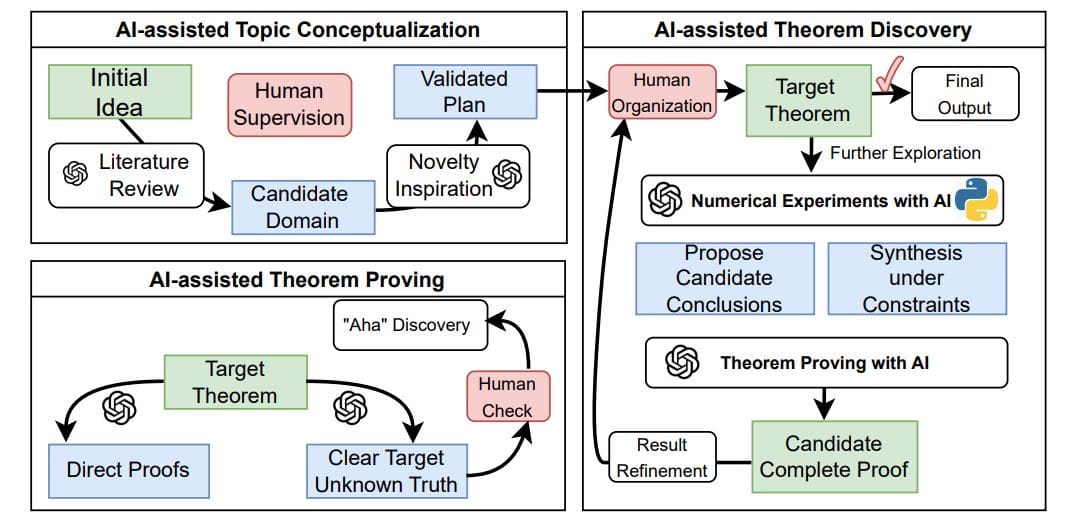
Researchers from the Beijing International Center for Mathematical Research at Peking University are pioneering a collaborative approach that harnesses the capabilities of artificial intelligence (AI) to expedite mathematical proof discovery. Led by Chenyi Li and Zhijian Lai, along with colleagues Dong An, Jiang Hu, and Zaiwen Wen, their innovative workflow integrates human expertise with large language models (LLMs). The system allows mathematicians to retain control over core problem logic while the AI explores potential proofs, suggests new properties, and constructs solutions that meet precise criteria.
This collaboration is particularly significant given the complexity of mathematical proofs, which often require both creativity and meticulous verification. The team successfully tested their framework on challenging problems that intertwine manifold optimization and Grover’s search algorithm. Their findings could not only accelerate mathematical discoveries but also enhance algorithm design, all while maintaining the rigorous transparency necessary for scientific progress.
In conjunction with this approach, scientists are achieving faster convergence rates in specific optimization algorithms, particularly in Riemannian gradient descent. By focusing on functions defined on unitary matrices, researchers have identified that analyzing the functions’ behavior allows for a more efficient search for optimal solutions. This research establishes a stronger link between a function’s value and the size of its gradient, significantly improving convergence speed and potentially lessening the computational effort required to solve complex optimization problems.
Moreover, the integration of large language models into mathematical research is transforming how theorem proving is conducted. The new system emphasizes a human-in-the-loop approach, where experts control problem formulation and acceptable assumptions, while the LLM engages in searching for proofs and identifying contradictions. This symbiotic relationship empowers researchers to refine AI-generated outputs into formal statements and rigorous proofs.
A notable case study exemplifying this integration connected manifold optimization with Grover’s quantum search algorithm, revealing invariant subspaces and examining Grover-compatible retractions. The experiments conducted demonstrated the pipeline’s ability to deliver convergence guarantees for the retraction-based gradient method, an essential breakthrough in optimizing complex systems. This framework facilitates a significant shift in mathematical research, promising a more efficient theorem-proving process.
This new workflow encompasses three critical stages of research: conceptualizing topics with AI assistance, goal-oriented proving for well-defined targets, and open-ended theorem discovery when the final conclusions remain uncertain. By melding human ingenuity with advanced computational power, researchers are redefining the landscape of mathematical exploration.
The implications of these advancements are profound. As AI continues to evolve, its role in mathematical research could lead to unprecedented efficiencies in discovery and validation. This fusion of human expertise with AI capabilities not only augments the mathematical toolkit but also sets the stage for future breakthroughs in both theoretical and applied mathematics.
With ongoing developments in AI and its integration into complex fields like mathematics, the potential for accelerated discoveries may redefine how scholars approach problem-solving in the years to come. The collaboration between AI and human researchers stands as a testament to the promise of technology in enhancing intellectual pursuits.
Peking University,
Beijing International Center for Mathematical Research,
Microsoft,
IBM,
Nvidia
 Trump’s Executive Order Centralizes AI Regulation, Sparks Controversy Over Safety and Innovation
Trump’s Executive Order Centralizes AI Regulation, Sparks Controversy Over Safety and Innovation AI Stocks Drop 1.69% as Broadcom, Oracle Spark Profitability Concerns Amid Rising Costs
AI Stocks Drop 1.69% as Broadcom, Oracle Spark Profitability Concerns Amid Rising Costs Bloom Energy (BE) Plummets 10% Amid AI Infrastructure Selloff Post-Oracle Update
Bloom Energy (BE) Plummets 10% Amid AI Infrastructure Selloff Post-Oracle Update AI’s Energy Demands Threaten U.S. Infrastructure and Market Stability Amid Growing Vulnerabilities
AI’s Energy Demands Threaten U.S. Infrastructure and Market Stability Amid Growing Vulnerabilities Google DeepMind Launches Gemini AI Lab in UK to Accelerate New Materials Discovery by 2026
Google DeepMind Launches Gemini AI Lab in UK to Accelerate New Materials Discovery by 2026