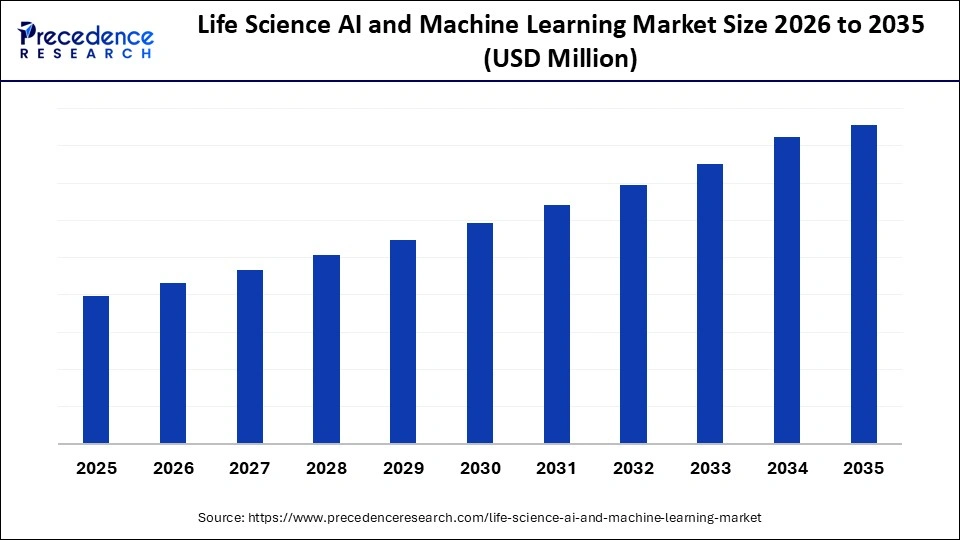
Middle Eastern and African governments are actively fostering digital health initiatives and enhancing the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in the life sciences sector. This push is exemplified by national programmes aimed at generating structured, research-grade datasets that can drive innovation in healthcare. Notably, Saudi Arabia is advancing the **Saudi Human Genome Program**, which focuses on sequencing large population cohorts to provide variant data for machine learning-driven biomarker discovery and disease risk models. Similarly, the **UAE** is implementing the **National Genome Strategy** in tandem with the **Abu Dhabi Genome Program**, both designed to integrate genomic sequencing with hospital information systems, thereby creating datasets that support AI-enabled clinical decision-making tools. Qatar is also expanding the **Qatar Genome Programme**, linking whole genome data with phenotypic records to train predictive models for hereditary and metabolic diseases.
In addition to these genome initiatives, governments are promoting biotechnology research through state-backed centres specializing in molecular biology, vaccine development, and sequencing. For instance, South Africa’s **Medical Research Council Genomics Centre** utilizes high-throughput sequencing to bolster infectious disease surveillance and computational biology studies. Egypt’s **Human Genome Project** further contributes to a repository of standardized genomic data aimed at AI-assisted variant interpretation and precision medicine. As these programmes scale, they significantly increase the volume of structured clinical and genomic information available for training AI systems across the region.
The **UAE** has emerged as a pivotal player in the region, prioritizing rapid advancements in AI integration, genomic science, and comprehensive digital health modernization. Launched in 2023, the **National Genome Strategy** and the **Abu Dhabi Genome Program** initiated in 2021 are at the heart of this evolution. These initiatives generate population-scale sequencing data and embed genomic insights into clinical workflows across hospitals in **Abu Dhabi** and **Dubai**. The **Artificial Intelligence Strategy 2031**, announced in 2017, provides the necessary policy framework to guide the deployment of machine learning tools in healthcare, research, and public health surveillance.
The UAE also acts as a hub for multinational biotechnology collaborations, with research institutions in **Abu Dhabi** and **Dubai** partnering with global firms to develop algorithms for genomic interpretation, oncology biomarker analysis, and computational drug discovery. Projects associated with the **Mohammed Bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences**, the **NYU Abu Dhabi Genome Technology Center**, and the **Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi** support AI-assisted modeling in critical areas such as hereditary blood disorders, metabolic diseases, and rare disease diagnostics. These collaborations enhance the region’s capabilities in addressing complex health challenges through innovative technology.
Looking ahead, the strategic initiatives in the UAE and other Middle Eastern and African nations signal a transformative shift in healthcare driven by genomic science and AI. As more structured data becomes available, the potential for AI to personalize medicine and improve patient outcomes is immense. The ongoing investment in digital health technologies, coupled with a collaborative approach to biotechnology research, positions the region to become a leader in precision medicine and health innovation on a global scale.
See also Verigram Unveils Machine Learning Model to Detect Virtual Camera Attacks in Biometric Systems
Verigram Unveils Machine Learning Model to Detect Virtual Camera Attacks in Biometric Systems Google Launches Gemini Deep Research API as OpenAI Reveals Powerful GPT-5.2 Model
Google Launches Gemini Deep Research API as OpenAI Reveals Powerful GPT-5.2 Model Machine Learning Enhances Lumbar Disc Degeneration Classification, Promises Personalized Treatment
Machine Learning Enhances Lumbar Disc Degeneration Classification, Promises Personalized Treatment TCU Launches $10M AI² Initiative with Dell to Expand AI Research and Education
TCU Launches $10M AI² Initiative with Dell to Expand AI Research and Education