopus between 2010 and 2025, underscoring both the growth of research and the challenges that remain in digital farming.
The bibliometric analysis indicates that research output in this field has seen exponential growth over the past decade, particularly after 2018, with a sharp peak around 2020–2021. This surge is driven by heightened global concerns regarding climate change, food security, and resource efficiency, coupled with advancements in data accessibility, sensor technology, and computational power. The field is primarily rooted in computer science and engineering, with machine learning applications frequently targeting optimization, predictive modeling, and automation tasks.
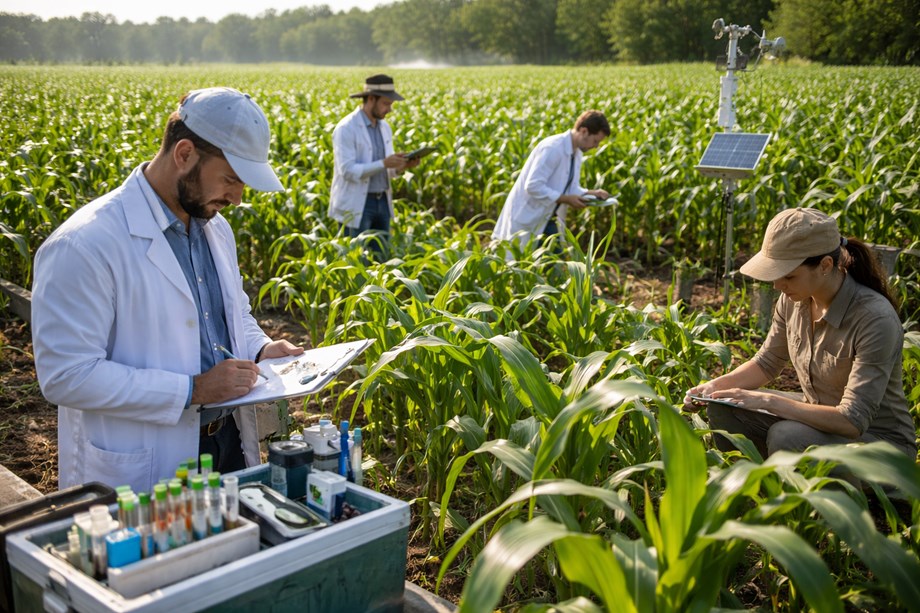
Key focal areas include crop yield prediction, pest and disease detection, irrigation management, and soil monitoring, with precision agriculture standing out as a central theme. Technologies utilizing algorithms trained on satellite imagery and sensor data are being implemented to enhance fertilizer application, optimize water usage, and refine harvest planning. This technological shift promises reductions in input waste while boosting resource efficiency and farm profitability.
Moreover, the review identifies a robust research interest in supply chain optimization. Machine learning models are now increasingly employed to forecast demand, minimize post-harvest losses, and streamline logistics. As food systems worldwide grow more interconnected, predictive analytics are expected to play a crucial role in improving resilience against disruptions.
However, the authors caution that many studies prioritize technical performance metrics rather than systemic sustainability outcomes. While improvements in accuracy rates and optimization gains are often documented, there is a notable scarcity of studies assessing long-term environmental or socio-economic impacts.
Geographically, the research landscape is predominantly led by China and India, which have made substantial investments in digital agriculture initiatives and artificial intelligence infrastructure. This rapid output corresponds with increasing domestic demands for modernization in food systems and climate adaptation strategies. Yet, the United States and European institutions frequently emerge as influential players when considering citation impact and international collaboration. Research produced through cross-border partnerships tends to yield higher visibility and broader knowledge dissemination.
Despite this, the bibliometric mapping reveals uneven collaboration, with many studies remaining confined to national silos and limited integration across regions. Developing countries facing significant agricultural sustainability challenges often lack representation in high-impact collaborative networks. Strengthening international research alliances could foster innovation and enhance contextual relevance, as agricultural practices are profoundly influenced by regional factors like climate conditions, soil characteristics, and socio-economic structures.
Patterns of institutional collaboration also expose fragmentation between technology-focused research communities and sustainability science networks. Researchers engaged in computer science frequently emphasize algorithmic efficiency, while agricultural and environmental scientists prioritize ecological impacts. Bridging this divide presents a key challenge for advancing machine learning applications in agriculture.
While machine learning is frequently positioned as a solution for agricultural sustainability, the review finds that environmental and social dimensions are inconsistently woven into research designs. Areas such as climate resilience, biodiversity conservation, equity, and governance receive less attention compared to production optimization. The authors argue for the development of more comprehensive analytical tools, including life-cycle assessments and systems-level modeling, to fully evaluate the environmental footprint of AI-driven agriculture.
Social sustainability aspects also remain insufficiently explored, with few studies addressing the accessibility and benefits of machine learning technologies for smallholder farmers. Issues of affordability, digital literacy, and rural infrastructure often languish in technical discussions. Climate adaptation, while increasingly recognized as essential, remains a fragmented area, as the integration of long-term climate risk scenarios into agricultural AI systems continues to evolve.
Additionally, the review notes that interdisciplinary collaboration is limited. Future research should integrate agronomy, environmental science, economics, and data science to ensure that machine learning applications align with sustainable development goals rather than merely enhancing efficiency. The authors indicate that the field may be entering a maturation phase following a period of rapid publication growth, with a shift toward more focused refinement.
Looking ahead, the next stage of machine learning in agriculture will hinge on transcending isolated optimization tasks and fostering systemic transformation. The integration of AI tools into broader sustainability frameworks, enhancement of cross-border collaboration, and the incorporation of social and ecological considerations into model development will be vital in determining the long-term resilience of digital agriculture.
See also AI Study Reveals Generated Faces Indistinguishable from Real Photos, Erodes Trust in Visual Media
AI Study Reveals Generated Faces Indistinguishable from Real Photos, Erodes Trust in Visual Media Gen AI Revolutionizes Market Research, Transforming $140B Industry Dynamics
Gen AI Revolutionizes Market Research, Transforming $140B Industry Dynamics Researchers Unlock Light-Based AI Operations for Significant Energy Efficiency Gains
Researchers Unlock Light-Based AI Operations for Significant Energy Efficiency Gains Tempus AI Reports $334M Earnings Surge, Unveils Lymphoma Research Partnership
Tempus AI Reports $334M Earnings Surge, Unveils Lymphoma Research Partnership Iaroslav Argunov Reveals Big Data Methodology Boosting Construction Profits by Billions
Iaroslav Argunov Reveals Big Data Methodology Boosting Construction Profits by Billions