Artificial intelligence (AI) and supercomputing are catalyzing unprecedented advancements in scientific discovery, as evidenced by the collaboration between the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and Dell Technologies Inc. Their joint effort has culminated in the development of Doudna, a sophisticated computing system that promises a tenfold increase in performance for complex scientific workflows.
Technical Details
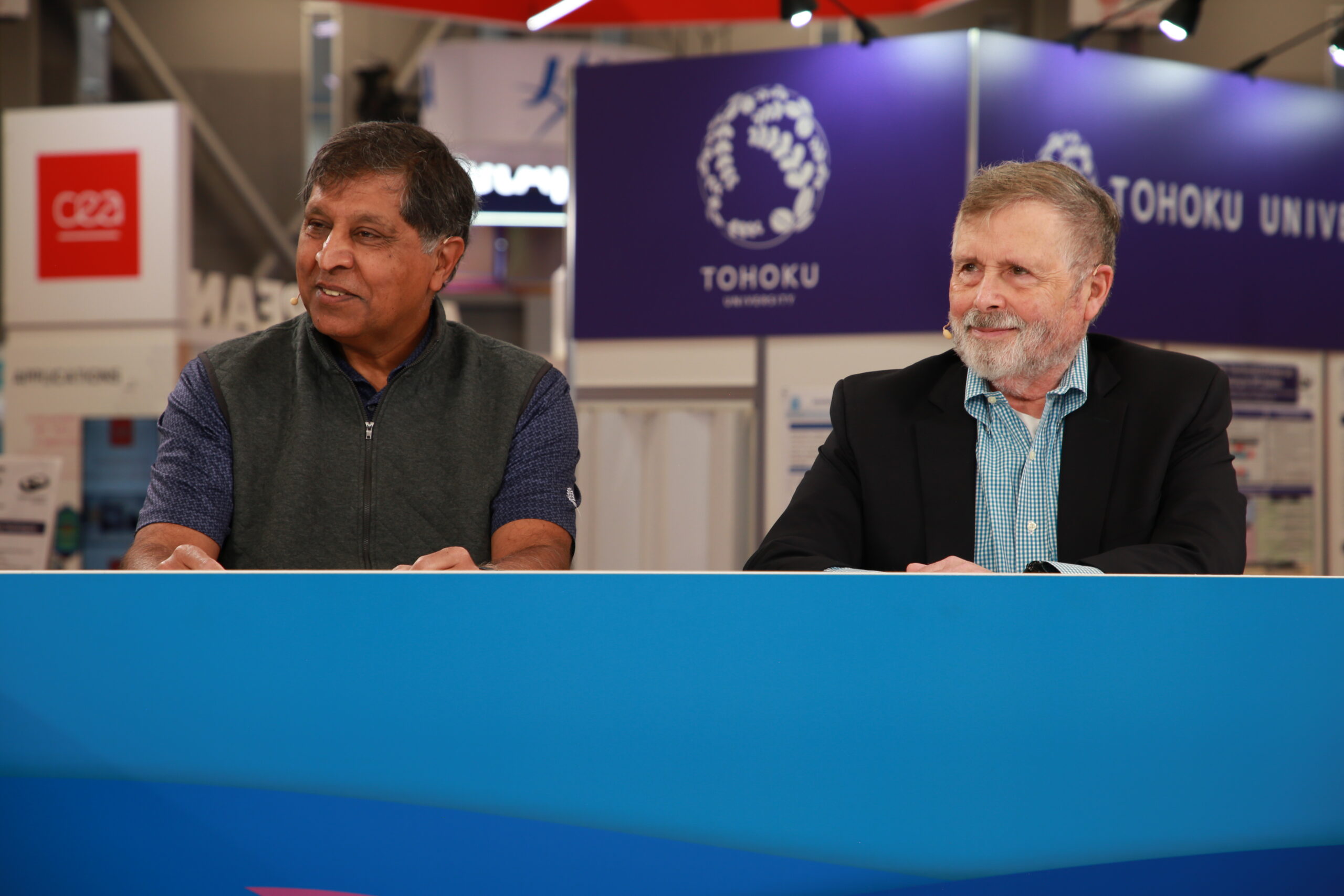
Doudna is built upon Nvidia’s Vera Rubin platform and integrates with Dell’s IR7000 rack, utilizing a water-cooling system to enhance sustainability. This innovative design reflects a commitment to energy efficiency, especially critical given NERSC’s operational context in Northern California, where water conservation is essential. The system is being strategically deployed to accommodate over 11,000 users, necessitating a collaborative approach as articulated by Sudip Dosanjh, the scientific division director at NERSC.
AI functionalities are incorporated into Doudna, particularly through the use of machine analytics for real-time data analysis. Dosanjh emphasizes that while AI is a central component, the main focus lies in orchestrating complex workflows. This capability is crucial for dynamic scientific experimentation. For instance, when operating a telescope, the system must provide rapid feedback to adjust focus based on incoming data streams. This responsiveness could significantly enhance experimental outcomes, allowing researchers to make timely adjustments.
The system’s architecture is designed to manage the increasing granularity and resolution of data from various scientific instruments, addressing the growing challenge of data deluge in contemporary research. Rea points out that the annual escalation in data output renders traditional modeling and simulation techniques insufficient, thus necessitating the advanced capabilities of Doudna.
Research Significance
By enabling the harmonization of large datasets and facilitating complex workflows, Doudna represents a paradigm shift in scientific computing. It exemplifies how AI can be leveraged to not only improve the efficiency of data processing but also enhance the quality of insights derived from data analysis. The collaboration between NERSC and Dell signifies a broader trend in the industry where the barriers to entry for scientific research are being lowered. This democratization of access to computational resources is empowering a wider array of researchers to engage in high-level scientific inquiry.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain. As Dosanjh notes, deploying Doudna requires meticulous planning to ensure that the capabilities meet the needs of a diverse user community. While the potential for increased productivity is significant, achieving seamless integration into existing workflows is a critical concern. Moreover, the transition to using dry chillers, while beneficial for water conservation, brings with it a slight decrease in energy efficiency that must be managed.
Context in the AI Research Landscape
The emergence of Doudna aligns with the broader movement toward integrating AI in scientific research, a trend epitomized by the increasing reliance on large-scale computing systems to process and analyze expansive datasets. This development is particularly relevant in fields such as climate science, genomics, and materials science, where the complexity and volume of data continue to grow. The collaboration between NERSC and Dell not only enhances computational power but also signifies a strategic move toward more sustainable computing practices in the face of environmental concerns.
Furthermore, this initiative reflects a growing recognition of the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing scientific discovery. By combining the expertise of computational scientists with industry leaders like Dell, NERSC is setting a precedent for how scientific institutions can harness technological advancements to drive innovation. The implications of this work extend beyond immediate computational enhancements; it positions NERSC as a pivotal player in the future landscape of scientific research, where AI and supercomputing converge.
Overall, the Doudna project showcases the potential of cutting-edge technology to accelerate scientific discovery. As researchers increasingly integrate AI into their methodologies, the pace of innovation is expected to continue its upward trajectory, fundamentally reshaping the scientific enterprise.
For further insights, the complete video interview featuring Dosanjh and Rea at SC25 can be accessed through SiliconANGLE’s and theCUBE’s coverage.
See also Nvidia Reports $10B Revenue Growth as Supply Chain Breakthrough Signals AI Demand Surge
Nvidia Reports $10B Revenue Growth as Supply Chain Breakthrough Signals AI Demand Surge SharkNinja Launches AI and Analytics Lab in Partnership with Boston University
SharkNinja Launches AI and Analytics Lab in Partnership with Boston University AI Tool Predicts Civil Unrest in India by Analyzing News Mentions and Events
AI Tool Predicts Civil Unrest in India by Analyzing News Mentions and Events Brown University Launches $20M AI Institute to Revolutionize Mental Health Care
Brown University Launches $20M AI Institute to Revolutionize Mental Health Care AI Model Achieves 95% Accuracy in Cardiovascular Disease Prediction Using Longitudinal Data
AI Model Achieves 95% Accuracy in Cardiovascular Disease Prediction Using Longitudinal Data