By Evan Pickworth
In a recent episode of Business Law Focus for 2026, Johan Steyn, a human-centred AI advocate and founder of AIforBusiness.net, highlighted the dual nature of artificial intelligence (AI) within the legal profession. While AI tools like ChatGPT are being increasingly adopted to enhance efficiency and streamline processes, Steyn cautioned against the risks associated with relying on unverified outputs, particularly as they pertain to the integrity of legal work.
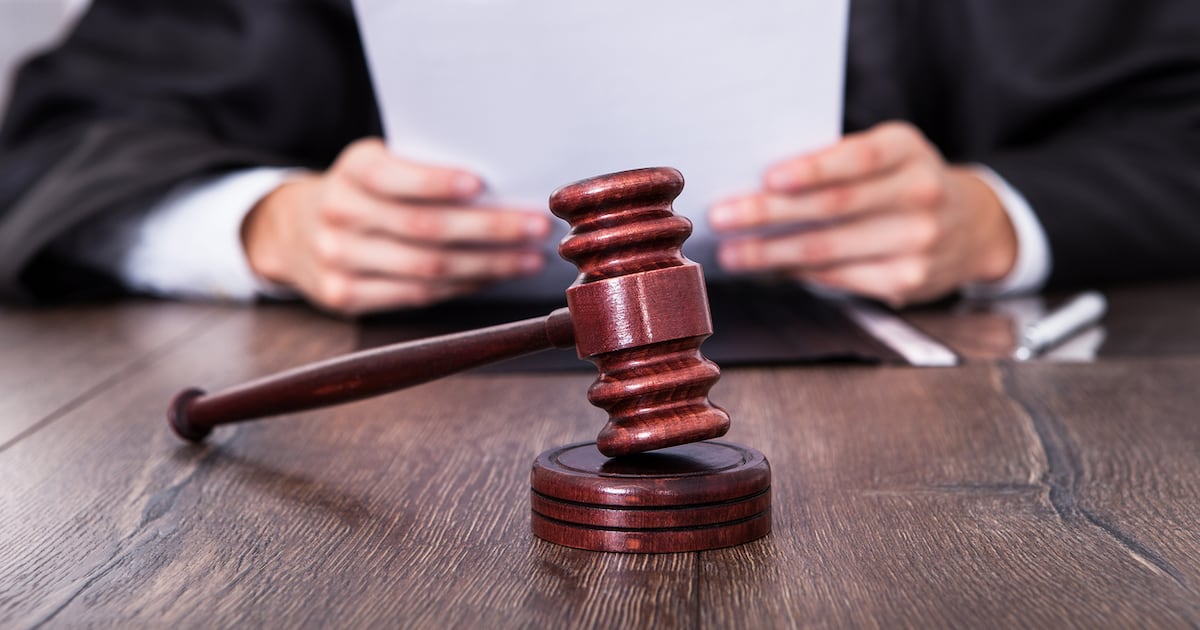
As legal professionals increasingly integrate AI into their operations, there is a growing concern about the ethical implications of using such technology as a shortcut rather than a support mechanism. Recent South African court cases have brought these risks to the forefront, with judges admonishing legal teams for submitting documents containing fabricated citations generated by AI. These incidents serve as a stark reminder that while AI can assist in legal tasks, it cannot substitute for the essential human elements of judgment and accountability.
Steyn addressed the ongoing development of a National AI Policy Framework in South Africa, noting the urgent need for stricter regulations and a more comprehensive understanding of AI’s practical benefits. As the legal landscape navigates a patchwork of existing laws, including the Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA) and the Electronic Communications and Transactions Act, Steyn emphasized that law firms should not wait for formal regulations to implement ethical safeguards. Instead, proactive measures are necessary to mitigate the risks that accompany AI adoption.
International legal technology giants like LexisNexis and Thomson Reuters have provided guidance on responsible AI use, underscoring the importance of transparency, data protection, and practitioner responsibility. Steyn pointed out that these principles must be at the core of how AI is utilized within the legal sector, especially as the technology continues to evolve.
The conversation surrounding AI in legal practice stresses the importance of continuous training and a clear understanding of the limitations inherent to AI tools. Steyn highlighted that the future impact of AI on the legal system will not hinge on the technology itself but rather on the ethical and wise application of these tools by legal professionals. He urged the legal community to cultivate a culture of responsibility and vigilance, leveraging AI to enhance their work while ensuring accuracy and integrity.
As law firms look ahead to a future increasingly intertwined with AI technology, the call for responsible governance has never been more critical. The legal profession stands at a crossroads, where the integration of AI can either enhance or undermine its foundations, depending on how diligently practitioners approach the ethical dimensions of this powerful tool. The stakes are high, and the path forward will require a concerted effort to balance innovation with accountability.
See also MetaMask Launches Native Tron Support, Enabling $21B Daily Transfers and Cross-Chain Management
MetaMask Launches Native Tron Support, Enabling $21B Daily Transfers and Cross-Chain Management Marvell Technology’s Stock Rises as RBC Upgrades to “Moderate Buy” Post $540M Acquisition
Marvell Technology’s Stock Rises as RBC Upgrades to “Moderate Buy” Post $540M Acquisition ManpowerGroup Leads Workforce Readiness Initiatives at Davos Amid AI Disruption
ManpowerGroup Leads Workforce Readiness Initiatives at Davos Amid AI Disruption Amazon Sees 700% Stock Surge Fueled by AI, While Alphabet’s Gemini Drives 34% Cloud Revenue Growth
Amazon Sees 700% Stock Surge Fueled by AI, While Alphabet’s Gemini Drives 34% Cloud Revenue Growth AI in Dermatology: Navigating Ethics and Equity for Enhanced Patient Outcomes in 2026
AI in Dermatology: Navigating Ethics and Equity for Enhanced Patient Outcomes in 2026