As the demand for artificial intelligence (AI) surges in the United States and China, both nations must navigate the complexities of energy generation to maintain their technological edge. The geopolitical rivalry intensifies as each country seeks to expand its energy access while managing the implications of their choices on global markets, infrastructure, and supply chains.
A recent forum by the Global China project gathered a diverse group of experts to explore how rising energy demand will influence AI development and the geopolitical landscape. Key questions arose about the nature of U.S.-China competition, the strategic importance of energy partnerships in emerging regions, and whether the U.S. should welcome or restrict Chinese investments in its clean energy sector.
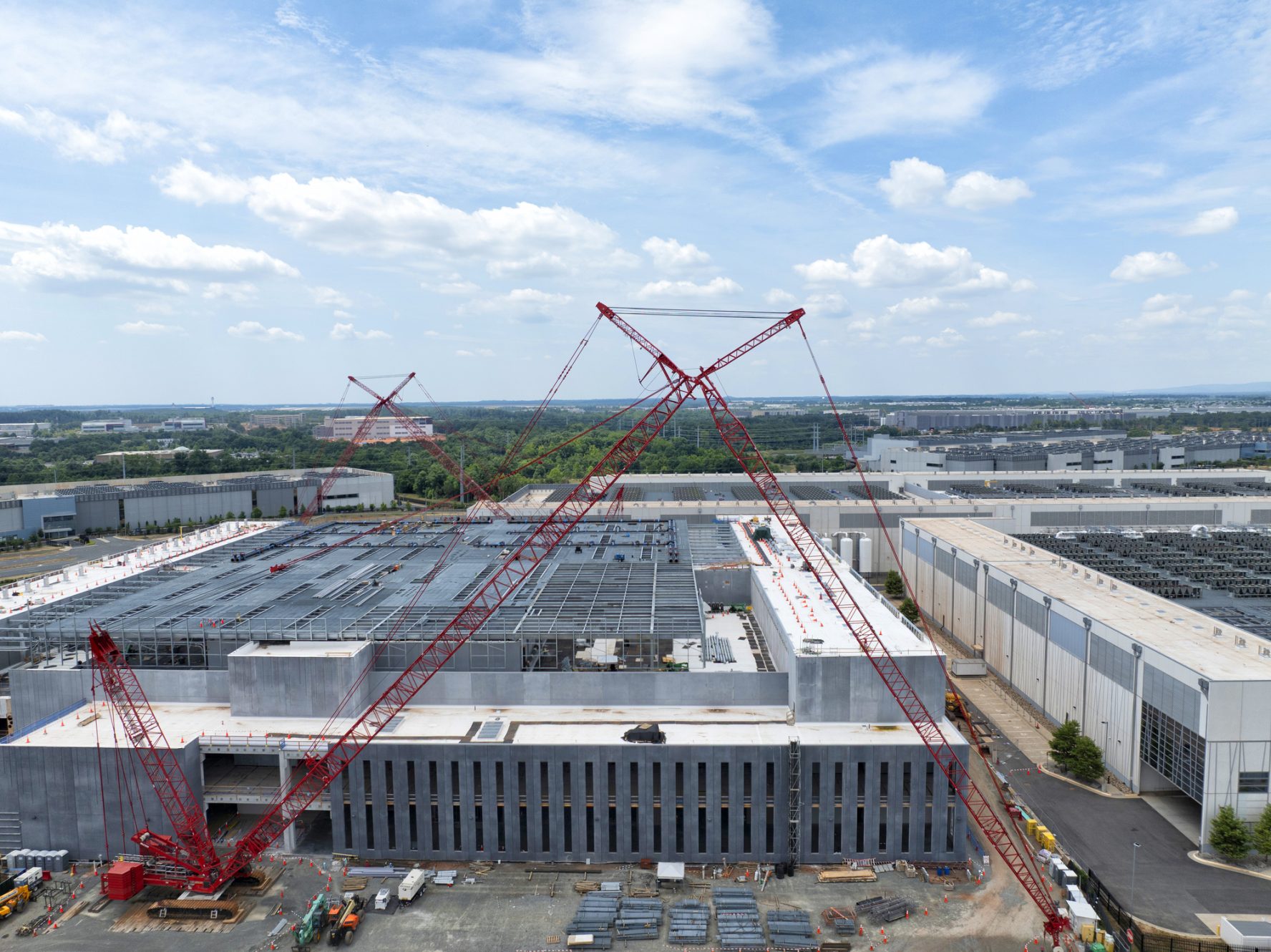
Kyle Chan highlighted that while the U.S. leads in AI semiconductor technology, China holds a significant advantage in energy. This “electron gap” poses potential challenges for U.S. firms as they face a bottleneck in energy supply for data centers. The International Energy Agency predicts U.S. electricity demand from data centers will exceed 426 terawatt-hours (TWh) by 2030, accounting for about 9% of total electricity demand. In contrast, China’s demand for data centers is projected to reach around 277 TWh in the same time frame, supported by a robust and rapidly expanding energy infrastructure.
Samantha Gross emphasized the urgency within the AI sector, noting that data centers now require up to one gigawatt of electricity—equivalent to the power needed for a small city. The speed of infrastructure development is critical, with China’s capacity for rapid construction potentially giving it an edge in the race for AI infrastructure. While the U.S. grapples with increasing demand after two decades of flat electricity use, China has consistently increased its power generation, with over half of that coming from clean sources.
David Victor provided a broader context, arguing that the energy demands of AI, while significant, will not alone redefine the geopolitical landscape. He pointed out that the competition lies more in how AI technology is applied economically and militarily. While both nations have access to inexpensive energy, the exact impact of energy demand on geopolitical dynamics remains uncertain, especially as AI technology continues to evolve.
As both countries forge new energy partnerships worldwide, Chan noted China’s global strategy includes investing in renewable energy projects, such as solar plants in Saudi Arabia and offshore wind farms in Laos. These initiatives position China as a formidable player in the AI infrastructure landscape, directly competing with American cloud service providers. Meanwhile, the U.S. is leveraging its strengths by supplying advanced AI chips to foreign data centers, exemplified by the “Stargate UAE” project in Abu Dhabi.
In considering China’s dominance in clean energy technology, Chan argued that China’s extensive investments have made clean energy products more accessible and affordable. This presents an opportunity for the U.S. to reduce energy constraints in its data center operations. As China expands its clean energy manufacturing capabilities, the U.S. could find itself reliant on Chinese solar panels and batteries for supplemental energy needs.
However, Gross identified significant challenges in rapidly meeting electricity demand for AI. She pointed to natural gas as a viable option in the U.S., given its abundance and low prices, but stressed that renewable energy sources like solar power offer a faster deployment timeline. Yet, with China controlling much of the solar manufacturing, this presents a strategic vulnerability for the U.S., which may need to explore other energy options if prices rise or supply issues arise.
The conversation also turned to the implications of Chinese investment in U.S. clean energy technology. Chan suggested that with appropriate safeguards, Chinese investment could alleviate domestic energy bottlenecks, recommending joint ventures that allow U.S. firms to maintain control over sensitive technologies. However, Liza Tobin cautioned against Chinese investment, arguing that China’s strategic intentions differ fundamentally from those of Japan in the 1980s. She likened potential investments to inviting adversaries to co-develop critical technologies, underscoring the risks of allowing China further access to U.S. infrastructure.
As the U.S. and China navigate these complex dynamics, the intersection of energy needs and AI advancement will continue to evolve, with significant implications not just for the two nations, but for global technological leadership and economic stability.
See also Acer Launches Gaming Monitor and AI Laptops to Boost Revenue Amid Component Challenges
Acer Launches Gaming Monitor and AI Laptops to Boost Revenue Amid Component Challenges Nvidia, AMD, Intel Launch New AI Chips; Lego Reveals Smart Building Blocks at CES 2026
Nvidia, AMD, Intel Launch New AI Chips; Lego Reveals Smart Building Blocks at CES 2026 Brookfield Signals 2026 Shift: AI Fuels $10B Infrastructure Investment Strategy
Brookfield Signals 2026 Shift: AI Fuels $10B Infrastructure Investment Strategy AI Revolutionizes Job Market: 70% of Companies Deploy AI Beyond Pilot Stage
AI Revolutionizes Job Market: 70% of Companies Deploy AI Beyond Pilot Stage India Partners with Nvidia to Develop Sovereign GPUs for Local AI Infrastructure
India Partners with Nvidia to Develop Sovereign GPUs for Local AI Infrastructure