Researchers at Lomonosov Moscow State University and Irkutsk National Research Technical University have made significant strides in theoretical chemistry by developing advanced machine-learning interatomic potentials that simulate chemical reactions with unprecedented accuracy. Led by Ivan V. Dudakov and Pavel M. Radzikovitsky, the team’s work focuses on the intricate behaviors of atoms during chemical transformations, a crucial aspect of understanding molecular dynamics, particularly in photochemical reactions. Their findings, detailed in a recent publication, promise to enhance both the precision and efficiency of simulations in ultrafast photodynamics.
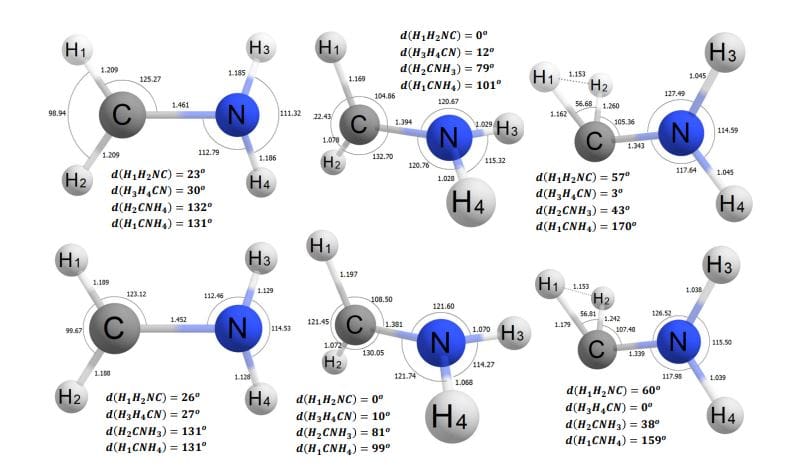
The study highlights a novel wavepacket oscillation model characterized by power-law decay. This model provides a clearer connection between fundamental quantum calculations and observed reaction rates. The researchers have demonstrated its utility by mapping the potential energy landscape of the methaniminium cation, revealing the various pathways that molecules can follow after absorbing light.
In addressing the challenges associated with simulating excited-state dynamics, the researchers employed a transfer learning approach to construct machine-learning interatomic potentials. By leveraging a limited set of precise quantum chemistry calculations, they succeeded in creating models that accurately predict energy and forces in complex molecular systems, significantly reducing the computational resources required for such simulations. This advancement allows scientists to explore larger and more complex photochemical reactions than previously feasible.
Accurate modeling of photochemical reactions hinges on understanding transitions between electronic states. Traditionally, this has been a computationally expensive endeavor, but the new machine-learning models reduce this burden. The potential energy surfaces generated by these models have shown a remarkable ability to reproduce reference data while maintaining good transferability across different molecular configurations and chemical environments.
Implications for Molecular Dynamics
The implications of this research extend into the realm of molecular photochemistry, where understanding the response of molecules to light is essential. Using precise quantum chemical calculations, the team simulated how molecules evolve on their potential energy surfaces after photon absorption. The combination of high-level quantum calculations and machine learning facilitates a more efficient exploration of molecular dynamics, allowing researchers to obtain reliable insights into photochemical pathways and energy dissipation mechanisms. Techniques such as Gaussian Process Regression and Deep Ensembles were employed to quantify and assess the reliability of the predictions made by these models.
One notable application of the research is in photodissociation mapping, where the team constructed highly accurate machine-learning interatomic potentials that rival advanced theoretical methods. This achievement enables high-level simulations of nonadiabatic dynamics that start in an excited state. The researchers mapped competing decay channels, including photoisomerization and hydrogen loss, providing a comprehensive understanding of the photodissociation landscape for specific molecules.
Moreover, the introduction of the wavepacket oscillation model enhances the interpretability of quantum transition probabilities in terms of classical rate constants. This breakthrough allows for a state-specific analysis of lifetimes derived from first-principles population dynamics, thus offering a clear mechanistic understanding of reactions. The study’s findings indicate that incorporating uncertainty corrections from an ensemble of models improves the agreement between different simulation approaches, underscoring the importance of quantifying uncertainty in complex chemical modeling.
The work also validates a newly discovered photochemical pathway facilitated by a novel conical intersection. This pathway had previously remained elusive, but the researchers successfully resolved a channel-specific lifetime for it, advancing the understanding of how certain reactions occur at the quantum level.
Overall, the contributions from Dudakov, Radzikovitsky, and their colleagues represent a significant step forward in the field of theoretical chemistry. Their framework for constructing accurate machine-learning potentials, alongside a robust mapping of photodissociation mechanisms, positions researchers to better understand and simulate ultrafast photochemical processes. As computational methods continue to evolve, the integration of machine learning into molecular dynamics promises to reveal new insights and applications in chemistry, potentially transforming how scientists approach complex reactions in the future.
👉 More information
🗞XMCQDPT2-Fidelity Transfer-Learning Potentials and a Wavepacket Oscillation Model with Power-Law Decay for Ultrafast Photodynamics
🧠 ArXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.07537
 Google Integrates Gemini AI into Search and Assistant, Enhancing User Experience with Smart Summaries
Google Integrates Gemini AI into Search and Assistant, Enhancing User Experience with Smart Summaries Kenya Achieves Historic UN Resolution on AI’s Environmental Sustainability at UNEA-7
Kenya Achieves Historic UN Resolution on AI’s Environmental Sustainability at UNEA-7 Purdue University Launches AI Working Competency Requirement for All Undergraduates
Purdue University Launches AI Working Competency Requirement for All Undergraduates UAE Advances AI in Life Sciences with National Genome Strategy and $10B Investment by 2031
UAE Advances AI in Life Sciences with National Genome Strategy and $10B Investment by 2031 Verigram Unveils Machine Learning Model to Detect Virtual Camera Attacks in Biometric Systems
Verigram Unveils Machine Learning Model to Detect Virtual Camera Attacks in Biometric Systems